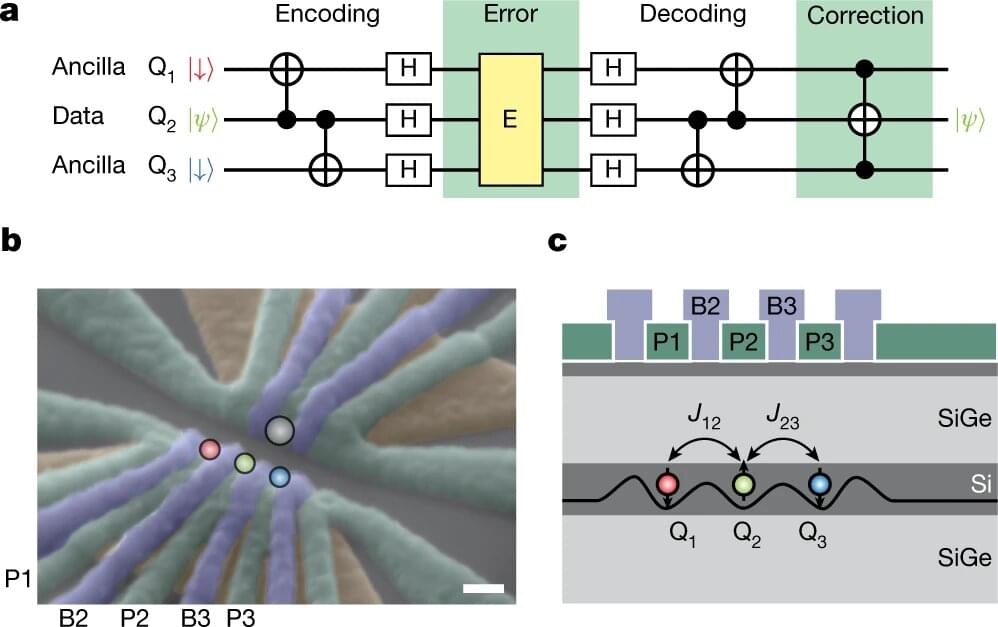
Researchers from RIKEN in Japan have achieved a major step toward large-scale quantum computing by demonstrating error correction in a three-qubit silicon-based quantum computing system. This work, published in Nature, could pave the way toward the achievement of practical quantum computers.
Quantum computers are a hot area of research today, as they promise to make it possible to solve certain important problems that are intractable using conventional computers. They use a completely different architecture, using superimposition states found in quantum physics rather than the simple 1 or 0 binary bits used in conventional computers. However, because they are designed in a completely different way, they are very sensitive to environmental noise and other issues, such as decoherence, and require error correction to allow them to do precise calculations.
One important challenge today is choosing what systems can best act as “qubits”—the basic units used to make quantum calculations. Different candidate systems have their own strengths and weaknesses. Some of the popular systems today include superconducting circuits and ions, which have the advantage that some form of error correction has been demonstrated, allowing them to be put into actual use albeit on a small scale. Silicon-based quantum technology, which has only begun to be developed over the past decade, is known to have an advantage in that it utilizes a semiconductor nanostructure similar to what is commonly used to integrate billions of transistors in a small chip, and therefore could take advantage of current production technology.