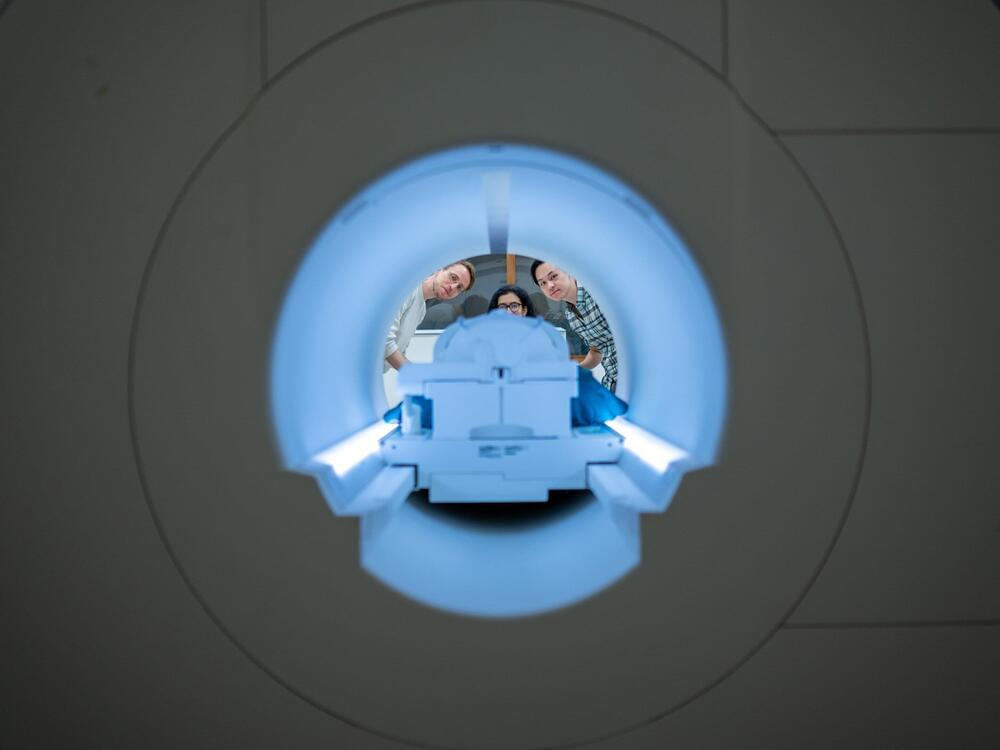
A new artificial intelligence system called a semantic decoder can translate a person’s brain activity—while listening to a story or silently imagining telling a story—into a continuous stream of text. The system developed by researchers at The University of Texas at Austin might help people who are mentally conscious yet unable to physically speak, such as those debilitated by strokes, to communicate intelligibly again.
The study, published in the journal Nature Neuroscience, was led by Jerry Tang, a doctoral student in computer science, and Alex Huth, an assistant professor of neuroscience and computer science at UT Austin. The work relies in part on a transformer model, similar to the ones that power Open AI’s ChatGPT and Google’s Bard.
Unlike other language decoding systems in development, this system does not require subjects to have surgical implants, making the process noninvasive. Participants also do not need to use only words from a prescribed list. Brain activity is measured using an fMRI scanner after extensive training of the decoder, in which the individual listens to hours of podcasts in the scanner. Later, provided that the participant is open to having their thoughts decoded, their listening to a new story or imagining telling a story allows the machine to generate corresponding text from brain activity alone.