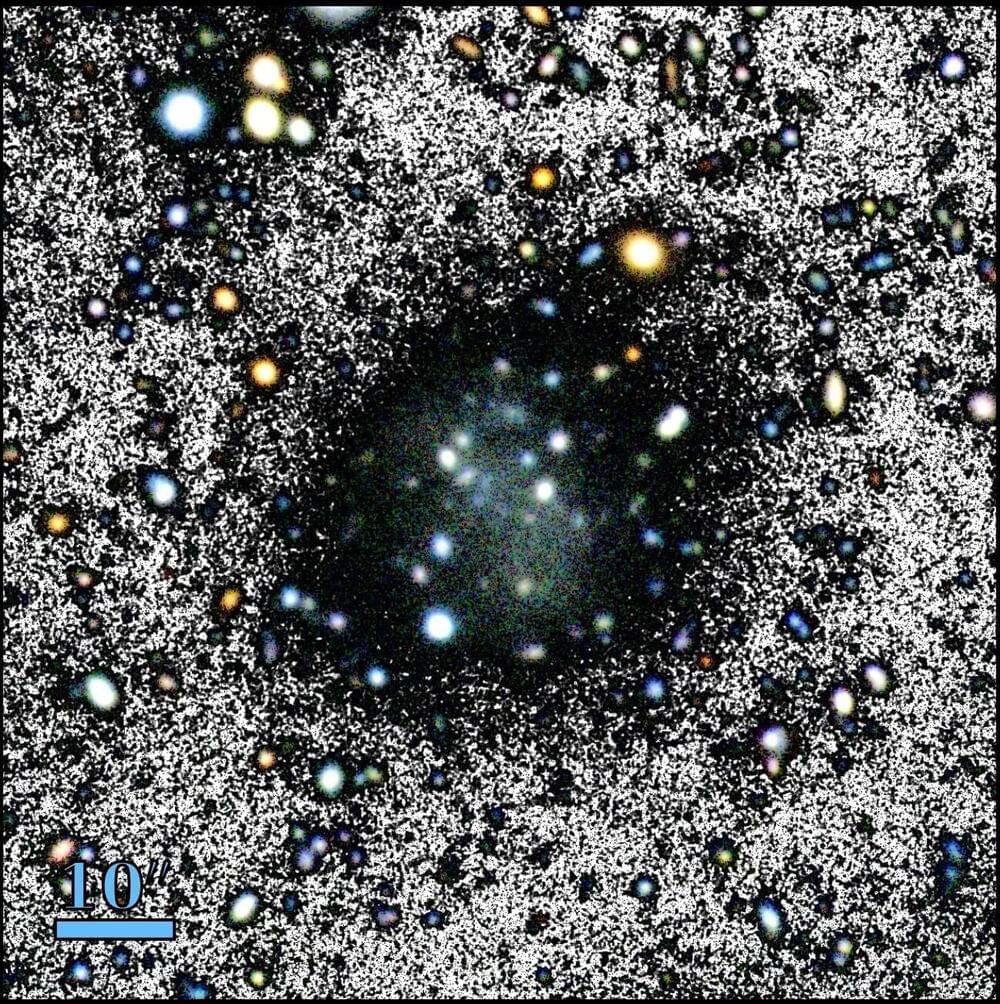
Nube is an almost invisible dwarf galaxy discovered by an international research team led by the Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias (IAC) in collaboration with the University of La Laguna (ULL) and other institutions.
The name was suggested by the 5-year-old daughter of one of the researchers in the group and is due to the diffuse appearance of the object. Its surface brightness is to faint that it had passed unnoticed in the various previous surveys of this part of the sky due to the object’s diffuse appearance as if it were some kind of ghost. This is because its stars are so spread out in such a large volume that “Nube” (Spanish for “Cloud”) was almost undetectable.
This newly discovered galaxy has a set of specific properties which distinguish it from previously known objects. The research team estimate that Nube is a dwarf galaxy 10 times fainter than others of its type, but also 10 times more extended than other objects with a comparable number of stars.