Obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD) is a mental health disorder associated with persistent, intrusive thoughts (i.e., obsessions), accompanied by repetitive behaviors (i.e., compulsions) aimed at reducing the anxiety arising from obsessions. Past studies have showed that people diagnosed with OCD can present symptoms that vary significantly, as well as distinct brain abnormalities.
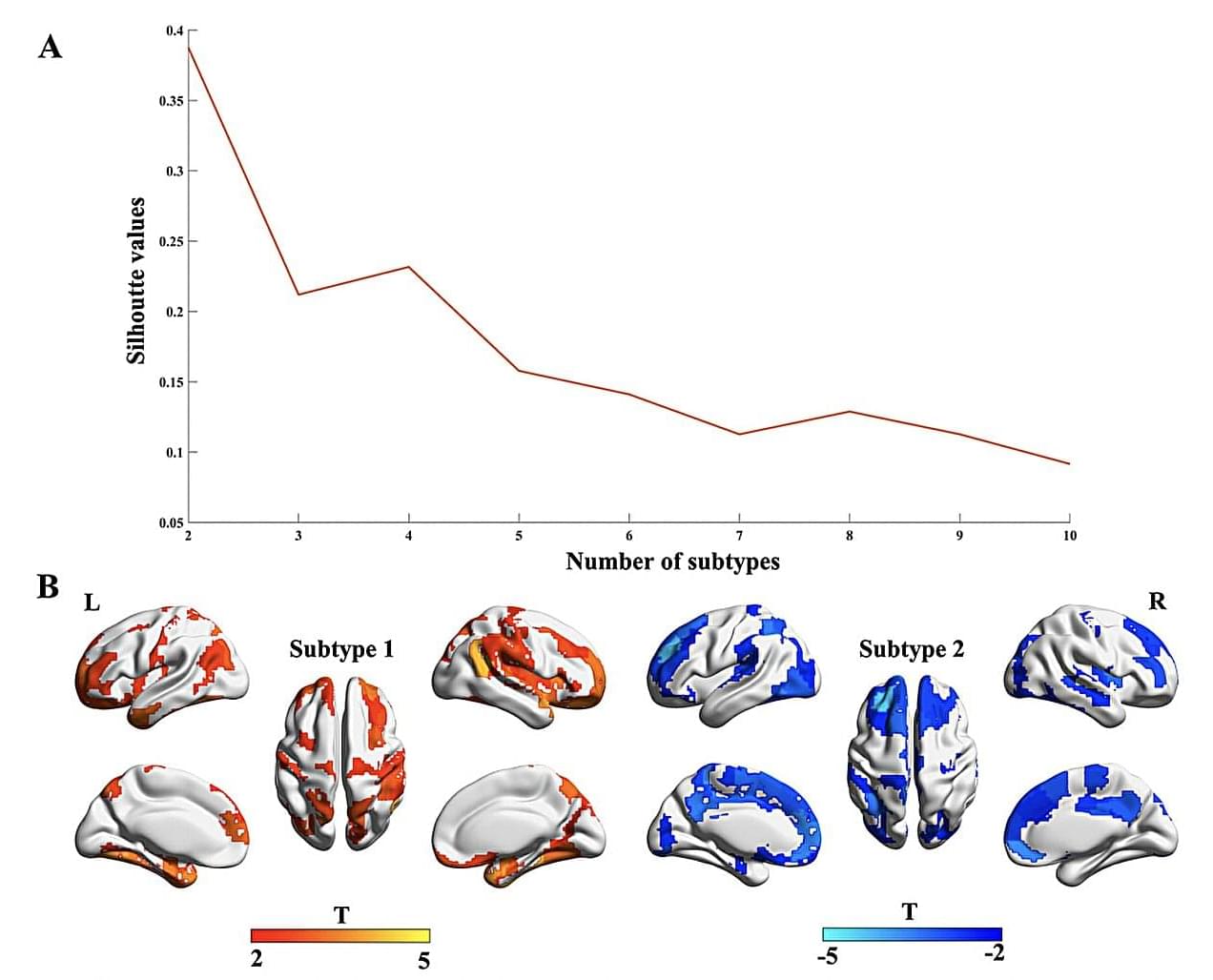
A team of researchers at the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University recently carried out a study aimed at further exploring the well-documented differences among patients with OCD. Their findings, published in Translational Psychiatry, allowed them to identify two broad OCD subtypes, which are associated with different patterns in gray matter volumes and disease epicenters.
“OCD is a highly heterogeneous disorder, with notable variations among cases in structural brain abnormalities,” wrote Baohong Wen, Keke Fang and their colleagues in their paper. “To address this heterogeneity, our study aimed to delineate OCD subtypes based on individualized gray matter morphological differences.”