The World Health Organization stated it’s possible but based this on limited evidence and no explanation of the mechanism for causing it.
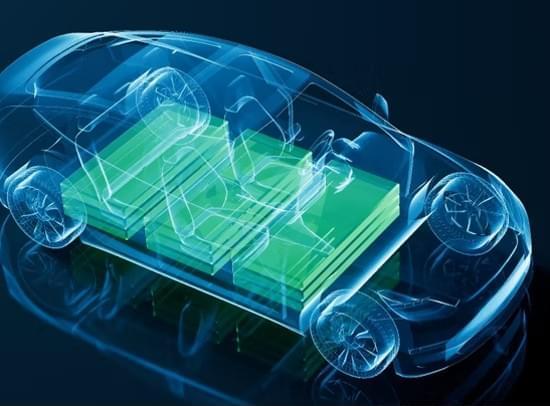



Sodium-ion (Na-ion) batteries and solid-state batteries have both been in the news recently. Why? Because the need for battery storage is growing rapidly as the global economy seeks carbon-based energy alternatives in pursuit of the goal to achieve net-zero emissions by the mid-century.
Na-ion Battery News
In April I wrote about BYD, a Chinese electric vehicle (EV) manufacturer, that is using sodium-ion (Na-ion) battery packs instead of lithium-ion (Li-ion) in some of its models. In its latest report, IDTechEx, out of Cambridge in the United Kingdom, states that although Na-ion batteries are not the answer to all battery-power applications, they do provide a complimentary addition to battery packs used not just in EVs but also for backup power within utilities and factories.
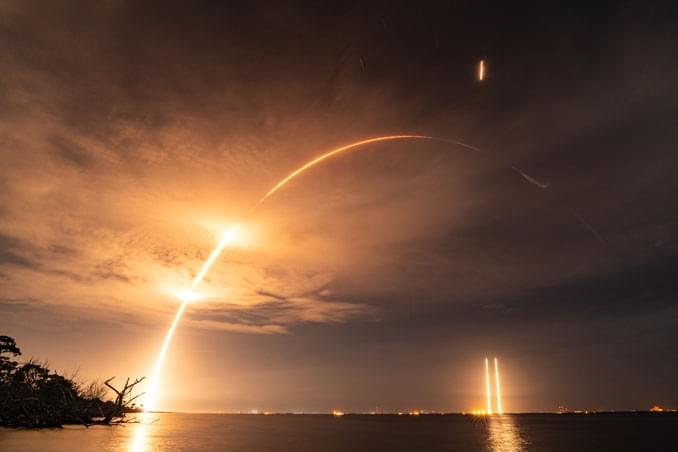

SpaceX launched the world’s heaviest commercial communications satellite atop a Falcon Heavy rocket on Friday. The triple-core rocket lifted off from Kennedy Space Center’s pad 39A with the Jupiter 3/EchoStar 24 satellite at 11:04 p.m. EDT (0304 UTC Saturday).
The successful launch came after a scrub on Wednesday and a 48-hour delay to replace a stuck liquid oxygen valve on the rocket’s port-side booster. After a week of stormy conditions on the Florida Space Coast the weather improved and the rocket lifted off in calm conditions, with just a thin layer of cloud in the sky.
It was the seventh mission for the Falcon Heavy and the third flight of the rocket this year. The Falcon Heavy’s twin side boosters, which have made two previous flights, returned to SpaceX’s Landing Zones 1 & 2 punching through a thin layer of cloud and announcing their arrival with sonic booms. The rocket’s core stage required all its capacity to loft the giant satellite into a geostationary transfer orbit and was not recovered.

Say hello to ionocaloric cooling. It’s a new way to lower temperatures with the potential to replace existing methods of chilling things with a process that is safer and better for the planet.
Typical refrigeration systems transport heat away from a space via a gas that cools as it expands some distance away. As effective as this process is, some of the choice gases we use are particularly unfriendly to the environment.
There is, however, more than one way a substance can be forced to absorb and shed heat energy.
In a high-tech laboratory, somewhere in San Francisco, sits a comma-shaped piece of metal that aims to change how the world sees the weather. The structure dominates the room. The horizontal part softly curves upwards until it’s taller than a person, with ridges that stretch from top to bottom. You’d be forgiven for thinking it’s a piece of modern art.
In fact, it is art, but it’s also much more than that. It’s an AI-powered, data-processing powerhouse from a startup called Atmo, and it could democratize weather forecasting, putting every country on a level meteorological playing field for the first time.
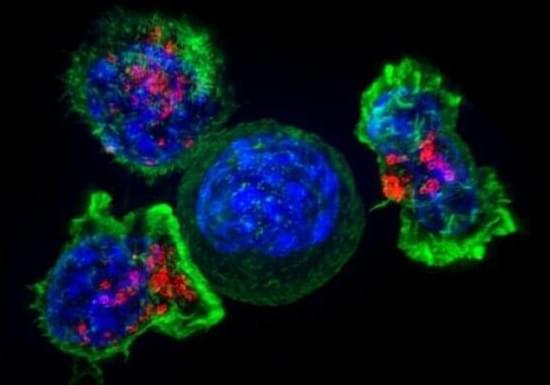
One of the challenges in treating cancer is stopping it from metastasizing, and a new study reveals one of the fundamental mechanisms through which this happens. Now we know about this mechanism, perhaps we can stop it.
Key to this newly discovered process is GRP78, and it’s what’s known as a chaperone protein. It’s a type of protein that lends a hand in the folding or unfolding of larger proteins, basically building them up (or tearing them down), which then affects whether they’re biologically active and functional.
A team led by the Keck School of Medicine at the University of Southern California (USC) in the US found that cancer cells can hijack GRP78, using the protein to spread further in the body and resist treatment.
In a recent study published in PLoS ONE, researchers examine a wide range of lifestyle variables in the context of multimorbidity of chronic non-communicable illnesses.
Study: Lifestyle factors related to prevalent chronic disease multimorbidity: A population-based cross-sectional study. Image Credit: Amorn Suriyan / Shutterstock.com.
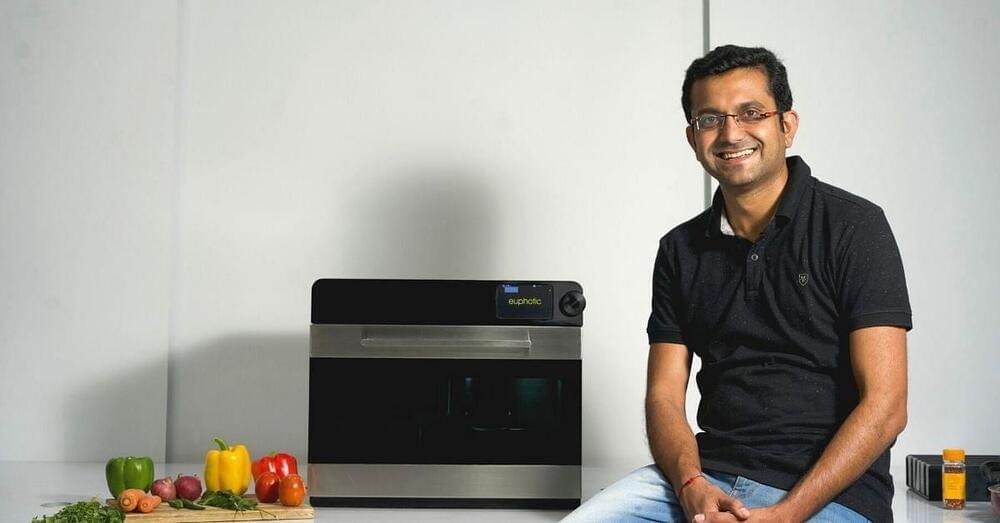

Imagine returning home from your evening walk or gym to the aroma of freshly cooked kadhai paneer or chicken curry, which instantly reminds you of home. Now, what if you were to know that it was no human that lovingly prepared this piping hot and delicious meal, but rather, a machine?
From booking cabs to ordering food right at your doorstep, technology makes human lives easy. So it’s about time it saves humans from having to cook after a long tiring day at work, or at times when you’re just not in the mood to enter the kitchen.
The NOSH device, developed by the Euphotic Labs, was conceived by Yatin Varachhia, co-founder of the Bengaluru-based startup. The 34-year-old says the inspiration to build a device stemmed from his struggle of having good food.
