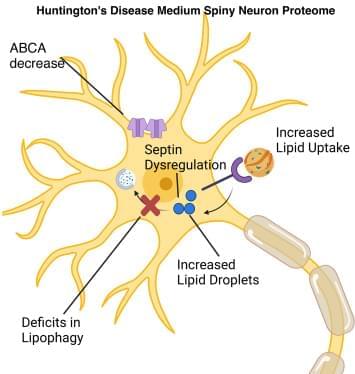
Huntington’s disease (HD) is a neurodegenerative disease caused by a CAG repeat expansion in the Huntingtin (HTT) gene. The resulting polyglutamine (polyQ) tract alters the function of the HTT protein. Although HTT is expressed in different tissues, the medium spiny projection neurons (MSNs) in the striatum are particularly vulnerable in HD. Thus, we sought to define the proteome of human HD patient–derived MSNs. We differentiated HD72 induced pluripotent stem cells and isogenic controls into MSNs and carried out quantitative proteomic analysis. Using data-dependent acquisitions with FAIMS for label-free quantification on the Orbitrap Lumos mass spectrometer, we identified 6,323 proteins with at least two unique peptides. Of these, 901 proteins were altered significantly more in the HD72-MSNs than in isogenic controls. Functional enrichment analysis of upregulated proteins demonstrated extracellular matrix and DNA signaling (DNA replication pathway, double-strand break repair, G1/S transition) with the highest significance. Conversely, processes associated with the downregulated proteins included neurogenesis-axogenesis, the brain-derived neurotrophic factor-signaling pathway, Ephrin-A: EphA pathway, regulation of synaptic plasticity, triglyceride homeostasis cholesterol, plasmid lipoprotein particle immune response, interferon-γ signaling, immune system major histocompatibility complex, lipid metabolism and cellular response to stimulus. Moreover, proteins involved in the formation and maintenance of axons, dendrites, and synapses (e.g., Septin protein members) were dysregulated in HD72-MSNs. Importantly, lipid metabolism pathways were altered, and using quantitative image, we found analysis that lipid droplets accumulated in the HD72-MSN, suggesting a deficit in the turnover of lipids possibly through lipophagy. Our proteomics analysis of HD72-MSNs identified relevant pathways that are altered in MSNs and confirm current and new therapeutic targets for HD.