The new contest aims to spur innovation into longer ‘healthspans’ with treatments that can actually reverse age-related degradation in body, mind and immune system.



How many fundamental forces are there in our universe? For particle physicists, answering this question can be tricky.
Of course, there’s the force of gravity, which keeps us from floating out of our seats. There’s also the strong nuclear force, which glues the nuclei of our atoms together. Then there’s the electromagnetic force, which is where we get electric currents and magnetic fields. And there’s the weak nuclear force, which mediates radioactive decay.
We’re up to four forces, right?
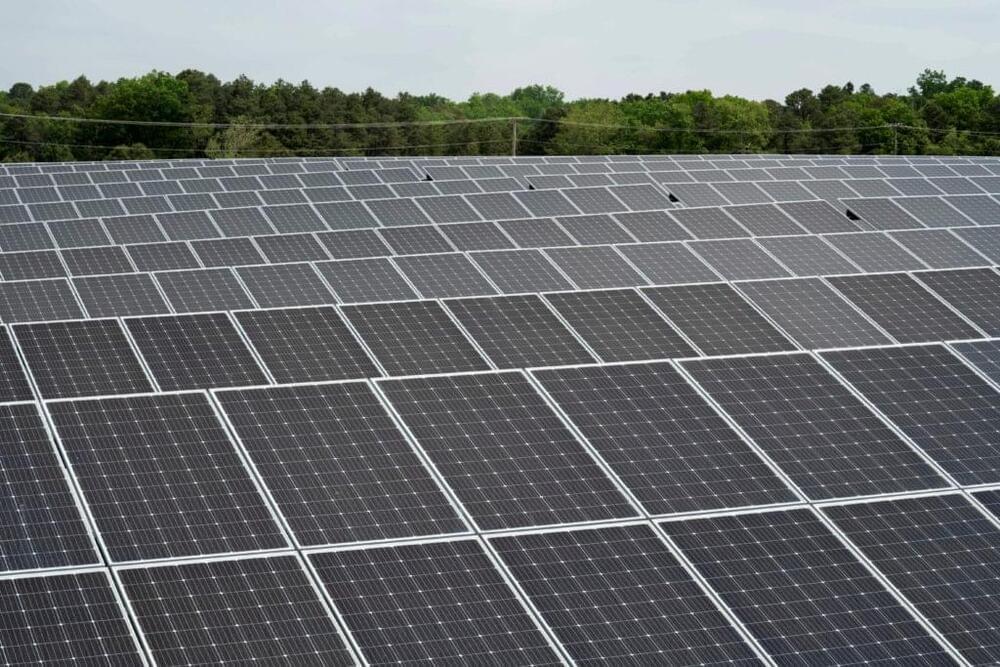



CHARLESTON, W.Va. (AP) — An entire county school system in coal-producing West Virginia is going solar, representing what a developer and U.S. Sen. Joe Manchin’s office touted on Wednesday as the biggest-ever single demonstration of sun-powered renewable electricity in Appalachian public schools.
The agreement between Wayne County Schools and West Virginian solar installer and developer Solar Holler builds on historic investments in coal communities made possible by the Inflation Reduction Act, which Democratic Sen. Manchin had a major role in shaping as chairman of the Senate Energy and Natural Resources Committee.
Manchin, who announced this month that he wouldn’t run for reelection in the deep-red state, citing an increasingly polarized political system, was quick Wednesday to tout U.S. President Joe Biden’s 2022 landmark climate, health and tax law, which placed special emphasis on creating new clean energy jobs.
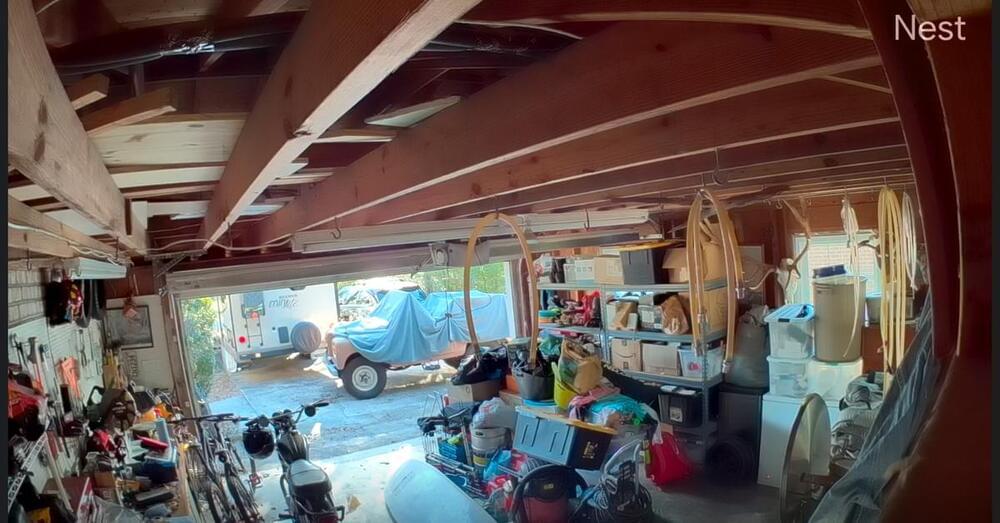

Google’s adding a new garage door detection feature to its Nest security cameras that will alert you if your garage door has been left open. The company is also bringing the first-gen Google Nest Outdoor Cam to the Google Home app and finally allowing Nest Cam users to create custom clips in the Google Home app.
These new features are part of the Google Home app’s public preview and are rolling out this week. Adina Roth, product manager of Google Home & Nest, announced the updates in a blog post on Wednesday.
The tech billionaire Elon Musk has come to define innovation, but he can also be a lightning rod for controversy; he recently endorsed antisemitic remarks on X, formerly known as Twitter, which prompted companies to pull their advertising. In his interview, Musk discusses his emotional state and why he has “no problem being hated.” This interview was with Andrew Ross Sorkin of The New York Times at the annual DealBook Summit and recorded live in front of an audience at Jazz at Lincoln Center.
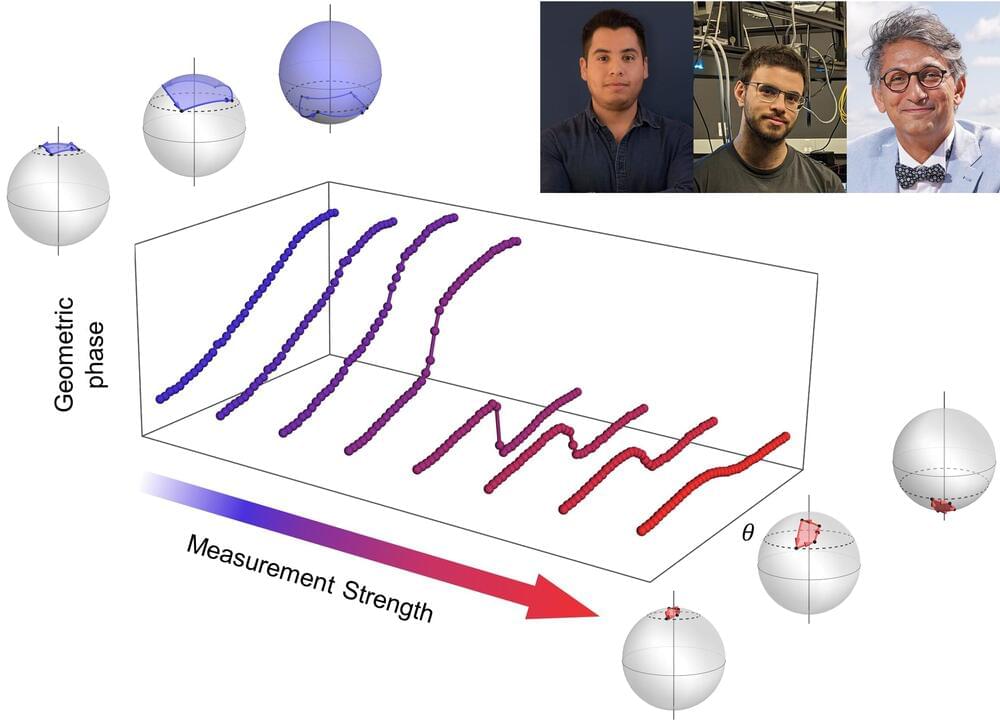
Researchers from the University of Ottawa (uOttawa), in collaboration with the Weizmann Institute of Science and Lancaster University, have observed a hidden quantum transition that can only be seen depending on how observers perform measurements.
The study “Topological Transitions of the generalized Pancharatnam-Berry phase” was published in Science Advances on 24 November 2023.
An essential part of the scientific method relies on the ability to measure the output of an experiment accurately and to juxtapose these findings with previous results. Scientists develop measurement devices, or meters, which enable them to precisely quantify the magnitude of physical properties. However, the “measurement process” raises a critical and intriguing question: does the process of measuring a parameter alter the system being measured?
XPRIZE has launched the largest prize in history–XPRIZE Healthspan, a competition that will revolutionize the way we approach human aging. In case you missed it, watch our launch event here.
The Earth’s magnetic field plays a big role in protecting people from hazardous radiation and geomagnetic activity that could affect satellite communication and the operation of power grids. And it moves.
Scientists have studied and tracked the motion of the magnetic poles for centuries. The historical movement of these poles indicates a change in the global geometry of the Earth’s magnetic field. It may even indicate the beginning of a field reversal—a “flip” between the north and south magnetic poles.
I’m a physicist who studies the interaction between the planets and space. While the north magnetic pole moving a little bit isn’t a big deal, a reversal could have a big impact on Earth’s climate and our modern technology. But these reversals don’t happen instantaneously. Instead, they occur over thousands of years.