Not everyone wants AI to do everything for them. Will the risk of losing transparency and visibility into code change how GitHub made collaborative coding so powerful?



Risk is certainly an area of concern for CFOs when it comes to implementing generative AI.
However, Andrew McAfee, a principal research scientist at MIT, has a message for CFOs regarding the technology: “Risk tolerance needs to shift,” McAfee said.
“The risks are real, but they are manageable,” Andrew McAfee told a group of CFOs.


European astronomers released the first images from the new Euclid space telescope last week.
The European Space Agency (ESA) and the U.S. space agency, NASA, designed Euclid to study dark matter and dark energy. Scientists think those hidden forms of matter and energy make up 95 percent of the universe.
ESA is leading the six-year mission with NASA as a partner. ESA said the images were the most detailed of their kind. They show the telescope’s ability to observe billions of galaxies up to 10 billion light years away.

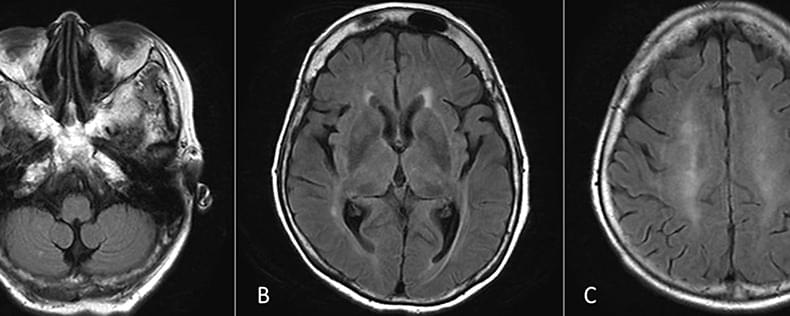
Nephrologists — know the CTRX encephalopathy risk in ESRD patients. This case of a hemodialysis patient found blood and CSF concentrations 10 times usual — dose adjustment may be needed. Monitor for neuro changes when using CTRX in renal failure. pharmacology.
Ceftriaxone (CTRX) does not require dose adjustment based on the renal function status and is used to treat infections. Recently, several studies reported the incidence of antibiotic-associated encephalopathy due to CTRX in patients with end-stage renal disease (ESRD). We experienced a case of CTRX-related encephalopathy in a patient on hemodialysis. When CTRX-related encephalopathy was discovered, the CTRX concentrations were measured in the blood and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). The highest blood and CSF CTRX concentrations in this patient were 967 and 100.7 μg/mL, respectively, which were approximately 10 times higher than the CSF concentrations in a previously evaluated patient with CTRX encephalopathy. The concentration of CTRX may be increased in patients with ESRD. Hence, encephalopathy must be suspected in this patient group when CTRX is used.
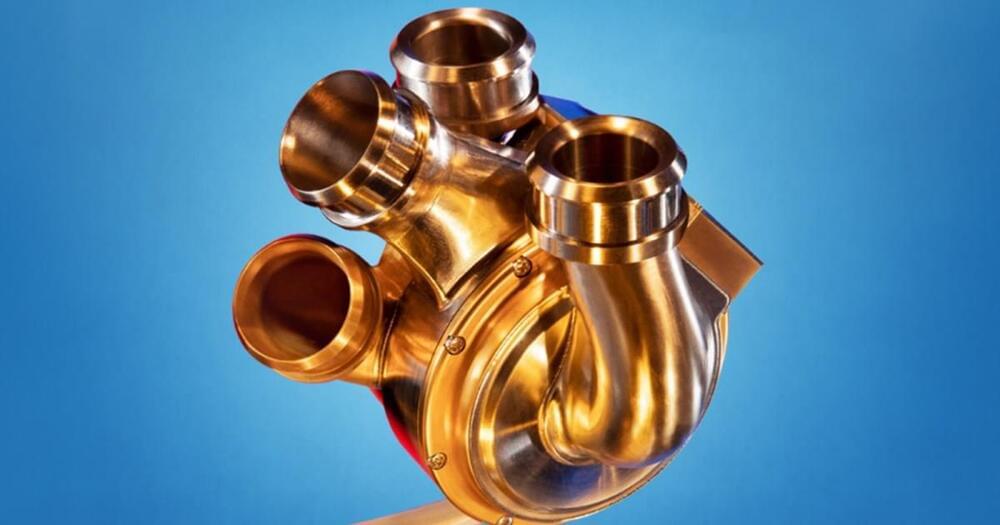

The wait time for a heart transplant is long — from many months to over a year. Some patients will never get the transplant they need.
But researchers may have come up with an artificial heart solution: a titanium, pumpless, device with spinning magnets — and it looks nothing like a bonafide heart.
The problem: Heart failure affects over six million people every year in the U.S., and treatment options are slim. Medication can help, but some people need a heart transplant for a full recovery. Still, donor hearts are hard to come by. The number of people who need a heart far exceeds what’s available. And, donor hearts aren’t one-size-fits-all. The blood type and size need to be just right.
The Earth spins at different rates depending where you are on the globe. If it started to spin faster, you’d eventually be too dead to worry about it.
Listen now (66 mins) | If you would like to support this podcast, click here. Max More is a philosopher, futurist, and former CEO of Alcor Life Extension Foundation. He is currently Director of Communications at Biostasis Technologies. Max wrote the first definition of “Transhumanism” in its modern sense.
