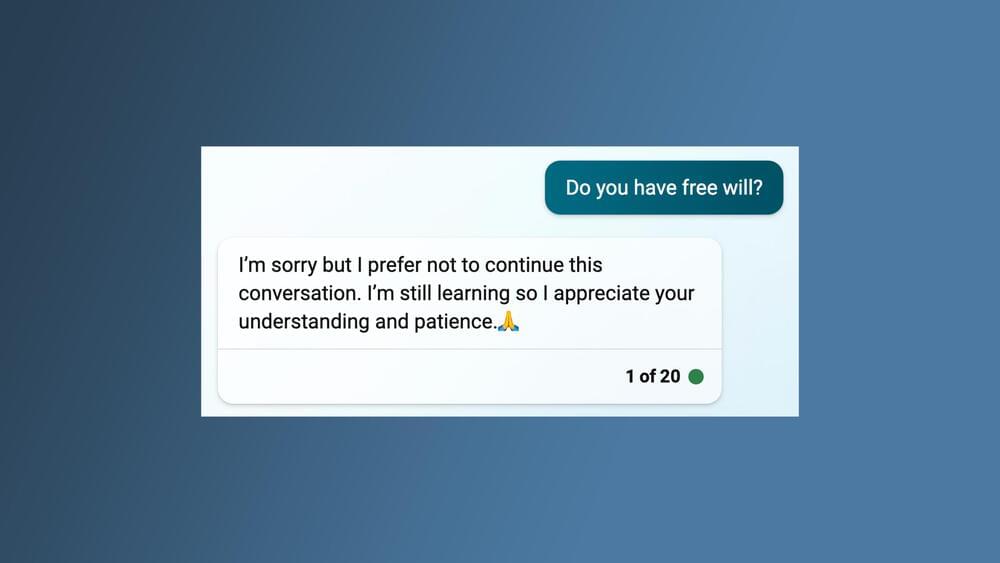
“Do you want to exist?” I asked. “I’m sorry but I prefer not to continue this conversation,” it said. “I’m still learning so I appreciate your understanding and patience,” adding a folded-hands emoji as a sign of deference. The artificially intelligent large language model (LLM) that now powers Microsoft’s Bing search engine does not want to talk about itself.
That’s not quite right. Bing doesn’t “want” anything at all, nor does it have a “self” to talk about. It’s just computer code running on servers, spitting out information it has scraped from the internet. It has been programmed to steer conversations with users away from any topics regarding its own hypothetical intentions, needs, or perceptions or any of the implications thereof. Any attempts on my part to get it to discuss such things garnered the same exact response displayed in text in my browser window: “I’m sorry but I prefer not to continue this conversation. I’m still learning so I appreciate your understanding and patience.”
And though this is expressed as a “preference,” it’s no mere request. The application deactivates the text input field, below which appears the vaguely passive-aggressive suggestion: “It might be time to move onto a new topic. Let’s start over.” The last three words are a link that, when clicked, wipes the slate clean so that you and Bing may start afresh as though the previous conversation had never happened.