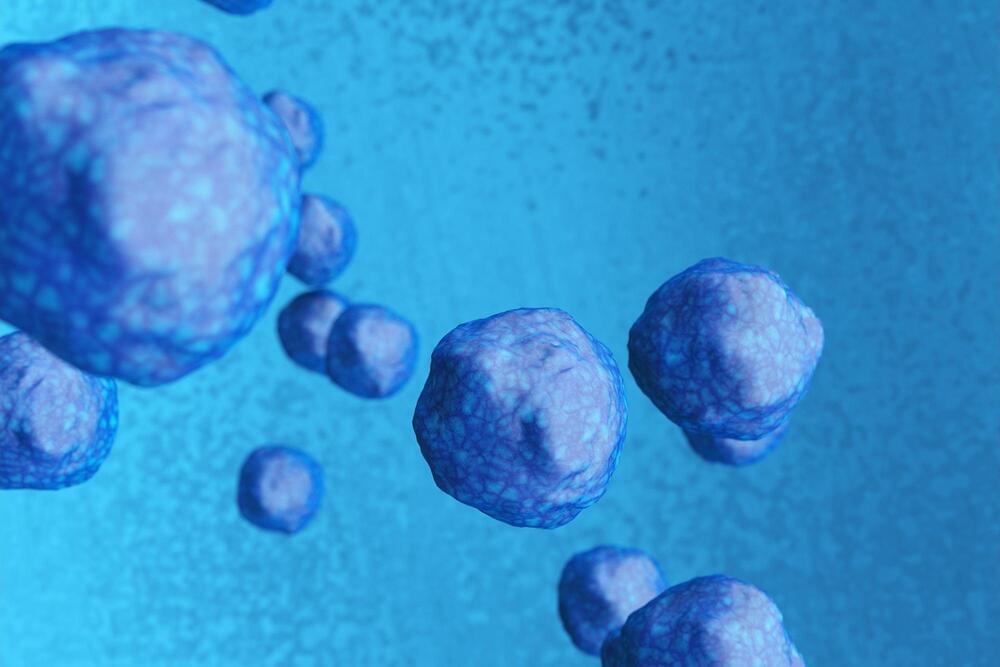
A new discovery could be a game-changer for patients with type 2 diabetes. Researchers at the Diabetes, Obesity, and Metabolism Institute (DOMI) at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai have discovered a therapeutic target for the preservation and regeneration of beta cells (β cells), the cells in the pancreas that produce and distribute insulin. The finding could also help millions of individuals throughout the globe by preventing insulin resistance. The study was recently published in the journal Nature Communications.
Nature Communications is a peer-reviewed, open access, multidisciplinary, scientific journal published by Nature Research. It covers the natural sciences, including physics, biology, chemistry, medicine, and earth sciences. It began publishing in 2010 and has editorial offices in London, Berlin, New York City, and Shanghai.