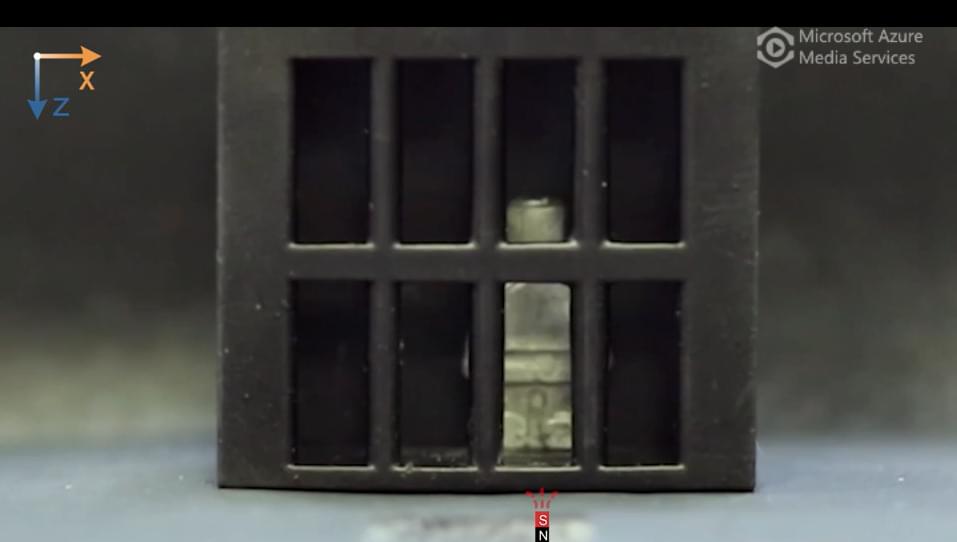
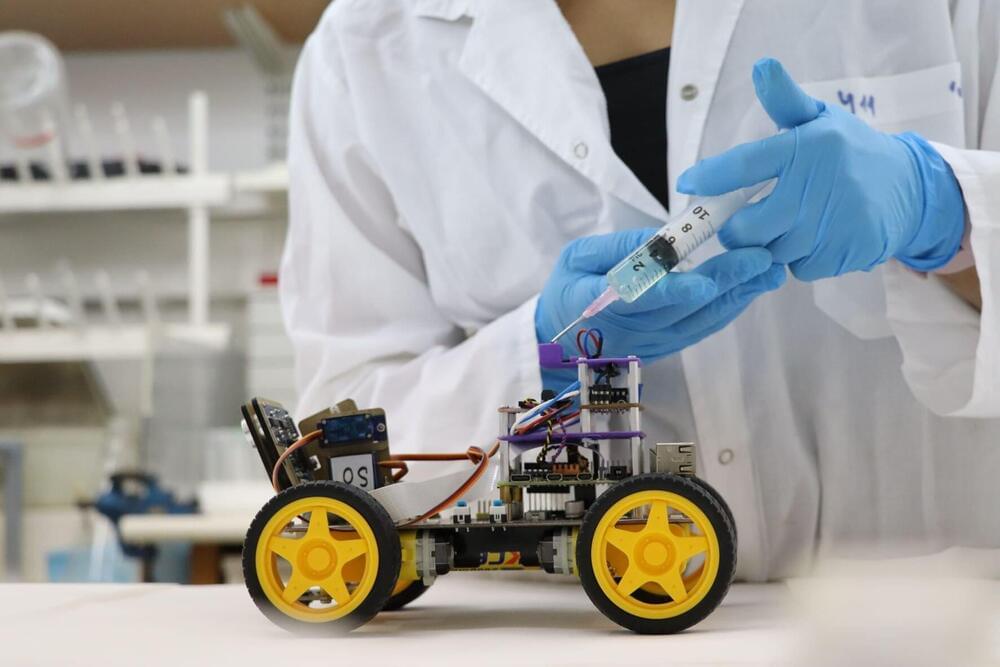
Inspired by sea cucumbers, engineers have designed miniature robots that rapidly and reversibly shift between liquid and solid states. On top of being able to shape-shift, the robots are magnetic and can conduct electricity. The researchers put the robots through an obstacle course of mobility and shape-morphing tests in a study publishing January 25 in the journal Matter.
Where traditional robots are hard-bodied and stiff, “soft” robots have the opposite problem; they are flexible but weak, and their movements are difficult to control. “Giving robots the ability to switch between liquid and solid states endows them with more functionality,” says Chengfeng Pan (@ChengfengPan), an engineer at The Chinese University of Hong Kong who led the study.
The team created the new phase-shifting material—dubbed a “magnetoactive solid-liquid phase transitional machine”—by embedding magnetic particles in gallium, a metal with a very low melting point (29.8 °C).