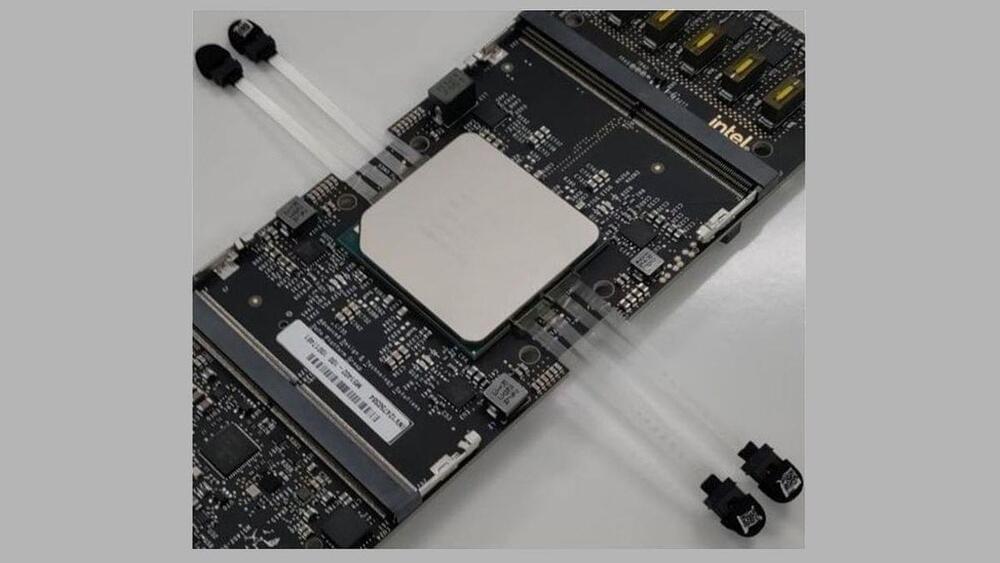
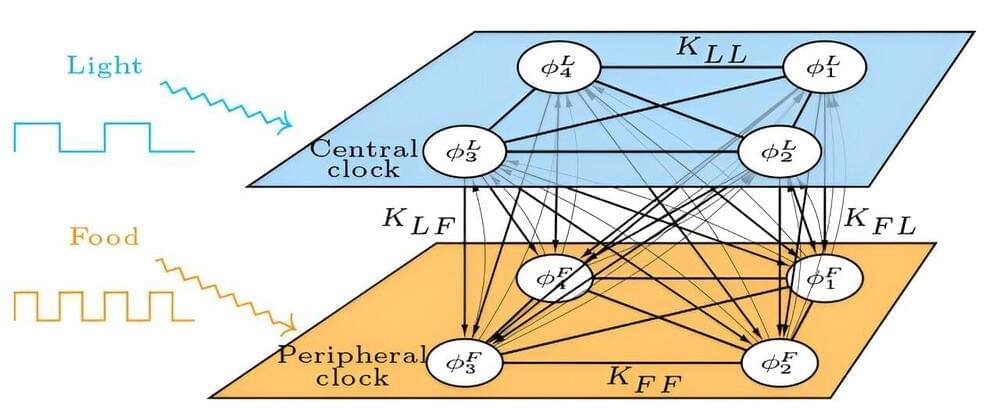
Other questions to the experts in this canvassing invited their views on the hopeful things that will occur in the next decade and for examples of specific applications that might emerge. What will human-technology co-evolution look like by 2030? Participants in this canvassing expect the rate of change to fall in a range anywhere from incremental to extremely impactful. Generally, they expect AI to continue to be targeted toward efficiencies in workplaces and other activities, and they say it is likely to be embedded in most human endeavors.
The greatest share of participants in this canvassing said automated systems driven by artificial intelligence are already improving many dimensions of their work, play and home lives and they expect this to continue over the next decade. While they worry over the accompanying negatives of human-AI advances, they hope for broad changes for the better as networked, intelligent systems are revolutionizing everything, from the most pressing professional work to hundreds of the little “everyday” aspects of existence.
One respondent’s answer covered many of the improvements experts expect as machines sit alongside humans as their assistants and enhancers. An associate professor at a major university in Israel wrote, “In the coming 12 years AI will enable all sorts of professions to do their work more efficiently, especially those involving ‘saving life’: individualized medicine, policing, even warfare (where attacks will focus on disabling infrastructure and less in killing enemy combatants and civilians). In other professions, AI will enable greater individualization, e.g., education based on the needs and intellectual abilities of each pupil/student. Of course, there will be some downsides: greater unemployment in certain ‘rote’ jobs (e.g., transportation drivers, food service, robots and automation, etc.).”