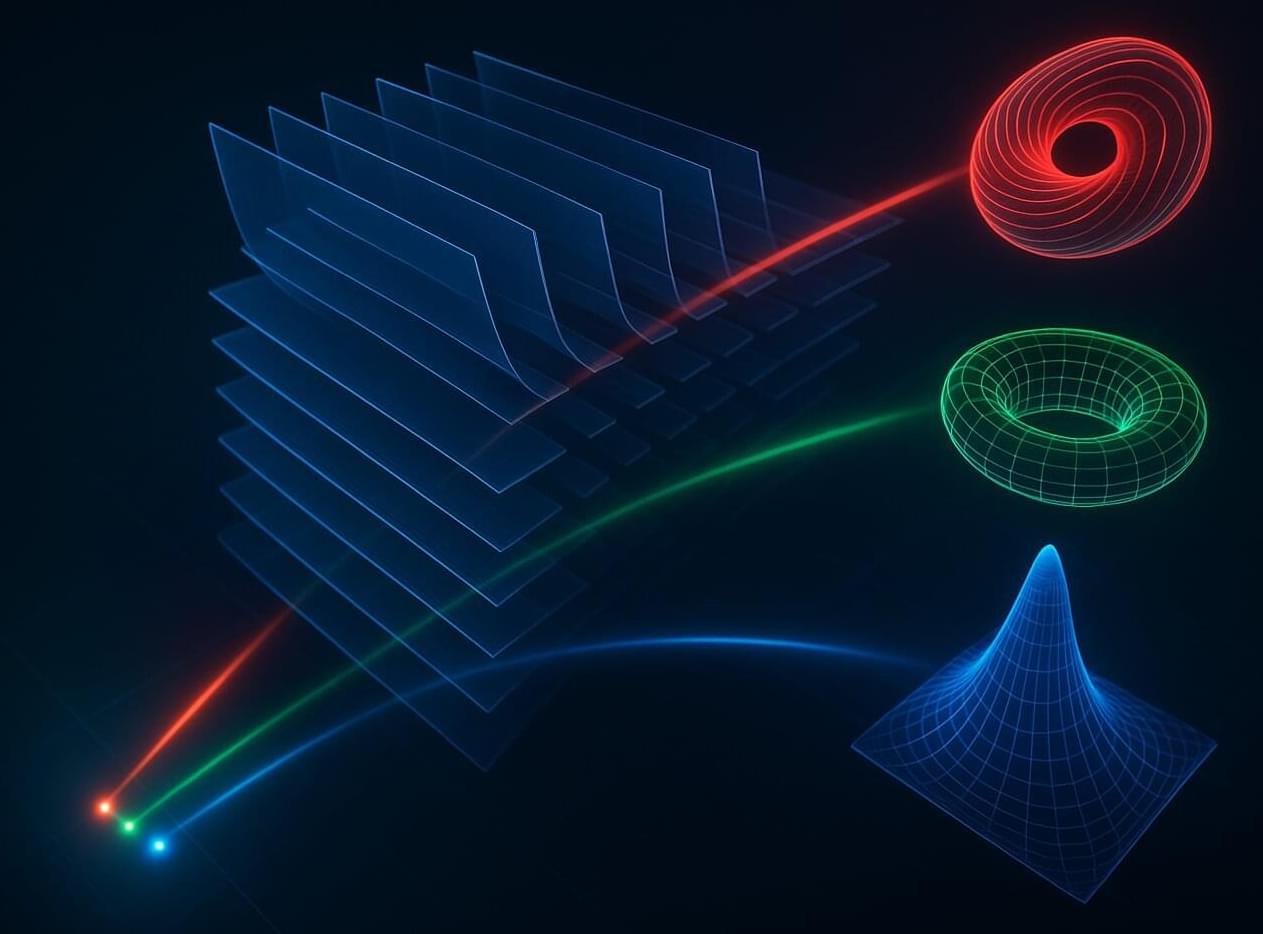
Engineers at the UCLA Samueli School of Engineering have introduced a universal framework for point spread function (PSF) engineering, enabling the synthesis of arbitrary, spatially varying 3D PSFs using diffractive optical processors. The research is published in the journal Light: Science & Applications.
This framework allows for advanced imaging capabilities—such as snapshot 3D multispectral imaging —without the need for spectral filters, axial scanning, or digital reconstruction.
PSF engineering plays a significant role in modern microscopy, spectroscopy and computational imaging. Conventional techniques typically employ phase masks at the pupil plane, which constrain the complexity and mathematical representation of the achievable PSF structures.