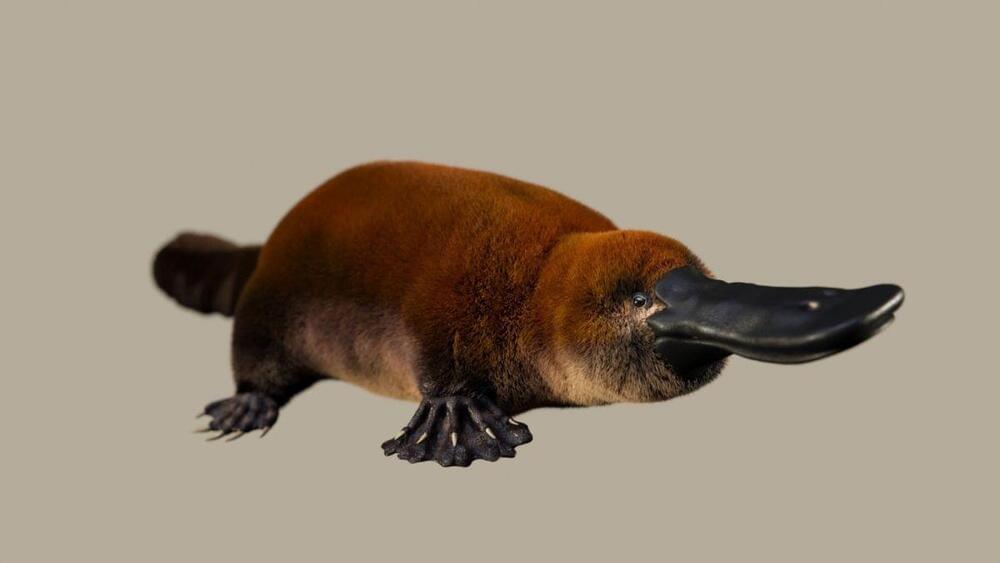
Fossils of a 70 million-year-old platypus relative called Patagorhynchus pascuali found in South America show that egg-laying mammals evolved on more than one continent.
A person who is lucidly aware of the miracles that surround him, who has learned to bear up under the loneliness, has made quite a bit of progress on the road to wisdom.
Quantum consciousness microtubules.
Share your videos with friends, family, and the world.
Research suggests inflammation may be just as important as cholesterol as a cause of heart attacks, suggesting different treatments should be considered for prevention.
Analysis By Clare Wilson
Researchers at the School of Cyber Security at Korea University, Seoul, have presented a new covert channel attack named CASPER can leak data from air-gapped computers to a nearby smartphone at a rate of 20bits/sec.
The CASPER attack leverages the internal speakers inside the target computer as the data transmission channel to transmit high-frequency audio that the human ear cannot hear and convey binary or Morse code to a microphone up to 1.5m away.
The receiving microphone can be in a smartphone recording sound inside the attacker’s pocket or a laptop in the same room.
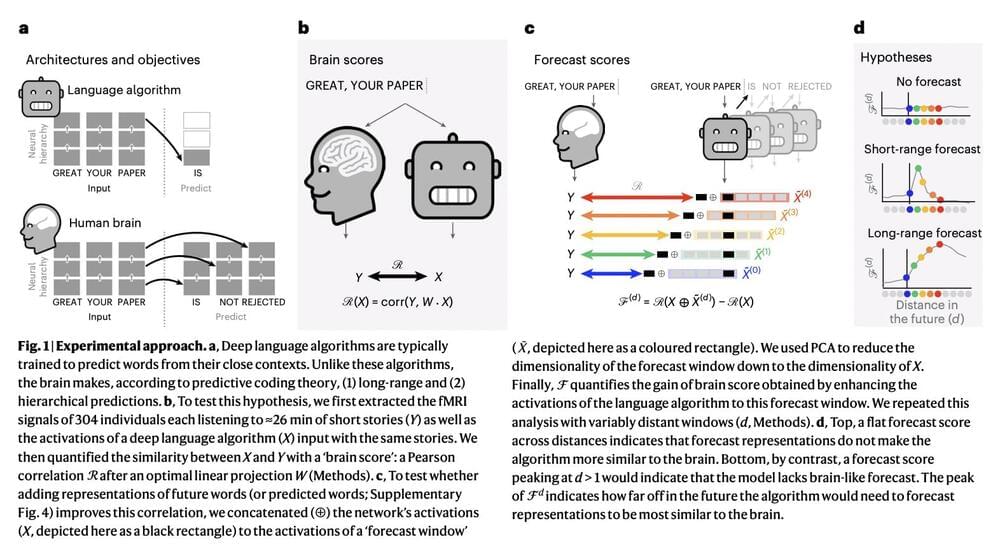
Deep learning has made significant strides in text generation, translation, and completion in recent years. Algorithms trained to predict words from their surrounding context have been instrumental in achieving these advancements. However, despite access to vast amounts of training data, deep language models still need help to perform tasks like long story generation, summarization, coherent dialogue, and information retrieval. These models have been shown to need help capturing syntax and semantic properties, and their linguistic understanding needs to be more superficial. Predictive coding theory suggests that the brain of a human makes predictions over multiple timescales and levels of representation across the cortical hierarchy. Although studies have previously shown evidence of speech predictions in the brain, the nature of predicted representations and their temporal scope remain largely unknown. Recently, researchers analyzed the brain signals of 304 individuals listening to short stories and found that enhancing deep language models with long-range and multi-level predictions improved brain mapping.
The results of this study revealed a hierarchical organization of language predictions in the cortex. These findings align with predictive coding theory, which suggests that the brain makes predictions over multiple levels and timescales of expression. Researchers can bridge the gap between human language processing and deep learning algorithms by incorporating these ideas into deep language models.
The current study evaluated specific hypotheses of predictive coding theory by examining whether cortical hierarchy predicts several levels of representations, spanning multiple timescales, beyond the neighborhood and word-level predictions usually learned in deep language algorithms. Modern deep language models and the brain activity of 304 people listening to spoken tales were compared. It was discovered that the activations of deep language algorithms supplemented with long-range and high-level predictions best describe brain activity.
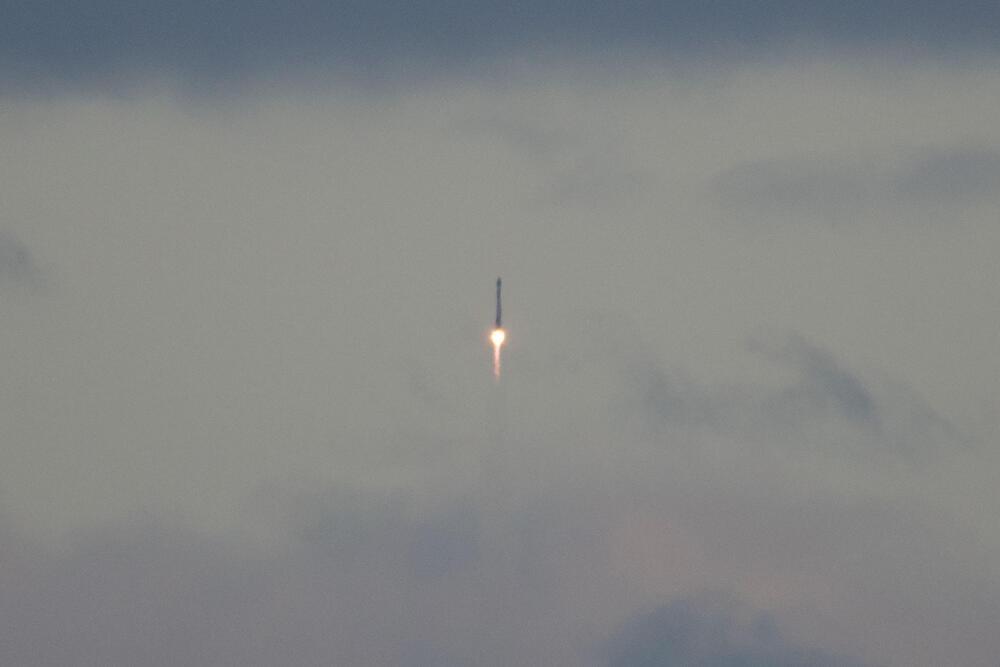
There’s a new sight to see in the skies over the eastern seaboard of the United States courtesy of Rocket Lab and NASA.
The space startup is beginning to make a habit of launching its Electron rockets from NASA’s Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia. Unlike the majority of space launches in the US that blast off from the far southeastern corner of the country in Florida, some of the nation’s largest population centers have a view of launches from Wallops.
The “Stronger Together” mission is the second launch of the space startup’s Electron rocket from Virginia. Before adding a second launch facility, all of the company’s previous launches were conducted from its primary launch pads in New Zealand over the past couple years.
There is a competition among technology companies to develop a humanoid robot that can perform various tasks, and one particular company, “Figure,” is at the forefront of this race.
A humanoid general-purpose robot is a robot that can mimic human actions and interact with the environment in a human-like way. This type of robot has the potential to perform various tasks, such as cooking, cleaning, and assisting people with disabilities.
The race to develop such robots is driven by the potential to revolutionize various industries, including manufacturing, healthcare, and retail. A successful humanoid robot could replace human workers in hazardous or repetitive tasks, increase productivity, and reduce costs.
The fact that “Figure” is leading this race suggests that they have made significant progress in developing a humanoid general-purpose robot. It is possible that they have developed new technology or software that gives them an advantage over their competitors.
Overall, it implies that there is intense competition among tech companies to develop the next generation of robots, and “Figure” is one of the frontrunners in this race.
Wondering if artificial intelligence will be taking your job anytime soon? We’re sure we speak for a lot of folks when we say: same.
Considering that AI is literally designed to model human capabilities and thus automate human tasks, it’s a fair question — and one that a group of professors from New York University (NYU), Princeton, and the University of Pennsylvania (UPenn) may have just helped to shed a little bit of light on in a new paper, aptly titled “How Will Language Modelers like ChatGPT Affect Occupations and Industries?”
Though the paper has yet to be peer-reviewed, the results are fascinating, not to mention ominous — especially, of course, for the folks most at risk.
A new experiment pulled off the most precise measurement of an electron’s self-generated magnetic field—and the universe’s subatomic model is at stake.