Artificial intelligence can ace medical exams and assess patient symptoms, but it doesn’t care whether you life or die.



Our civilization has leveraged humanism, science, technology, and a can-do attitude to make our world radically better than it ever has been before. Yet unimaginable tragedies still happen on a continuous basis. We will keep seeking solutions, improving the world, and making progress. Data support the idea that we are on the way. I urge us all to not lose faith in the power of progress. It is vital for the future of every living creature that we keep using science to change the world for the better.
From the article: “It is wrong to think that these three statements contradict each other. We need to see that they are all true to see that a better world is possible.”
The world is much better. The world can be much better. All three statements are true at the same time.
Discussions about the state of the world too often focus on the first statement: The news highlights what is going wrong, rarely mentioning any positive development.
A pushback on this narrative takes it to the other extreme, which is equally damaging. Solely communicating the progress that the world has achieved becomes unhelpful, or even repugnant, when it glosses over the problems that are real today.
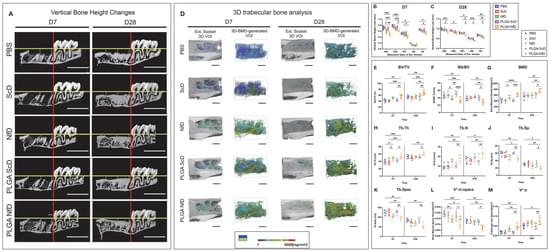
Residual ridge resorption combined with dimensional loss resulting from tooth extraction has a prolonged correlation with early excessive inflammation. Nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) decoy oligodeoxynucleotides (ODNs) are double-stranded DNA sequences capable of downregulating the expression of downstream genes of the NF-κB pathway, which is recognized for regulating prototypical proinflammatory signals, physiological bone metabolism, pathologic bone destruction, and bone regeneration. The aim of this study was to investigate the therapeutic effect of NF-κB decoy ODNs on the extraction sockets of Wistar/ST rats when delivered by poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) nanospheres.
The QCD vacuum (i.e., the ground state of vacuum in the quantum chromodynamics regime) is theoretically characterized by the presence of non-zero expectation values of condensates, such as gluons and quark–antiquark pairs. Instead of being associated with a lack of particles and interactions in an empty space, physics theory regards this state as filled with the so-called condensates, which have the same quantum numbers as the vacuum and cannot be directly observed.
While many theoretical physicists have discussed the properties of the QCD vacuum, experimentally validating these theoretical predictions has so far proved challenging, simply because the condensates in this state are elusive and cannot be directly detected. A hint of experimental “observation” can be found in the theoretical predictions of the properties of the QCD vacuum.
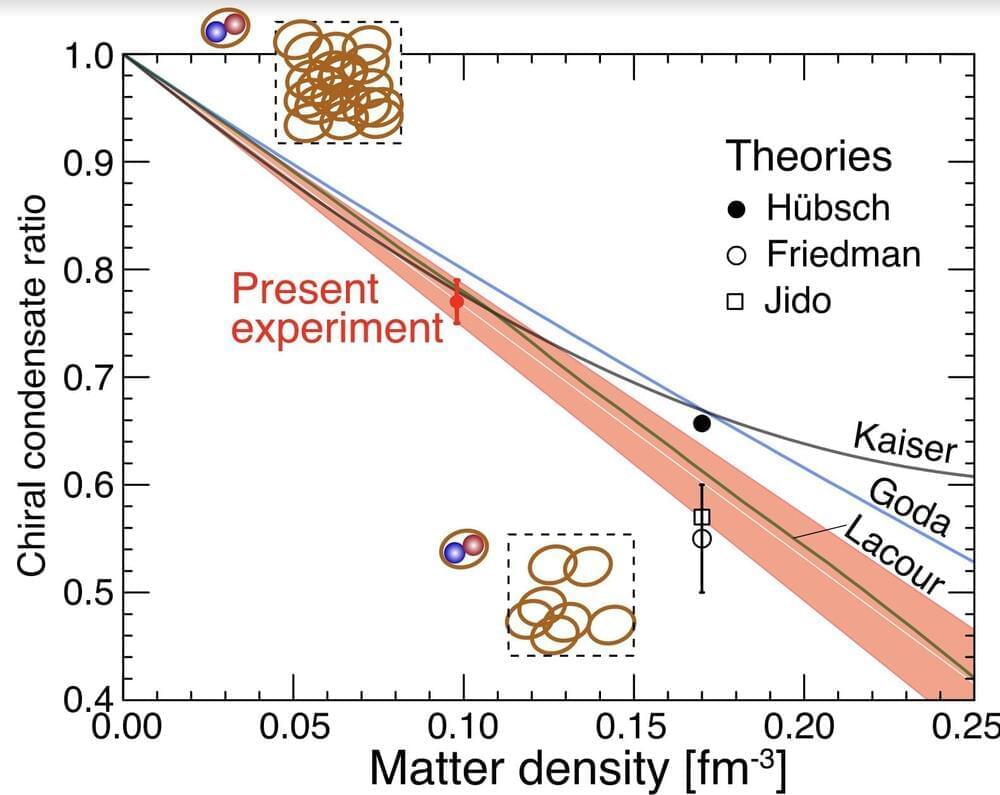
Theories predict that the condensate may decrease in the high temperature and/or at a high matter density due to the partial restoration of the so-called chiral symmetry. To prove these theories, some researchers collected measurements during ultra-relativistic, head-on collisions of heavy ions at particularly high temperatures. Other efforts in this area tried to probe properties of the QCD vacuum by measuring so-called “medium effects.” These are essentially effects that alter the QCD vacuum and its structure, prompted by the presence of high matter density such as nuclear matter.
Michael Levin’s 2019 paper “The Computational Boundary of a Self” is discussed. The main topics of conversation include Scale-Free Cognition, Surprise & Stress, and the Morphogenetic Field. Michael Levin is a scientist at Tufts University; his lab studies anatomical and behavioral decision-making at multiple scales of biological, artificial, and hybrid systems. He works at the intersection of developmental biology, artificial life, bioengineering, synthetic morphology, and cognitive science.
🚩The Computational Boundary of a Self: Developmental Bioelectricity Drives Multicellularity and Scale-Free Cognition (can read in browser or download as pdf)
https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpsyg.2019.02688/full.
❶ Scale-Free Cognition.
3:05 Ultimate question of the embodied mind.
5:50 The most difficult interview to prepare for.
6:55 One of my favorite papers of all time (screenshare)
7:40 The Computational Boundary of a Self.
9:25 Defining intelligence (cybernetics)
10:30 Cognitive light cones.
16:50 All intelligence is collective intelligence.
17:35 Nested selves vs. one integrated self (Not Integrated Information Theory)
21:10 The same dynamics in the brain occur in every tissue of the body.
22:50 Why scale “free” cognition?
❷ Stress & Surprise.
27:22 Stress = Surprise?
30:30 Intelligence within a salamander example (homeostatic capability of collective intelligence)
33:35 The scale-free importance of stress.
37:30 Stress is an exported error signal.
40:45 Stress means your problem becomes everyone’s problem (cooperation without altruism)
42:25 Stress has no ownership metadata (gap junctions permit mind meld)
❸ The Morphogenetic Field.
49:00 About 99% of the Shannon information in a cell is in the membrane and transmembrane gradient (Bob Gatenby)
52:25 Shannon information doesn’t distinguish meaning… 55:53 Cancer cells have the wrong scope of “self” 1:01:17 Manipulating cells via retraining vs micromanaging 1:04:45 “Drugs and words have the same mechanisms of action”-Fabrizio Benedetti 1:07:10 Morphogenetic field of signals coordinating cell behavior, bioelectricity special layer (screenshare) 1:11:13 Harold Saxton Burr predicted this 100 years ago! 1:14:50 Connections to Zen Buddhism 1:18:18 Find more of Levin’s work 🚩Links to Levin 🚩 https://youtube.com/watch?v=YnObwxJZpZc&feature=share https://twitter.com/drmichaellevin https://www.drmichaellevin.org/ https://as.tufts.edu/biology/levin-lab Technological Approach to Mind Everywhere: An Experimentally-Grounded Framework for Understanding Diverse Bodies and Minds (2022) https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/.… Buddhism, and AI: Care as the Driver of Intelligence (2022) https://www.mdpi.com/1099-4300/24/5/710 Emergence of informative higher scales in biological systems: a computational toolkit for optimal prediction and control (2020) https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/.… 🚾 Works Cited Jeremy Quay (visual artist) at https://peregrinecr.com/ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/William… https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Harold_… There’s Plenty of Room Right Here: Biological Systems as Evolved, Overloaded, Multi-Scale Machines (Bongard & Levin 2023) https://www.mdpi.com/2313-7673/8/1/110 Bob Gatenby talk on “Information Dynamics in Living Systems” • Bob Gatenby talk…
🚨 Note.
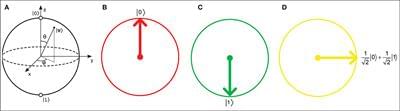
Many current computational models that aim to simulate cortical and hippocampal modules of the brain depend on artificial neural networks. However, such classical or even deep neural networks are very slow, sometimes taking thousands of trials to obtain the final response with a considerable amount of error. The need for a large number of trials at learning and the inaccurate output responses are due to the complexity of the input cue and the biological processes being simulated. This article proposes a computational model for an intact and a lesioned cortico-hippocampal system using quantum-inspired neural networks. This cortico-hippocampal computational quantum-inspired (CHCQI) model simulates cortical and hippocampal modules by using adaptively updated neural networks entangled with quantum circuits. The proposed model is used to simulate various classical conditioning tasks related to biological processes. The output of the simulated tasks yielded the desired responses quickly and efficiently compared with other computational models, including the recently published Green model.
Several researchers have proposed models that combine artificial neural networks (ANNs) or quantum neural networks (QNNs) with various other ingredients. For example, Haykin (1999) and Bishop (1995) developed multilevel activation function QNNs using the quantum linear superposition feature (Bonnell and Papini, 1997).
The prime factorization algorithm of Shor was used to illustrate the basic workings of QNNs (Shor, 1994). Shor’s algorithm uses quantum computations by quantum gates to provide the potential power for quantum computers (Bocharov et al., 2017; Dridi and Alghassi, 2017; Demirci et al., 2018; Jiang et al., 2018). Meanwhile, the work of Kak (1995) focused on the relationship between quantum mechanics principles and ANNs. Kak introduced the first quantum network based on the principles of neural networks, combining quantum computation with convolutional neural networks to produce quantum neural computation (Kak, 1995; Zhou, 2010). Since then, a myriad of QNN models have been proposed, such as those of Zhou (2010) and Schuld et al. (2014).
Scientists at MIT have unlocked a major breakthrough in the battle to reverse the effects of Alzheimer’s disease — one that shows “dramatic reductions” in neurodegeneration, a report stated. The exciting achievement came about after researchers were able to interfere with an enzyme typically found to be overactive in the brains of Alzheimer’s patients.
