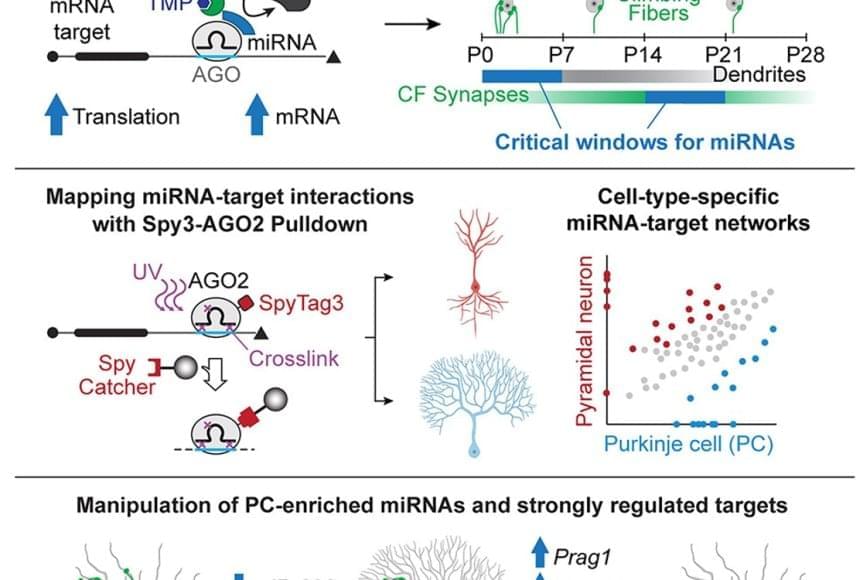
Previous studies have suggested that microRNAs are critical for brain development, but their specific role in differentiation—the process of stem cells maturing into specialized cells—remained unclear.
“When neurons develop, they need to at some point decide what subtype they will become, but we really didn’t know much about the blueprint that instructs this differentiation,” says the author. “There was a lot of evidence suggesting that microRNAs might have a very important role here, but because the tools were not good enough, we couldn’t really nail down that question until now.”
The team focused on Purkinje cells, which comprise less than 1% of cells in the cerebellum. Purkinje cells integrate information from different parts of the brain and body, enabling us to make smooth, controlled movements. They are some of the largest brain cells and have a tree-like appearance—a single axon “trunk” that supports a system of “branches” known as the dendritic arbor. Purkinje cells are also surrounded by structures called climbing fibers that wrap around the cells’ dendrites and deliver information from other parts of the brain.
To attain their large size and elaborate arbor, Purkinje cell development involves prolonged periods of growth and branching. In mice, the long process of Purkinje cell development is complete around four weeks after birth.
To investigate how microRNAs are involved in neuron differentiation, the team developed new tools that temporarily turn off microRNA function during specific developmental windows. They found that microRNAs are critical during two phases in Purkinje cell development: inhibiting microRNAs during the first week after birth resulted in Purkinje cells with less complex dendritic arbors and smaller cerebellums. In contrast, inhibiting microRNAs during the third week after birth prevented the Purkinje cells from forming synaptic connections with climbing fibers. These findings shed light on how microRNAs control the precise timing of different aspects of Purkinje cell development that were previously thought to happen concurrently.
The team also developed a mouse model to identify which genes the microRNA molecules were targeting. Using this system, they identified two microRNAs critical for Purkinje cell development (miR-206 and miR-133) and four gene targets (Shank3, Prag1, Vash1, and En2). When they compared the Purkinje cell microRNA-target map to a map for pyramidal neurons—a functionally different but similar-looking brain cell—they showed that the two cell types follow very different microRNA blueprints during development.