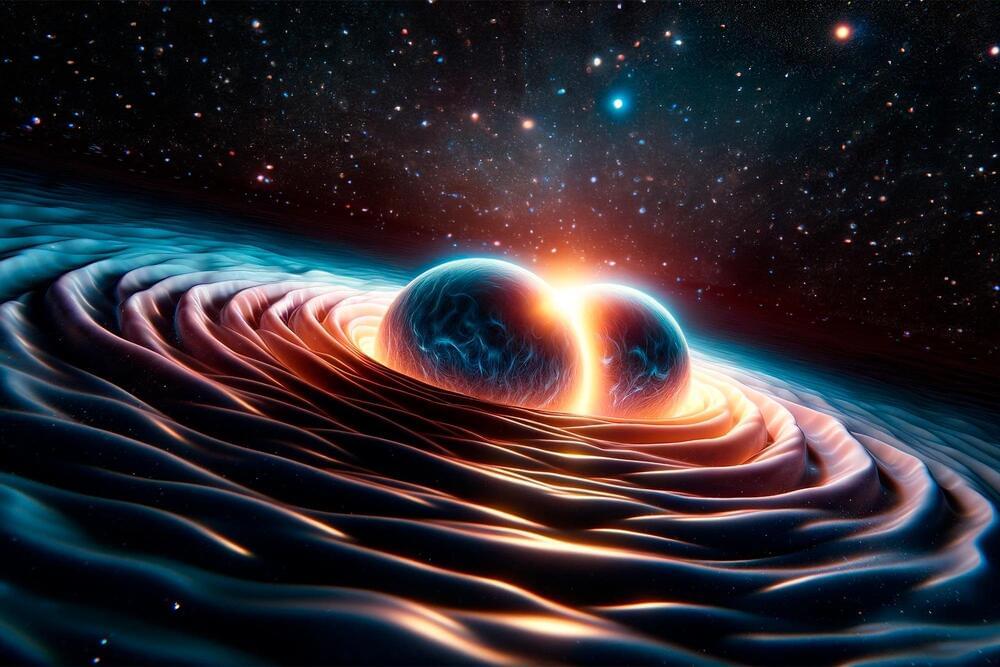
Simulations of binary neutron star mergers suggest that future detectors will distinguish between different models of hot nuclear matter.
Researchers used supercomputer simulations to explore how neutron star mergers affect gravitational waves, finding a key relationship with the remnant’s temperature. This study aids future advancements in detecting and understanding hot nuclear matter.
Exploring neutron star mergers and gravitational waves.