Nov 11, 2021
Surprise! Our Bodies Have Been Hiding a Trojan Horse for Gene Therapy
Posted by Shailesh Prasad in categories: biotech/medical, genetics
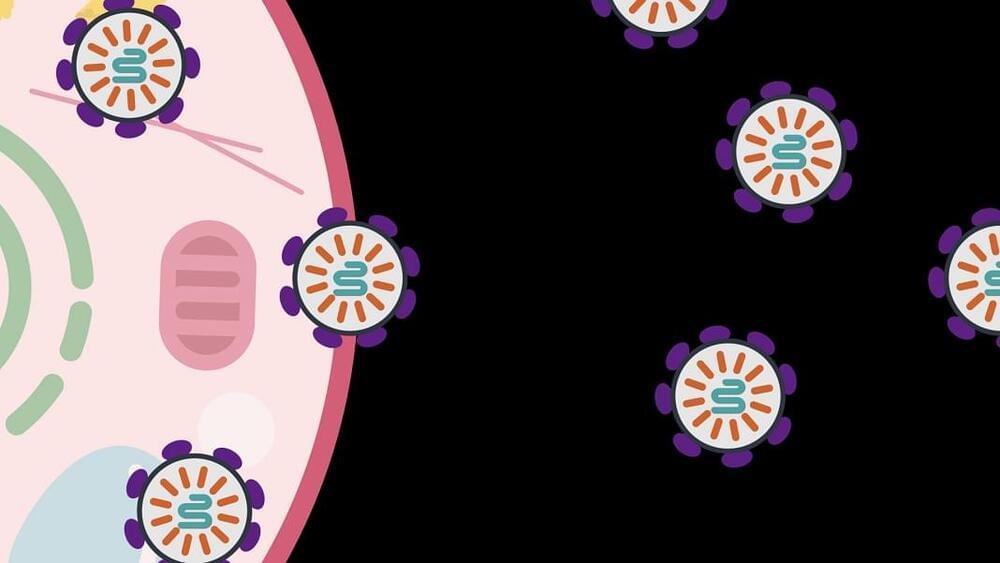
The problem? Our bodies aren’t big fans of foreign substances—particularly ones that trigger an undesirable immune response. What’s more, these delivery systems aren’t great with biological zip codes, often swarming the entire body instead of focusing on the treatment area. These “delivery problems” are half the battle for effective genetic medicine with few side effects.
“The biomedical community has been developing powerful molecular therapeutics, but delivering them to cells in a precise and efficient way is challenging,” said Zhang at the Broad Institute, the McGovern Institute, and MIT.
Continue reading “Surprise! Our Bodies Have Been Hiding a Trojan Horse for Gene Therapy” »