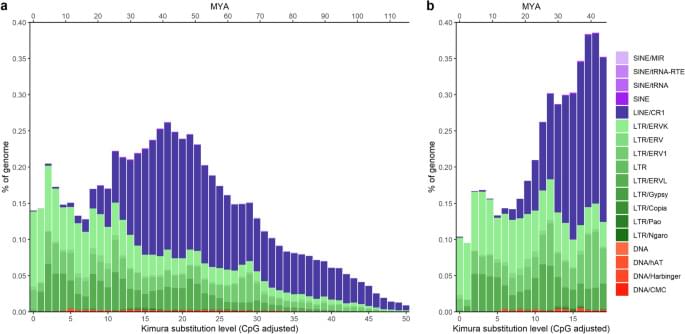
The effect of a TE on its host can be classified analogous to the effect of point mutations. In the majority of cases, the consequences of a TE their activity (transposition to a new genomic site) is either neutral or deleterious. The latter occurs, when TEs disrupt genes and their functions, or when, they trigger de-novo genomic instability by transposition or TE-mediated chromosomal rearrangements, which can lead to disease1, 3. TEs can occasionally have a positive impact on the host genome, for example, by impacting gene regulatory networks. In the British peppered moth (Biston betularia), a TE inserted within the first intron of the cortex gene, resulted in increased transcription levels, subsequently affecting cell cycle regulation during wing-disc development through the amount of cortex protein product, resulting in the iconic melanic form4. However, more research is needed to understand these different evolutionary impacts that TEs can have when interacting with their host genome.
The increased accessibility to high throughput sequencing technologies has greatly increased our ability to analyse genetic differences caused by changes at the nucleotide level, and patterns of natural selection on coding sequences, and simultaneously allowed us to disentangle phenotypic differences at the nucleotide level. Mounting evidence has started to shed light on non-coding regions having important effects on genomic variation3. While TEs can be found in the genomes of virtually all organisms, large proportions of TEs are often absent from reference genomes, as their repetitive nature impedes their assembly and can result in collapsed regions within the reference genome2, 5. These difficulties have led to an increased demand for reference genomes that are of a higher quality and are more complete. More importantly, a new demand for high-quality annotations of non-coding regions in reference genomes has surfaced. Annotations of non-coding regions are imperative to study the evolution of these regions between and within species. Improvements in sequencing techniques, especially the addition of long-read sequencing, and improved bioinformatic analytical tools are resulting in the assembly of increasingly gapless reference genomes, enabling the curation of high-quality TE annotations.
The current efforts of large consortia, such as the VGP6 and the B10K7 to create high-quality references for a wide variety of organisms provide invaluable data to improve our endeavours for a better understanding of TEs. With these new resources we can take our research into TEs and their effects on host genomes further, for example, to better understand the evolution of complex traits across phylogenomic scales. One such a complex trait is seasonal bird migration and recent research across a migratory divide in willow warblers identified a diagnostic TE correlated with migratory direction8. Here we focus on the Eurasian blackcap (Sylvia atricapilla), another iconic model species for bird migration, and consequently, the resource published here may be able to add insight to the quest to resolve the genetic background of migratory behaviour.