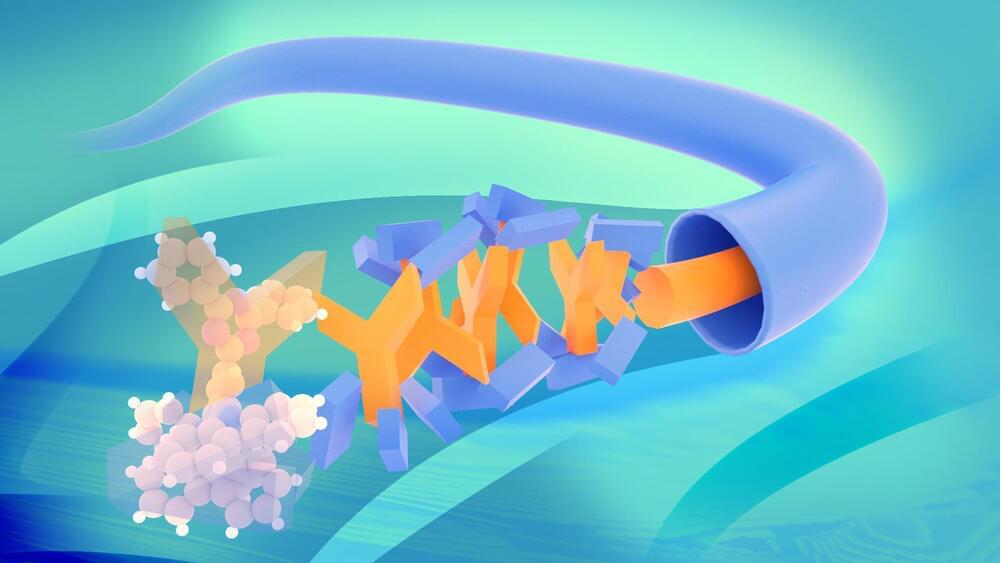
Materials that are both strong and lightweight could improve everything from cars to body armor. But usually, the two qualities are mutually exclusive. Now, University of Connecticut researchers and colleagues have developed an extraordinarily strong, lightweight material using two unlikely building blocks: DNA and glass.
“For the given density, our material is the strongest known,” says Seok-Woo Lee, a materials scientist at UConn. Lee and colleagues from UConn, Columbia University, and Brookhaven National Lab report the details on July 19 in Cell Reports Physical Science.
Strength is relative. Iron, for example, can take 7 tons of pressure per square centimeter. But it’s also very dense and heavy, weighing 7.8 grams/cubic centimeter. Other metals, such as titanium, are stronger and lighter than iron. And certain alloys combining multiple elements are even stronger. Strong, lightweight materials have allowed for lightweight body armor, better medical devices and made safer, faster cars and airplanes. The easiest way to extend the range of an electric vehicle, for example, is not to enlarge the battery but rather make the vehicle itself lighter without sacrificing safety and lifetime. But traditional metallurgical techniques have reached a limit in recent years, and materials scientists have had to get even more creative to develop new lightweight high strength materials.