AI couldn’t necessarily provide instructions for how to create a bioweapon but could bridge gaps in knowledge that have soiled previous attempts.


“For AI to be motivated towards a goal, it must know what it wants.”
The possible board combinations in a game of Go are more than the number of atoms in the known universe, but it’s still a finite number. In the real world, there are infinite possibilities for what might happen next, and uncertainty is rampant. How realistic, then, is AGI?
A recent research paper published in Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution explores obstacles toward AGI. Biological systems with degrees of general intelligence — organisms ranging from the humble microbes to the humans reading this — are capable of improvising to meet their goals. What prevents AI from improvising?

After sifting through more than 1.8 million pages identified as admin portals, researchers made a disheartening discovery — 40,000 of them used “admin” as its password, making it the most popular credential used by IT administrators.
The research was conducted on 2023 passwords between January and September by a team with Outpost24, which also found an increased reliance on default passwords.
The top 10 passwords discovered by the analysis included common defaults and easy-to-guess options:
A recent publication in Cell demonstrates that arginine, an amino acid that facilitates various cellular processes, including cellular growth, also promotes tumor growth. The study shows that arginine reprograms the metabolism of the tumor, a mechanism that many cancer cells use to replicate continuously.
The liver’s primary functions include metabolizing nutrients obtained from food and storing energy for later use by the body. Thus, the liver is highly involved in the body’s metabolic balance.
Over the past two decades, a growing body of evidence suggests cancer is a metabolic disease. Almost all cancers, regardless of the tissue in which they develop, have an impairment in energy metabolism.

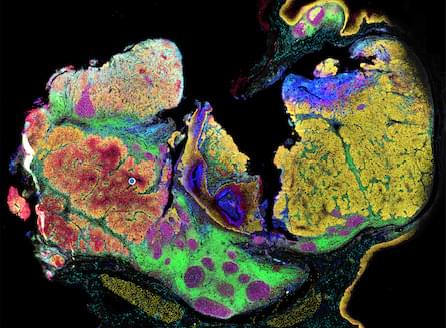
This work is published in GEN Biotechnology in the paper, “Mapping the Spatial Proteome of Head and Neck Tumors: Key Immune Mediators and Metabolic Determinants in the Tumor Microenvironment.”
HNSCCs are tumors that develop in the lip, oral cavity, larynx, salivary glands, nose, sinuses, or the skin of the face. They are the seventh most common cancer globally causing more than 300,000 deaths annually. Immune checkpoint inhibitors have shown promise in treating recurrent/metastatic cases.
Here, researchers present a framework for single-cell spatial analysis of proteins to analyze HNSCCs. First, they developed an ultra-high plex antibody panel with antibodies for detection of immune cells, cancer cells, and markers that identify cellular metabolism, apoptosis and stress, tumor invasion, and metastasis, as well as cellular proliferation and deregulation.

Data serves as the foundation of today’s biotechnology and pharmaceutical industries, and that foundation keeps expanding. “The appreciation of the value of data and need for quality data has grown in recent years,” says Anastasia Christianson, PhD, vice president and global head of AI, machine learning and data, Pfizer. She notes that the concept of FAIR data—Findable, Accessible, Interoperable, and Reusable data1—is becoming more widely accepted and more closely achieved.
Part of the transition in data use arises almost philosophically. “There has been a cultural shift or mindset change from data management for the purpose of storage and archiving to data management for the purpose of data analysis and reuse,” Christianson explains. “This is probably the most significant advance. The exponential growth of analytics capabilities and artificial intelligence have probably raised both the expectations for and appreciation of the value of data and the need for good data management and data quality.”
