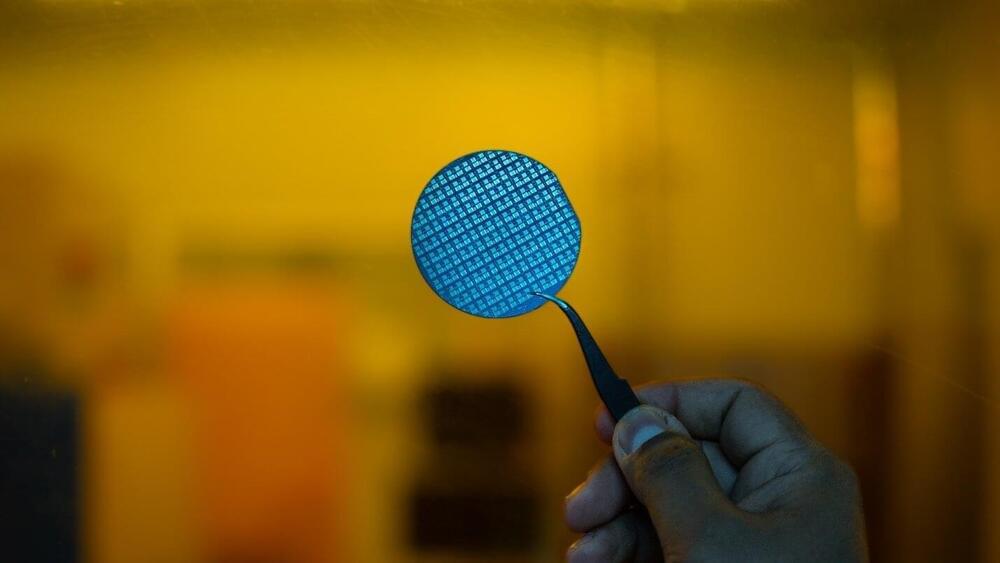
Researchers at the Indian Institute of Science (IISc) have developed a fully indigenous gallium nitride (GaN) power switch that can have potential applications in systems like power converters for electric vehicles and laptops, as well as in wireless communications. The entire process of building the switch—from material growth to device fabrication to packaging—was developed in-house at the Center for Nano Science and Engineering (CeNSE), IISc.
Due to their high performance and efficiency, GaN transistors are poised to replace traditional silicon-based transistors as the building blocks in many electronic devices, such as ultrafast chargers for electric vehicles, phones and laptops, as well as space and military applications such as radar.
“It is a very promising and disruptive technology,” says Digbijoy Nath, Associate Professor at CeNSE and corresponding author of the study published in Microelectronic Engineering. “But the material and devices are heavily import-restricted … We don’t have gallium nitride wafer production capability at commercial scale in India yet.” The know-how of manufacturing these devices is also a heavily-guarded secret with few studies published on the details of the processes involved, he adds.