The gala will be held on December 5, 2025, at London’s Natural History Museum.



Say a person takes their French Bulldog, Bowser, to the dog park. Identifying Bowser as he plays among the other canines is easy for the dog owner to do while onsite.
But if someone wants to use a generative AI model like GPT-5 to monitor their pet while they are at work, the model could fail at this basic task. Vision-language models like GPT-5 often excel at recognizing general objects, like a dog, but they perform poorly at locating personalized objects, like Bowser the French Bulldog.
To address this shortcoming, researchers from MIT and the MIT-IBM Watson AI Lab have introduced a new training method that teaches vision-language models to localize personalized objects in a scene.

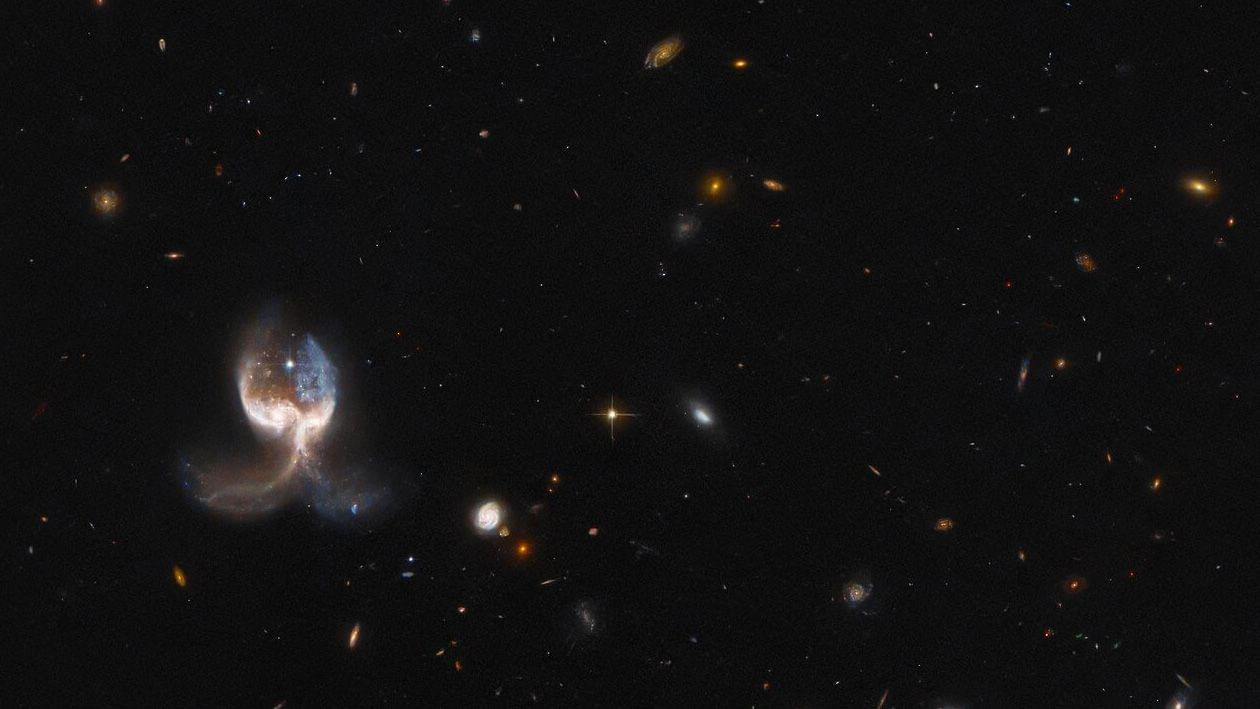
A new study led by UNLV scientists sheds light on how planets, including Earth, formed in our galaxy—and why the life and death of nearby stars are an important piece of the puzzle.
In a paper published in the Astrophysical Journal Letters, researchers at UNLV, in collaboration with scientists from the Open University of Israel, for the first time, modeled details about how the timing of planet formation in the history of the galaxy affects planetary composition and density. The paper is titled “Effect of Galactic Chemical Evolution on Exoplanet Properties.”
“Materials that go into making planets are formed inside of stars that have different lifetimes,” says Jason Steffen, associate professor with the UNLV Department of Physics and Astronomy and the paper’s lead author.
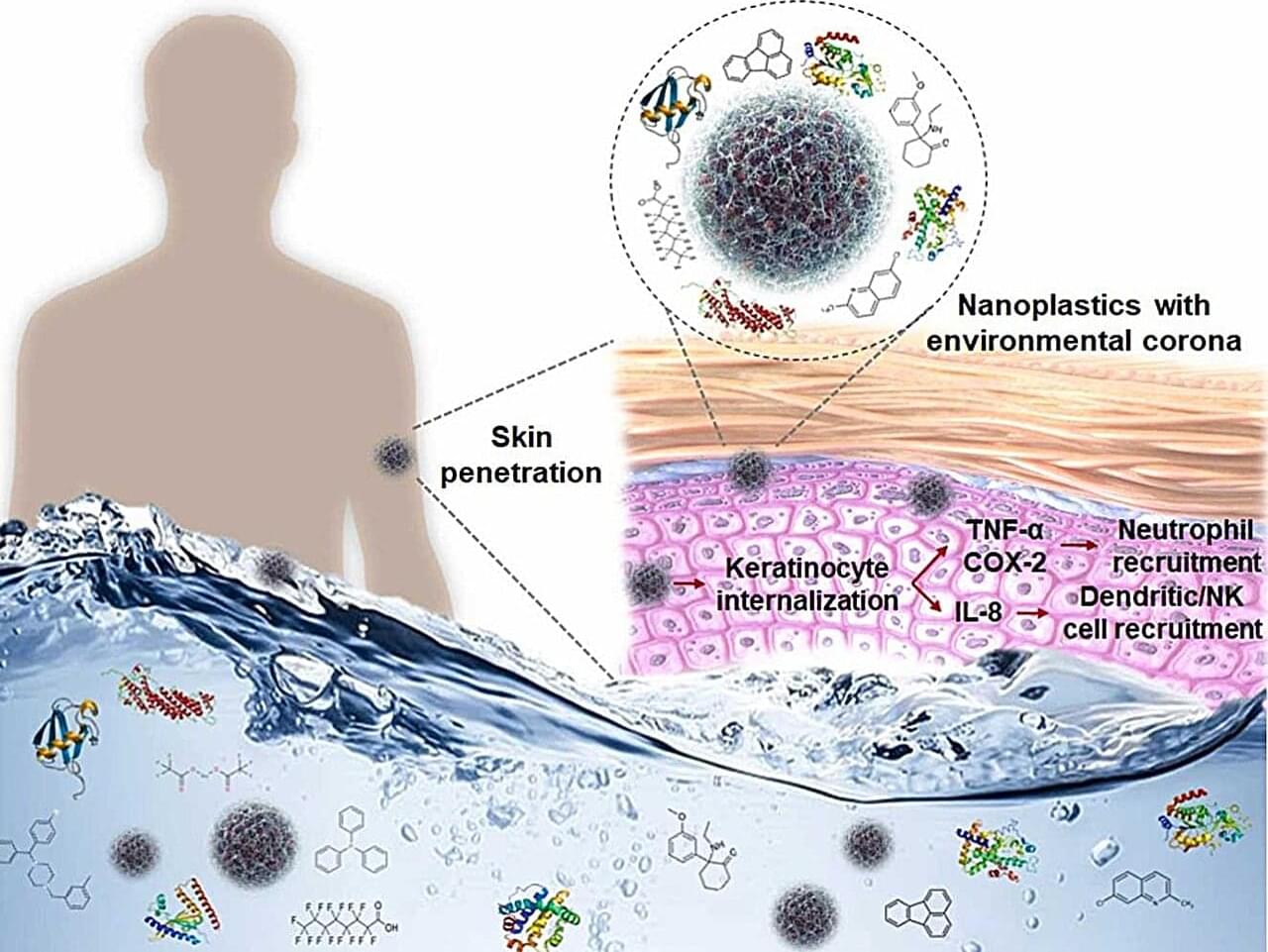
Plastic is ubiquitous in the modern world, and it’s notorious for taking a long time to completely break down in the environment—if it ever does.
But even without breaking down completely, plastic can shed tiny particles —called nanoplastics because of their extremely small size—that scientists are just now starting to consider in long-term health studies.
One of those scientists is Dr. Wei Xu, an associate professor in the Texas A&M College of Veterinary Medicine and Biomedical Sciences’ Department of Veterinary Physiology & Pharmacology. Xu’s current work is focused on what happens when nanoplastics interact with seawater, where they can pick up some curious hitchhikers in the form of chemicals and organic components.

IonQ and D-Wave, two publicly traded U.S. quantum computing companies, are joining as founding members of Q-Alliance, a new initiative in Lombardy described by organizers as the foundation of “the world’s most powerful quantum hub.”
The alliance, formalized in Como with a memorandum of understanding, is designed to accelerate quantum research and industrial applications as part of Italy’s broader digital transformation agenda, according to a news release. It is backed by the Italian government’s Interministerial Committee for Digital Transition and supported by Undersecretary of State Senator Alessio Butti.
Q-Alliance will serve as an open platform connecting universities, research institutions, and private industry. The program aims to train young researchers through scholarships and internships, promote collaboration across scientific disciplines, and position Italy as a European center for quantum development.
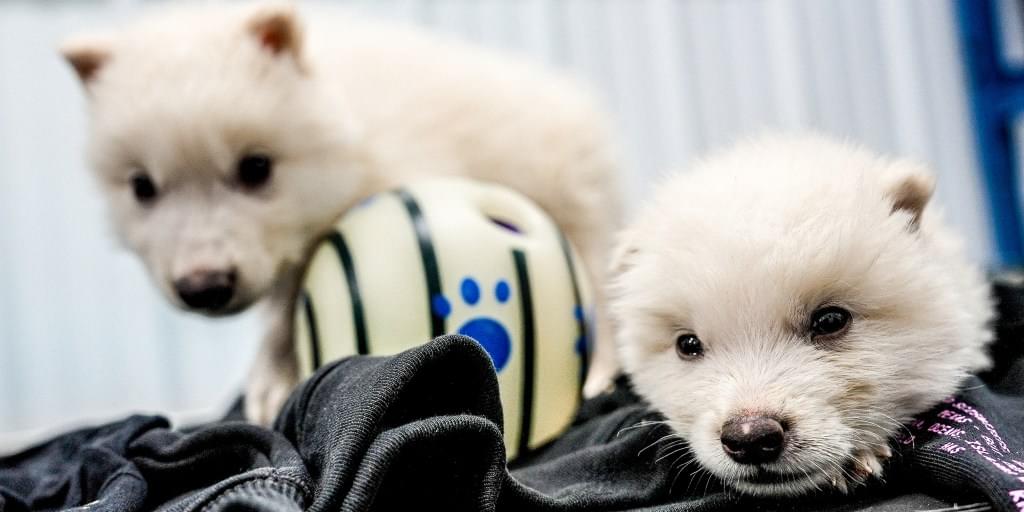

She said that the new framework represents a “landmark step,” and that the measure could allow conservationists to consider new ways to address the risks of climate change or test new methods of suppressing disease.
The IUCN — a large group of conservation organizations, governments and Indigenous groups with more than 1,400 members from about 160 countries — meets once every four years. It is the world’s largest network of environmental groups and the authority behind the red list, which tracks threatened species and global biodiversity.
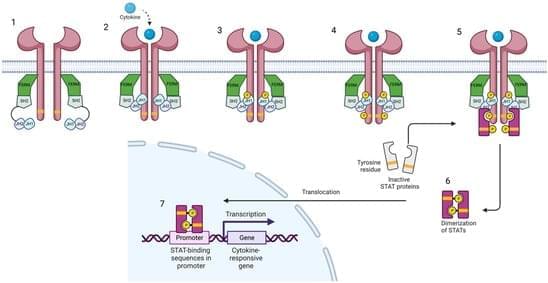
The Janus kinase (Jak)/signal transducer and activating protein (STAT) pathways mediate the intracellular signaling of cytokines in a wide spectrum of cellular processes. They participate in physiologic and inflammatory cascades and have become a major focus of research, yielding novel therapies for immune-mediated inflammatory diseases (IMID). Genetic linkage has related dysfunction of Tyrosine kinase 2 (Tyk2)—the first member of the Jak family that was described—to protection from psoriasis. Furthermore, Tyk2 dysfunction has been related to IMID prevention, without increasing the risk of serious infections; thus, Tyk2 inhibition has been established as a promising therapeutic target, with multiple Tyk2 inhibitors under development.