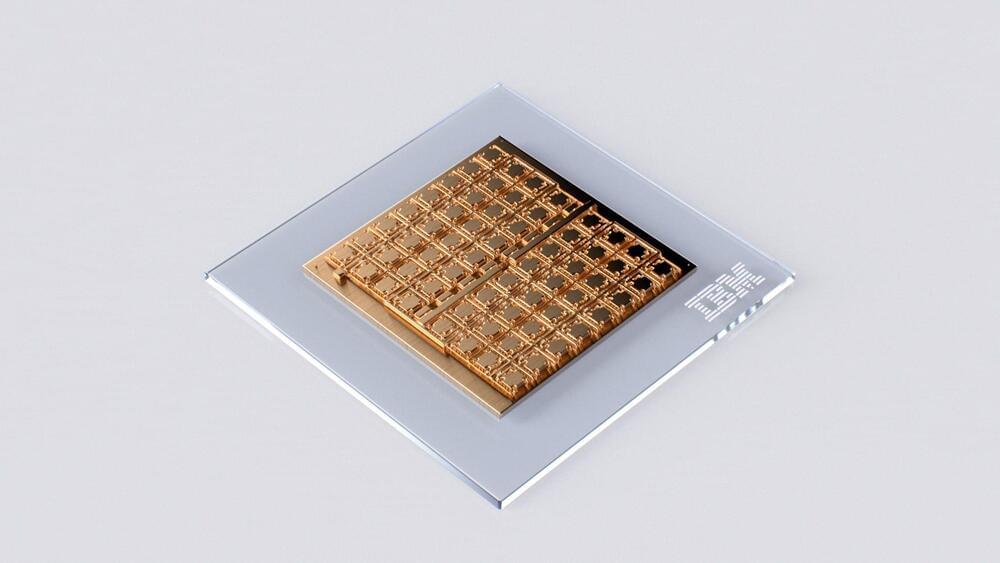
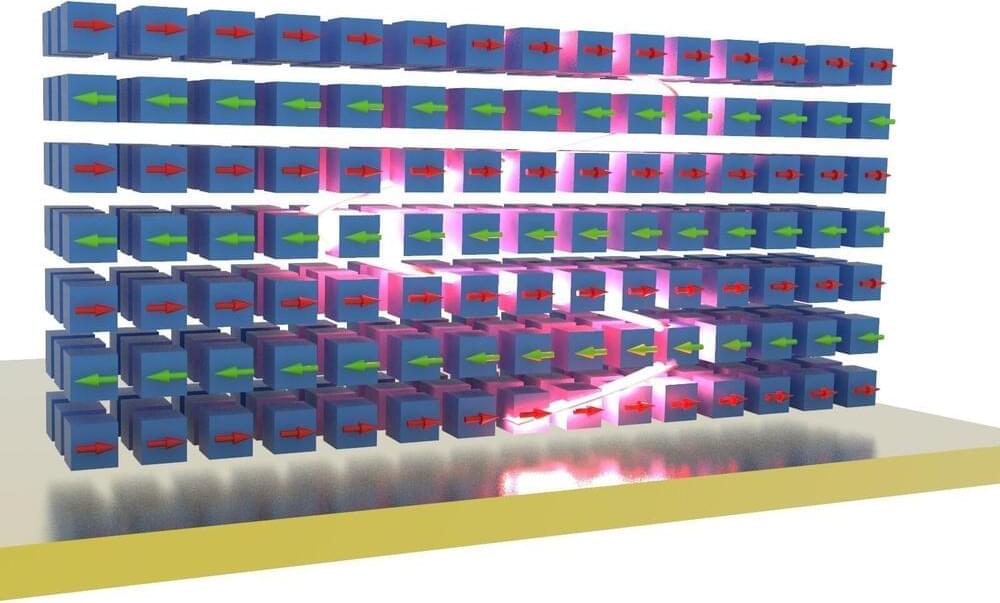
We’re just at the beginning of an AI revolution that will redefine how we live and work. In particular, deep neural networks (DNNs) have revolutionized the field of AI and are increasingly gaining prominence with the advent of foundation models and generative AI. But running these models on traditional digital computing architectures limits their achievable performance and energy efficiency. There has been progress in developing hardware specifically for AI inference, but many of these architectures physically split the memory and processing units. This means the AI models are typically stored in a discrete memory location, and computational tasks require constantly shuffling data between the memory and processing units. This process slows down computation and limits the maximum achievable energy efficiency.
Dunno if anyone has already posted this.
The chip showcases critical building blocks of a scalable mixed-signal architecture.