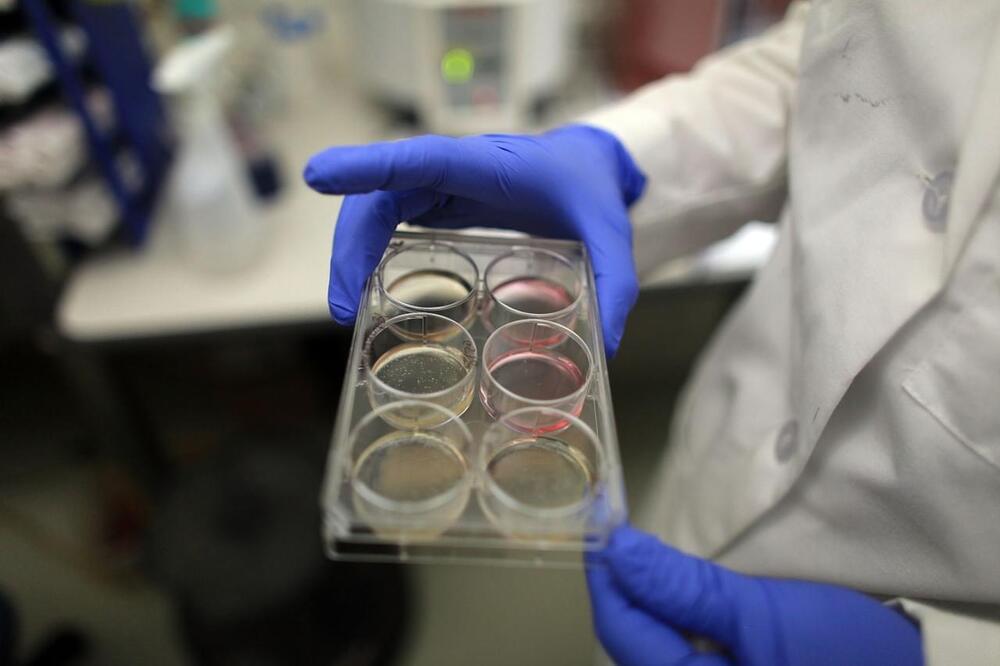
(NewsNation) — A new study claims to have found chemical compounds that can actually reverse the effects of aging, though so far results have been limited to animal studies.
Harvard Medical School, University of Maine and Massachusetts Institute of Technology scientists collaborated on the study, published in the journal Aging. Researchers found it was possible to reverse cellular engineering rather than simply delay it.
They used six chemical compounds to reverse aging in cells, returning them to a youthful state without having them revert too far and become cancerous.