Year 2023 😗
Data from patients with AMD, retinal dystrophies, and diabetic retinopathy indicate an important role of immune cells, including microglia, in the pathogenesis of these retinal diseases1. The accumulation of drusen components provides an environment rich in chemoattractants for microglia and leads to their translocation to the subretinal space in AMD2,4. The involvement of microglia in the activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome and the promotion of proinflammatory cytokine secretion has been confirmed in in vitro and animal studies11,12,14. In patients with retinal dystrophies like retinitis pigmentosa, it has been shown that microglia become activated in response to signals from degenerating rod photoreceptors and migrate to the outer retinal layers4. There, they participate in the phagocytosis of debris and dying cells and secrete proinflammatory factors. Mouse models of retinal degeneration (e.g. rd1, rd7, rd8, and rd10 models) confirm many of these conclusions9,10,13,15, but make it clear that the role of microglia may also be homeostatic, depending on both stimuli and anatomical location within the retina7,20. Activated microglia are observed at all the stages of human diabetic retinopathy3,8 and also feature prominently in many animal models of the disease44,45. Finally, accumulations of activated microglia are also seen in a variety of animal models of retinal degeneration, including light-induced retinal degeneration and models based on complement dysregulation34,46,47.
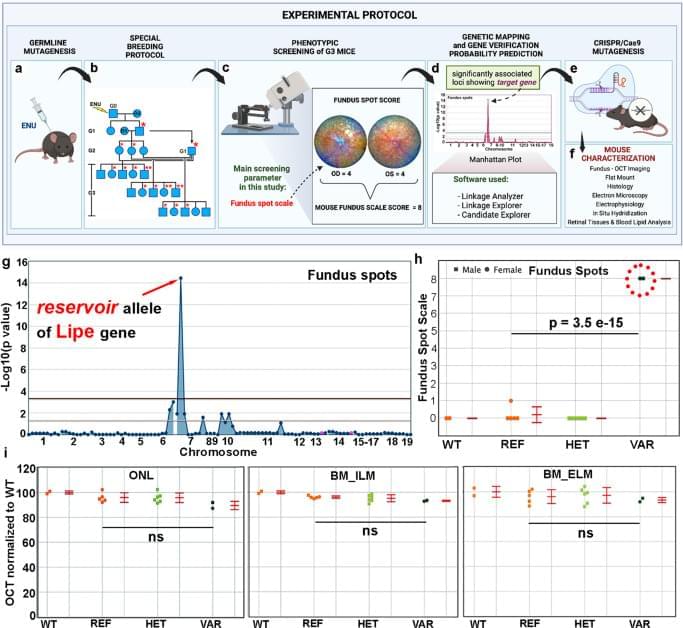
The pathways regulating immune surveillance, cell trafficking, and neuroinflammation in the retina are not well understood. A large number of molecules and processes have been implicated, ranging from chemokines involved in chemotaxis, cytokines involved in activation, factors that regulate oxidative stress and complement activation, and immunoregulatory proteins. In such a complex biological system, the unbiased nature of a forward genetics approach is particularly valuable in identifying genes affecting these immune cell processes. Furthermore, the accumulation of subretinal microglia, visible as or correlated with the accumulation of fundus spots, can serve as a marker for retinal pathology and thus as a screen for genes essential to retinal homeostasis. Our approach here has two important advantages relative to all prior forward genetics studies of the retina: 1. We are systematically applying a semiquantitative fundus spot scale to fundus photographs, and 2. Our pipeline is the only one in which all mice screened are G3 mice that have been pre-genotyped at all mutant loci. Our unbiased identification of 6 gene-phenotype associations to retinal pathology with strong literature support using our fundus spot scale screen is proof of concept supporting the efficacy of our approach. We identified other associations that had not been reported in the literature at the time of the screening. From those, we first concentrated our efforts on the gene Lipe, partly because the fundus spot scale was the only parameter leading to its identification.
In order to confirm our findings in ENU-mutagenized mice and also to explore the role of Lipe in retinal homeostasis, a CRISPR-generated Lipe−/− mouse line was generated. Imaging of the retinas on these mice confirmed an early and prominent accumulation of fundus spots. Furthermore, we found a similar widespread accumulation of hyperautofluorescent spots in these mice. We were also able to show that Lipe−/− mice have increased accumulation of subretinal Iba1+/CD16+/TMEM119+/CCR2− cells consistent with activated microglia. It can be argued that microglia migrating to the subretinal space are by definition showing some level of activation48,49,50. But our findings of well-accepted morphological signs of activation and co-staining with CD16, a marker of microglial activation10,34,51,52, further support this conclusion.