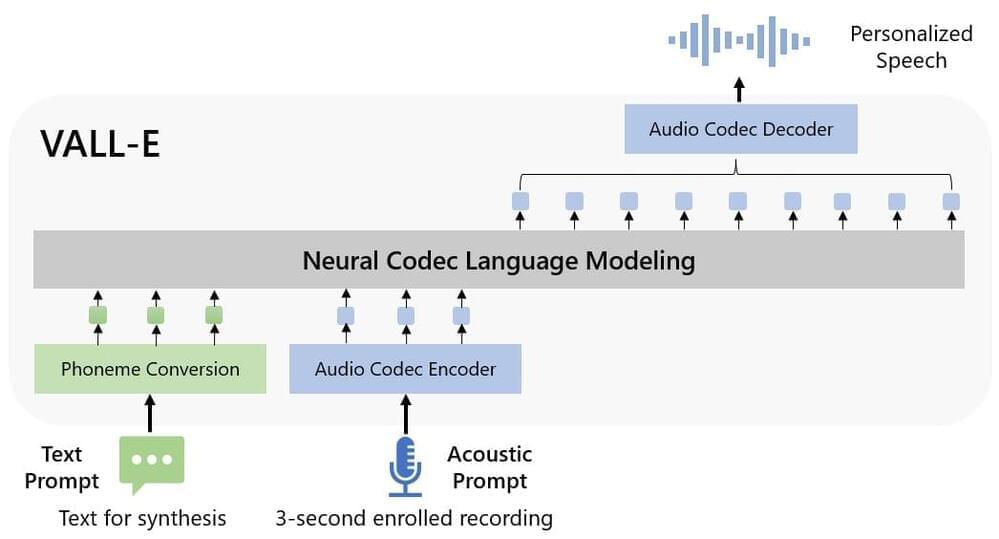
Ray Kurzweil on the Law of accelerating returns:
Ray Kurzweil: Acceleration of technology is the implication of what I call the law of accelerating returns. The nature of technological progress is exponential. If I count linearly 30 steps: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5… I get to 30. If I count exponentially: 2, 4, 8, 16… 30 steps later I’m at a billion. It makes a dramatic difference.
TRANSCENDENT MAN chronicles the life and ideas of Ray Kurzweil, the inventor and futurist known for his bold vision of the Singularity, a point in the near future when technology will be changing so rapidly, that we will have to enhance ourselves with artificial intelligence to keep up. Ray predicts this will be the dawning of a new civilization in which we will no longer be dependent on our physical bodies, we will be billions of times more intelligent and there will be no clear distinction between human and machine, real reality and virtual reality.
http://transcendentman.com.
https://facebook.com/TranscendentMan/
Tweets by TranscendentMan