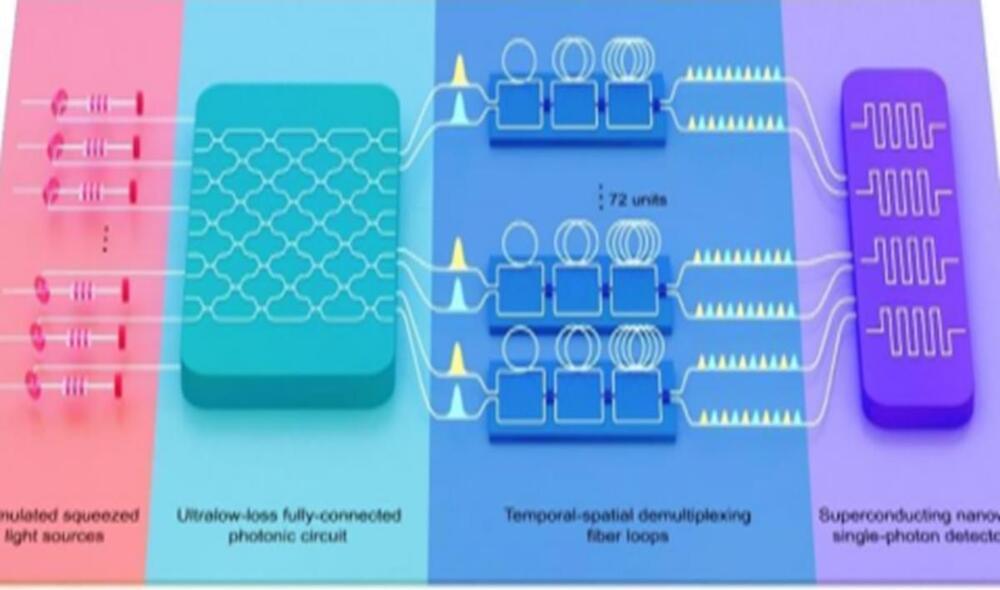
With the successful development of the Jiuzhang 3.0 quantum computer prototype, which makes use of 255 detected photons, China continues to hold a world-leading position in the field of quantum computer research and development, lead scientists for the program told the Global Times on Wednesday.
The research team, composed of renowned quantum physicists Pan Jianwei and Lu Chaoyang from the University of Science and Technology of China in collaboration with the Shanghai Institute of Microsystem and Information Technology under the Chinese Academy of Sciences and the National Parallel Computer Engineering Technology Research Center, announced the successful construction of a 255-photon-based prototype quantum computer named Jiuzhang 3.0 early Wednesday morning.
The quantum computing feat accomplished by the team of talents achieves a speed that is 10 quadrillion times faster in solving Gaussian boson sampling (GBS) problems compared with the world’s fastest supercomputers.