AlexLXM/iStock.
However, there may be a solution on the way. Machine learning is being used by a group of academics from the National Research Council (NRC) and the University of Waterloo to address this age-old problem.
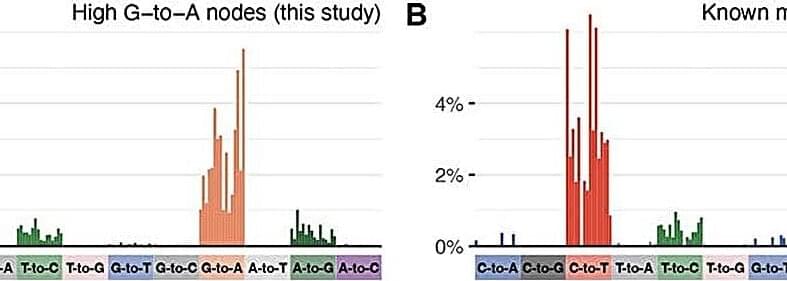
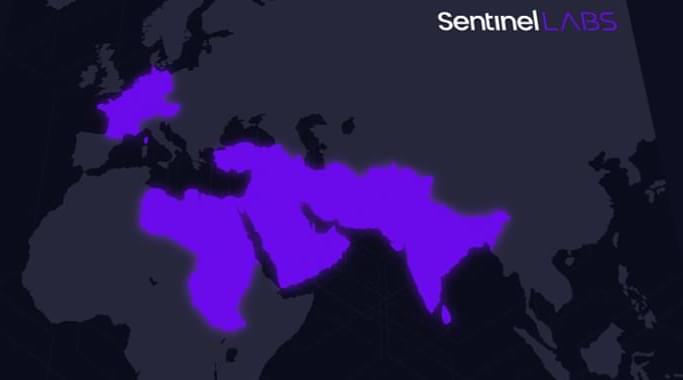
Researchers at the Francis Crick Institute, the University of Cambridge, Imperial College London, the University of Liverpool, the University of Cape Town and UKHSA have uncovered a link between an antiviral drug for COVID-19 infections called molnupiravir and a pattern of mutations in the SARS-CoV-2 virus.
Molnupiravir works by inducing mutations in the virus’s genetic information, or genome, during replication. Many of these mutations will damage or kill the virus, reducing viral load in the body. It was one of the first antivirals available on the market during the COVID-19 pandemic and was widely adopted by many countries.
In research published in Nature, the scientists used global sequencing databases to map mutations in the SARS-CoV-2 virus over time. They analyzed a family tree of 15 million SARS-CoV-2 sequences so that at each point in each virus’s evolutionary history they could see which mutations had occurred.
A team of mechanical engineers at Nanyang Technological University in Singapore has found a way to electronically control cockroaches without injuring them. In their paper published in the journal npj Flexible Electronics, the group describes the new technology they used to remotely control the cockroaches and the benefits of doing so.
Prior research teams have created a variety of cyborg cockroaches, but they all had one feature in common—they all involved attaching probes to the insect’s nervous system—procedures that led to damage to the insect, and likely some degree of pain.
In this new effort, the researchers noted that damaging cockroaches during attempts to control them results in a very short life expectancy, which then results in very little payoff for a lot of work. They also suggest such research is unethical because of the pain inflicted on the cockroaches. In this new effort, they have found a way to control cockroaches that does not involve cutting into them, resulting in a much longer lifespan.

Intel Corp. Chief Executive Officer Pat Gelsinger, plotting a comeback for the once-dominant chipmaker, made the case that the company’s technology will be vital to an industrywide boom in artificial intelligence computing.
Speaking at Intel’s annual Innovation conference, Gelsinger pointed to advances that his company is making in production technology and software developer tools for AI. The opportunity will only grow as more artificial intelligence capabilities are powered by personal computers, he said.
“AI represents a generational shift, giving rise to a new era of global expansion where computing is even more foundational to a better future for all,” Gelsinger said. “For developers, this creates massive societal and business opportunities to push the boundaries of what’s possible, to create solutions to the world’s biggest challenges.”
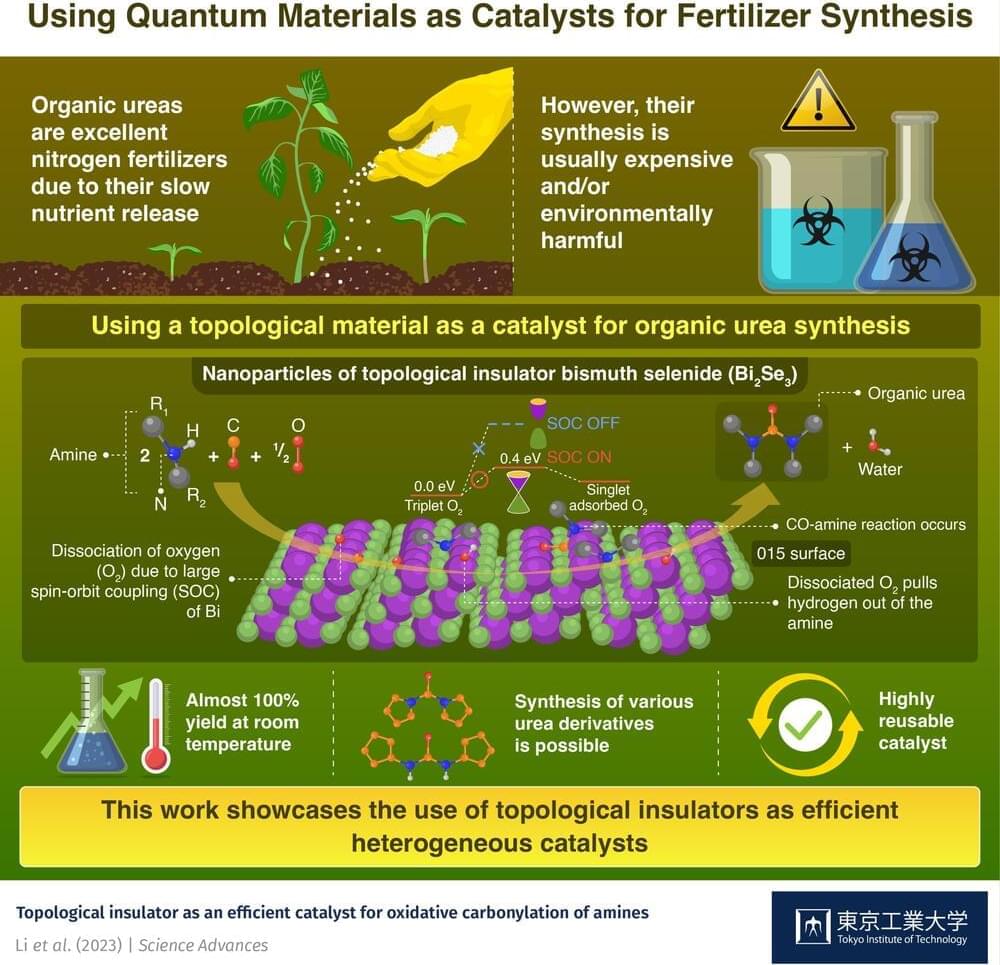
Synthetic fertilizers, one the most important developments in modern agriculture, have enabled many countries to secure a stable food supply. Among them, organic ureas (or organoureas) have become prominent sources of nitrogen for crops. Since these compounds do not dissolve immediately in water, but instead are slowly decomposed by soil microorganisms, they provide a stable and controlled supply of nitrogen, which is crucial for plant growth and function.
However, traditional methods to synthesize organoureas are environmentally harmful due to their use of toxic substances, such as phosgene. Although alternative synthesis strategies have been demonstrated, these either rely on expensive and scarce noble metals or employ catalysts that cannot be reused easily.
In a recent effort to address these challenges, a research team including Honorary Professor Hideo Hosono from Tokyo Institute of Technology, Japan, has leveraged the quantum properties of bismuth selenide (Bi2Se3) to synthesize organoureas. Their study is published in Science Advances.

Amazon is looking to position itself as the one-stop shop for AI. The e-commerce giant designs its own chips for training huge AI models. Through Amazon Bedrock customers can also design their own generative AI applications using existing models, which are all run on the Amazon cloud. The company sells its own AI applications too.
Anthropic already counts some high-profile backers, including Google and Salesforce Ventures. This support comes as tech giants continue to make massive bets on AI companies, a move sparked by Microsoft’s multi-billion dollar investment in ChatGPT maker OpenAI in January.
OpenAI’s ChatGPT can now “see, hear and speak,” or, at least, understand spoken words, respond with a synthetic voice and process images, the company announced Monday.
The update to the chatbot — OpenAI’s biggest since the introduction of GPT-4 — allows users to opt into voice conversations on ChatGPT’s mobile app and choose from five different synthetic voices for the bot to respond with. Users will also be able to share images with ChatGPT and highlight areas of focus or analysis (think: “What kinds of clouds are these?”).
The changes will be rolling out to paying users in the next two weeks, OpenAI said. While voice functionality will be limited to the iOS and Android apps, the image processing capabilities will be available on all platforms.
When the spinal cords of mice and humans are partially damaged, the initial paralysis is followed by the extensive, spontaneous recovery of motor function. However, after a complete spinal cord injury, this natural repair of the spinal cord doesn’t occur and there is no recovery. Meaningful recovery after severe injuries requires strategies that promote the regeneration of nerve fibers, but the requisite conditions for these strategies to successfully restore motor function have remained elusive.
“Five years ago, we demonstrated that nerve fibers can be regenerated across anatomically complete spinal cord injuries,” says Mark Anderson, a senior author of the study. “But we also realized this wasn’t enough to restore motor function, as the new fibers failed to connect to the right places on the other side of the lesion.” Anderson is the director of Central Nervous System Regeneration at. NeuroRestore and a scientist at the Wyss Center for Bio and Neuroengineering.
Working in tandem with peers at UCLA and Harvard Medical School, the scientists used state-of-the-art equipment at EPFL’s Campus Biotech facilities in Geneva to run in-depth analyses and identity which type of neuron is involved in natural spinal-cord repair after partial spinal cord injury.

A. There are so many mundane but essential administrative and clerical tasks that clog up a clinician’s workday. A computer screen is actively competing for our attention. It’s the part of the industry we – as physicians – were never trained for. But, years of “we’ve always done it that way” created this anchor on us all, leading to burnout and driving thousands out of the industry during the pandemic.
Processes vastly simplified and improved by generative AI can be a powerful recruitment tool to bring a new generation into the healthcare industry and patient care without arcane and difficult processes in their way. By eliminating needless note-taking and long nights of billing and coding for reimbursement purposes, doctors can get back to solving the real issues of patient care.