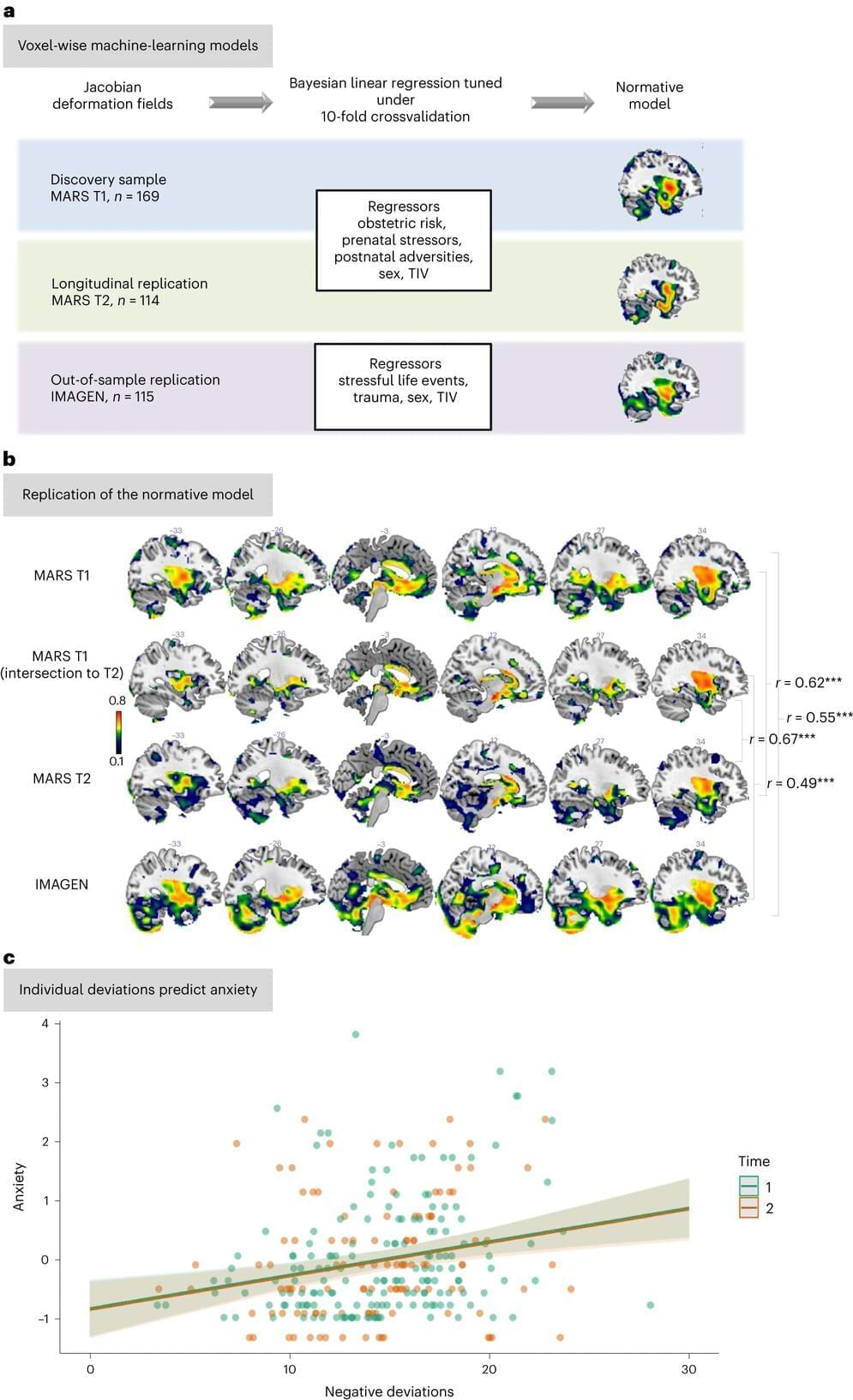
Neuroscientists at Radboud University show that adversities permanently change the functioning of the brain. Furthermore, an aberrant reaction of the brain to adversities is related to anxiety symptoms. This may have predictive value for the development of psychiatric disorders.
Your brain is shaped by the things you experience. That sounds logical, but can you really measure that? And what can you do with it? Neuroscientists at Radboud University medical center investigated the influence of adversities in life on patterns in the brain. They found remarkable associations that may have predictive value for the development of psychiatric disorders.
The researchers conducted their study on approximately 170 people—a special group, because all kinds of data have been collected from them during their lifetime. For this study, the scientists specifically focused on adversities: factors or events that are known to have a negative effect on development. Consider, for example, the mother’s smoking during pregnancy, complications during childbirth, abuse, or a major accident.