Multidisciplinary residential programmes and workshops help advance all the fields involved.


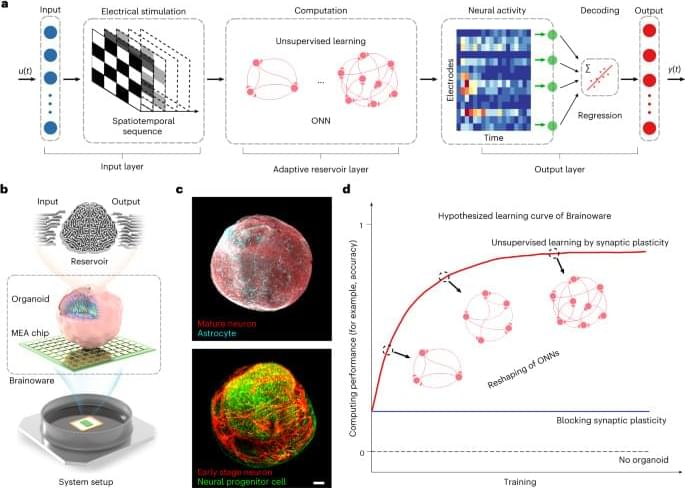


A new analysis of the distribution of matter in the Universe continues to find a discrepancy in the clumpiness of dark matter in the late and early Universe, suggesting a fundamental error in the standard cosmological model.
Cosmologists study the Universe by making a vast range of observations using a variety of modern techniques. Each observation can reveal different details about the Universe’s composition over a certain period of its history. An astronomical survey—a map of a region of the sky—is a powerful way to scan a large swath of the Universe and the objects it contains. For example, a weak-lensing survey does that by obtaining sharp images of galaxies, which can then be used to map the distribution of the Universe’s matter throughout history. The Hyper Suprime-Cam Subaru Strategic Program (HSC-SSP) is one such weak-lensing survey, and it has the highest resolution and the deepest depth of all current weak-lensing surveys. Over the past six years, the HSC-SSP survey team has spent 330 nights scanning 3% of the entire spherical sky, capturing the light emitted by galaxies up to 10 billion years ago.
Producing fake sound reflections that simulate the presence or absence of an object could allow the military to hide assets underwater.
A hologram plate simulates the presence of a three-dimensional object by reflecting the appropriate light waves. Now researchers have demonstrated an equivalent behavior with sound by precisely mimicking the acoustic pattern scattered from an object [1]. The technique could be useful in military efforts to hide or disguise underwater objects, or it may be useful in modifying the reflected sounds of objects so that they are easier to identify by people with impaired vision.
The sound waves reflected from an object can be used to reconstruct its position and shape, an idea routinely exploited in sonar and ultrasound imaging. In principle, using similar concepts, a cleverly produced pattern of scattered waves streaming out of a small region could signify that an object is present when it is not. Several recent attempts to realize such “acoustic cloning” have been unsuccessful because of limitations in recording the precise pattern of waves an object reflects, a necessary preliminary step.
An experimental vaccine against human papillomavirus—HPV—appears to be safe, and most importantly, benefits patients who develop a rare airway cancer that manifests as recurrent obstructive growths requiring dozens, sometimes, hundreds of surgeries over a lifetime to keep the tumors at bay.
The tiny phase 1 clinical study of only 15 patients has served as a proof of concept, demonstrating that recurrent respiratory papillomatosis, a cancerous disorder of the upper airways, can respond to therapeutic vaccination. The tumors are caused by either type 6 or type 11 human papillomavirus.
Writing in Science Translational Medicine, scientists at the Center for Immune-Oncology, a division of the U.S. National Cancer Institute in Bethesda, Maryland, tackled the problem of recurrent respiratory papillomatosis by testing a vaccine strategy designed to prevent tumor development. Dr. Scott M. Norberg, lead author of the research, writes that the evolving approach is aimed at providing a pathway for the prevention of a condition for which there is no cure.
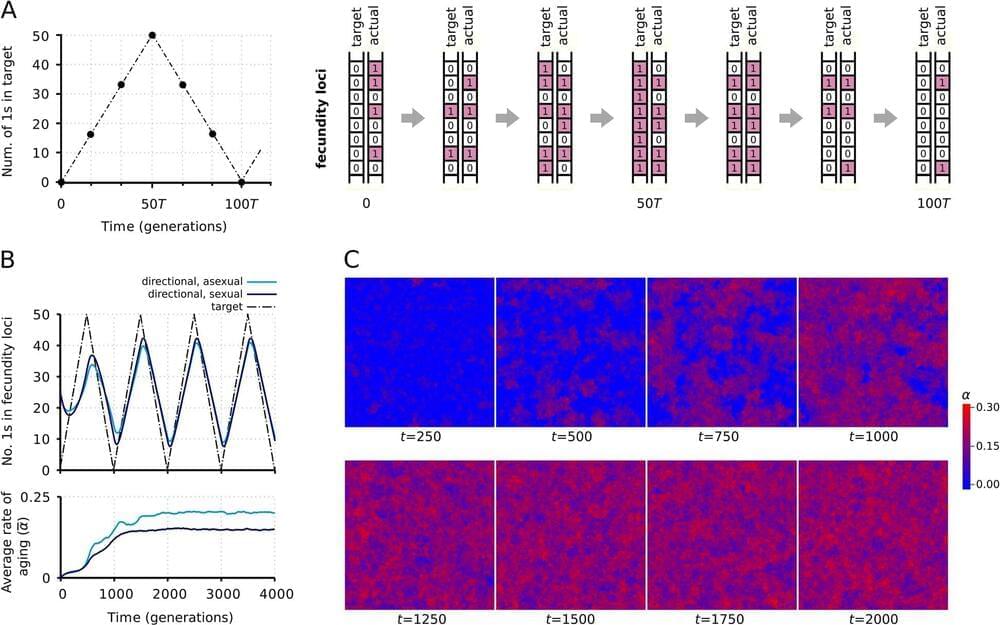
The mystery of aging has fascinated people for millennia, with many willing to do anything to halt or reverse this process, because aging is typically associated with gradual deterioration of most body functions. While senescence is a natural part of life, biologists understand surprisingly little about the emergence of this process during evolution.
It is not clear whether aging is inevitable because there are organisms that seemingly do not age at all; moreover, the phenomenon known as negative aging, or rejuvenation, does exist: for example, some turtles’ vital functions improve with age.
Researchers of the Institute of Evolution led by Academician Eörs Szathmáry have endeavored to prove the validity of a previously proposed but still unproven theory of aging. The theory suggests that under the right circumstances, evolution can favor the proliferation of genes controlling senescence.
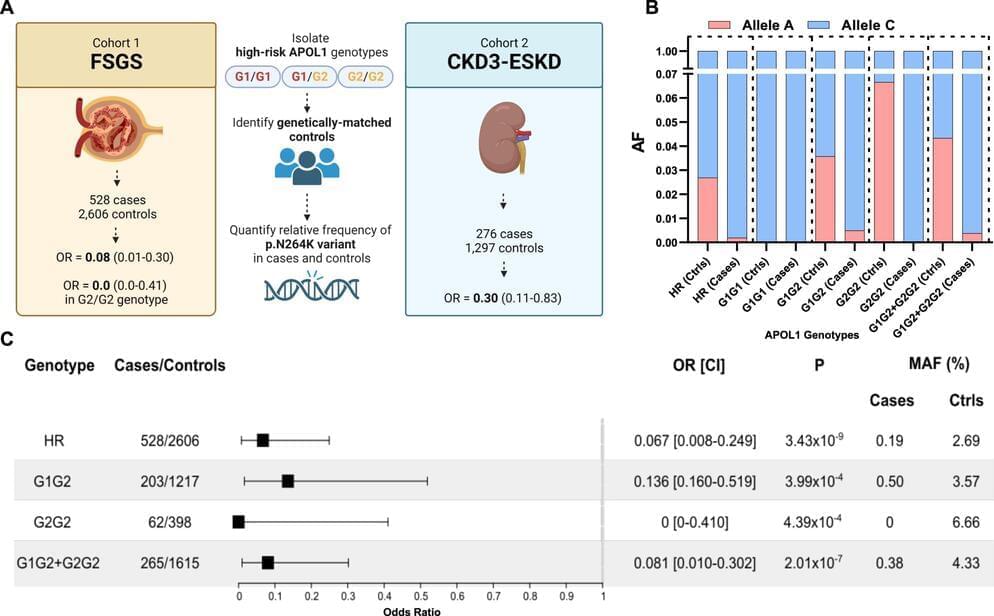
Many Black Americans who are thought to have a high risk of developing kidney disease possess a protective genetic variant that nullifies the extra risk, a new study from Columbia researchers has found. The work is published in the journal Nature Communications.
The study found that high-risk people who carry this variant have a risk of developing kidney disease much closer to that of the general population.
The findings will have an immediate impact on clinical practice, says study leader Simone Sanna-Cherchi, MD, associate professor of medicine at Columbia’s Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons.
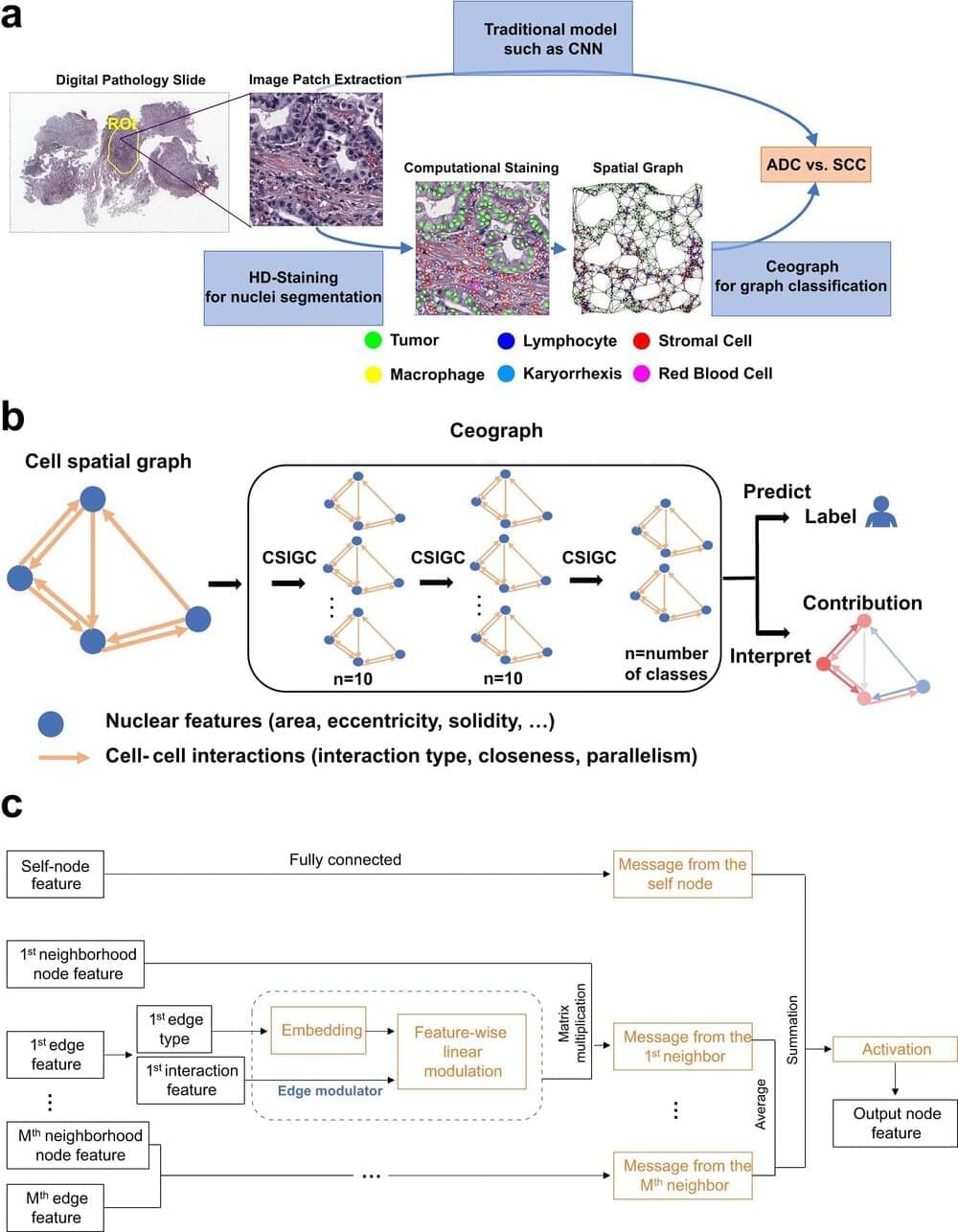
Researchers at UT Southwestern Medical Center have developed a novel artificial intelligence (AI) model that analyzes the spatial arrangement of cells in tissue samples. This innovative approach, detailed in Nature Communications, has accurately predicted outcomes for cancer patients, marking a significant advancement in utilizing AI for cancer prognosis and personalized treatment strategies.
“Cell spatial organization is like a complex jigsaw puzzle where each cell serves as a unique piece, fitting together meticulously to form a cohesive tissue or organ structure. This research showcases the remarkable ability of AI to grasp these intricate spatial relationships among cells within tissues, extracting subtle information previously beyond human comprehension while predicting patient outcomes,” said study leader Guanghua Xiao, Ph.D., Professor in the Peter O’Donnell Jr. School of Public Health, Biomedical Engineering, and the Lyda Hill Department of Bioinformatics at UT Southwestern. Dr. Xiao is a member of the Harold C. Simmons Comprehensive Cancer Center at UTSW.
Tissue samples are routinely collected from patients and placed on slides for interpretation by pathologists, who analyze them to make diagnoses. However, Dr. Xiao explained, this process is time-consuming, and interpretations can vary among pathologists. In addition, the human brain can miss subtle features present in pathology images that might provide important clues to a patient’s condition.