While immunotherapies have shown great promise in treating blood cancers, most clinical trials aimed at treating solid tumors such as pancreatic or lung cancer have failed. Researchers have long thought that solid tumors’ resistance to treatment is due to the tumor microenvironment—the cells and matrix that surround solid tumors—but the exact mechanisms behind this blockade were unclear, until now.
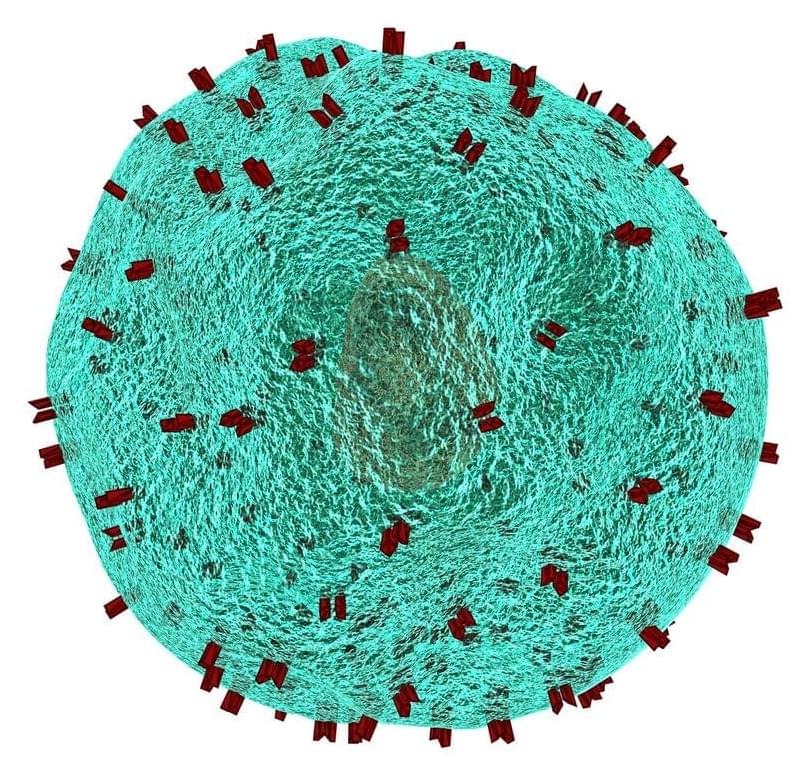
In a new study, University of Pennsylvania researchers reveal how the tumor microenvironment prevents T cells from attacking tumors. Using mouse models, they showed that cancer-associated fibroblasts along with extracellular matrix within the tumor microenvironment create a physical barrier to T cell entry, and these cells also actively suppress T cell function. When the researchers used CAR T cells to target and remove these fibroblasts, rather than targeting the tumor cells themselves, T cells were able to infiltrate and attack the tumor.
“The physical barrier and immunosuppressive environment derived from cancer-associated fibroblasts limits or traps T cells and prevents them from entering into the tumor,” says first author Zebin Xiao, a physician and postdoctoral researcher in the School of Veterinary Medicine. “We showed that targeting those fibroblasts can disrupt that barrier and has a very great tumor inhibition effect.”