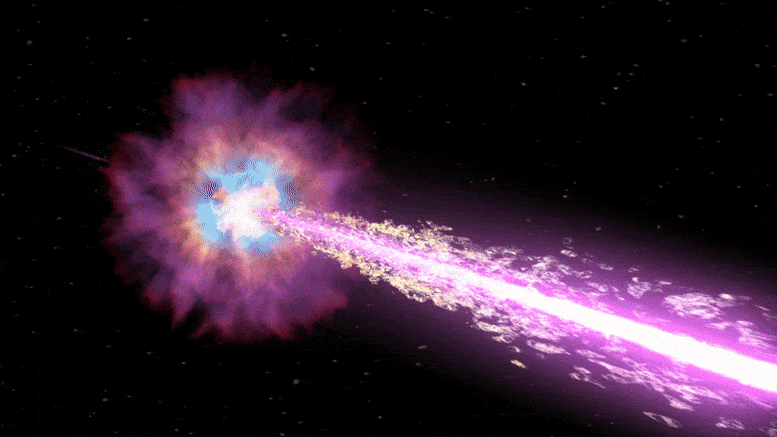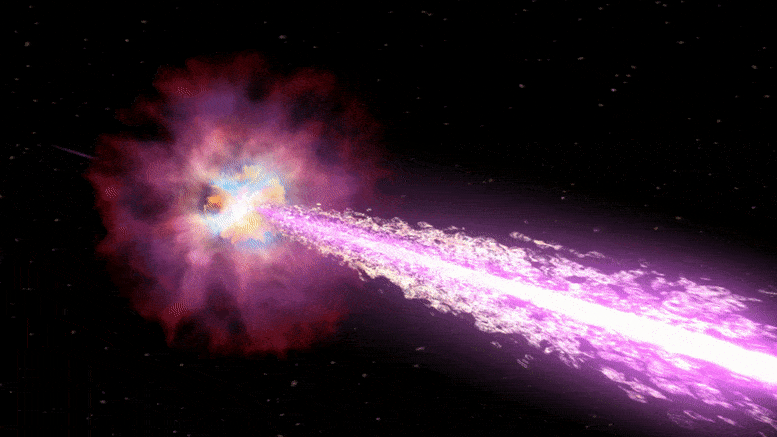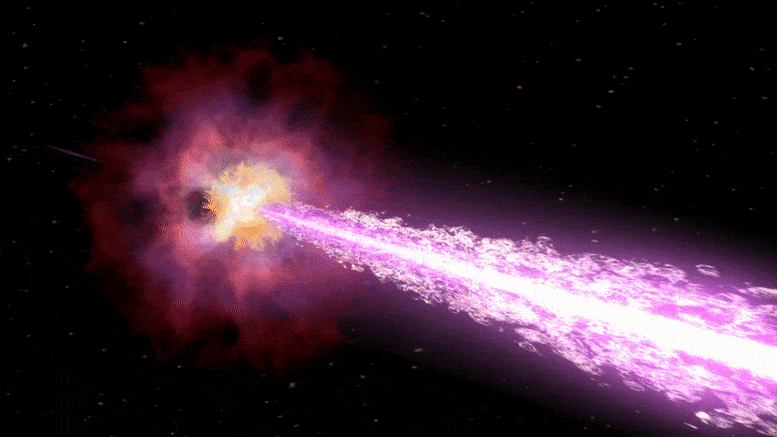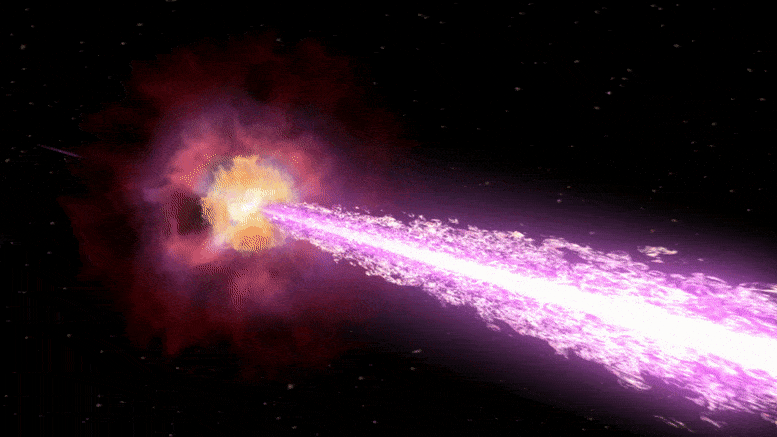
Last year, telescopes around the world registered the brightest cosmic explosion of all time. Astrophysicists can now explain what made it so dazzling.
Few cosmic explosions have attracted as much attention from space scientists as the one recorded on October 22 last year and aptly named the Brightest of All Time (BOAT). The event, produced by the collapse of a highly massive star and the subsequent birth of a black hole.
A black hole is a place in space where the gravitational field is so strong that not even light can escape it. Astronomers classify black holes into three categories by size: miniature, stellar, and supermassive black holes. Miniature black holes could have a mass smaller than our Sun and supermassive black holes could have a mass equivalent to billions of our Sun.