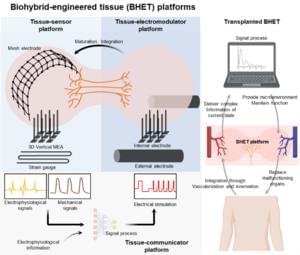
An abstract is unavailable.

Stevia may provide more benefits than as a zero-calorie sugar substitute. When fermented with bacteria isolated from banana leaves, stevia extract kills off pancreatic cancer cells but doesn’t harm healthy kidney cells, according to a research team at Hiroshima University.
The researchers published their findings on April 28 in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences.
“Globally, the incidence and mortality rates of pancreatic cancer continue to rise, with a five-year survival rate of less than 10%,” said co-author Narandalai Danshiitsoodol, associate professor in Department of Probiotic Science for Preventive Medicine, Graduate School of Biomedical and Health Sciences.

In the Voltaire Lecture 2025, Professor Anil Seth will set out an approach to understanding consciousness which, rather than trying to solve the mystery head-on, tries to dissolve it by building explanatory bridges from physics and biology to experience and function. In this view, conscious experiences of the world around us, and of being a ‘self’ within that world, can be understood in terms of perceptual predictions that are deeply rooted in a fundamental biological imperative – the desire to stay alive.
At this event, Professor Seth will explore how widely distributed beyond human beings consciousness may be, with a particular focus on AI. He will consider whether consciousness might depend not just on ‘information processing’, but on properties unique to living, biological organisms, before ending with an exploration of the ethical implications of an artificial intelligence that is either actually conscious – or can convincingly pretend to be.
Considering that the distillation requires access to the innards of the teacher model, it’s not possible for a third party to sneakily distill data from a closed-source model like OpenAI’s o1, as DeepSeek was thought to have done. That said, a student model could still learn quite a bit from a teacher model just through prompting the teacher with certain questions and using the answers to train its own models — an almost Socratic approach to distillation.
Meanwhile, other researchers continue to find new applications. In January, the NovaSky lab at the University of California, Berkeley, showed that distillation works well for training chain-of-thought reasoning models, which use multistep “thinking” to better answer complicated questions. The lab says its fully open-source Sky-T1 model cost less than $450 to train, and it achieved similar results to a much larger open-source model. “We were genuinely surprised by how well distillation worked in this setting,” said Dacheng Li, a Berkeley doctoral student and co-student lead of the NovaSky team. “Distillation is a fundamental technique in AI.”

In spite of having plagued humans for millennia, t yphoid fever is rarely considered in developed countries today. But this ancient threat is still very much a danger in our modern world.
According to research published in 2022, the bacterium that causes typhoid fever is evolving extensive drug resistance, and is rapidly replacing strains that aren’t resistant.
Currently, antibiotics are the only way to effectively treat typhoid, which is caused by the bacterium Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi (S Typhi). Yet over the past three decades, the bacterium’s resistance to oral antibiotics has been growing and spreading.

In 2024, a quantum state of light was successfully teleported through more than 30 kilometers (around 18 miles) of fiber optic cable amid a torrent of internet traffic – a feat of engineering once considered impossible.
The impressive demonstration by researchers in the US may not help you beam to work to beat the morning traffic, or download your favourite cat videos faster.
However, the ability to teleport quantum states through existing infrastructure represents a monumental step towards achieving a quantum-connected computing network, enhanced encryption, or powerful new methods of sensing.

On the morning of April 26, Tsinghua University held an inauguration ceremony for Tsinghua AI Agent Hospital and the 2025 Tsinghua Medicine Townhall Meeting at the Main Building Reception Hall. Tsinghua President Li Luming and Vice President Wang Hongwei attended the event.
President Li Luming reviewed the progress of Tsinghua University’s medical programs over the past year, emphasizing the University’s strong commitment to the development of medical disciplines. He highlighted Tsinghua’s strength in fundamental research in Artificial intelligence, which has already led to a series of high-level innovations at the intersection of AI and medicine. The establishment of the Tsinghua AI Agent Hospital represents a new initiative by Tsinghua to leverage its strengths in science and engineering to empower the advancement of medicine.
President Li encouraged Tsinghua Medicine to remain committed to fostering virtue and talent, cultivating a new generation of medical innovators with both a strong medical foundation and AI literacy. He also called for deeper integration across disciplines, particularly between engineering and medicine, as well as closer ties between clinical practice and technology. Finally, he urged Tsinghua Medicine to align its work with cutting-edge global trends and national strategic needs, driving medical advancement and contributing to the protection of public health.