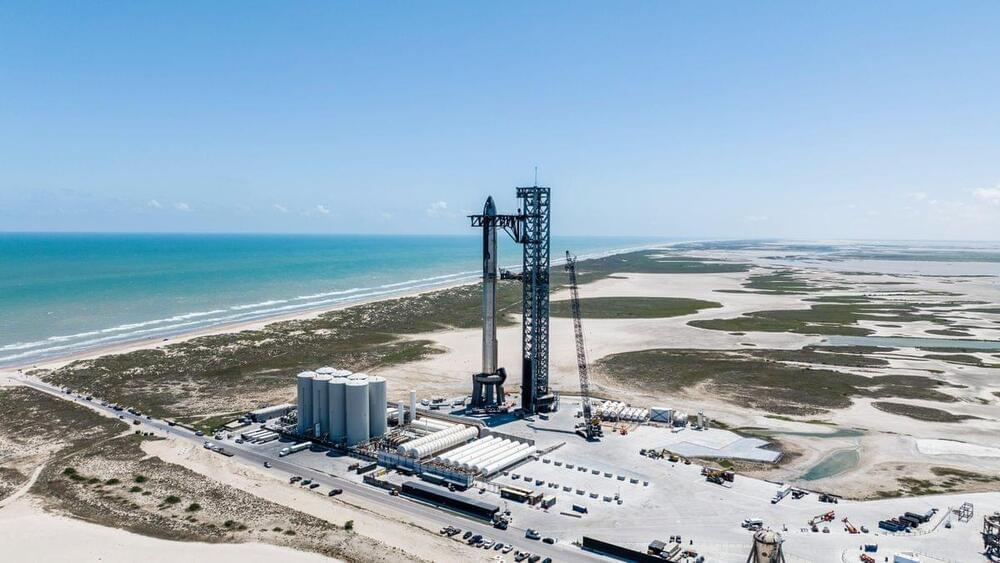
SpaceX delayed its second test flight of a Starship rocket and Super Heavy booster to no earlier than Saturday (Nov. 18), to replace a rocket part.



The Great Resignation may be over for most workers — but for some top honchos, it’s only just begun.
The number of chief executive resignations this year hit a record high, according to a recent report by Challenger, Gray and Christmas Inc.
Over 1,400 CEOs have stepped down from their positions between January to September, marking an almost 50% rise from the 969 departures over the same period last year. The career consultancy firm noted that the figure is the highest since it started compiling data in 2002.
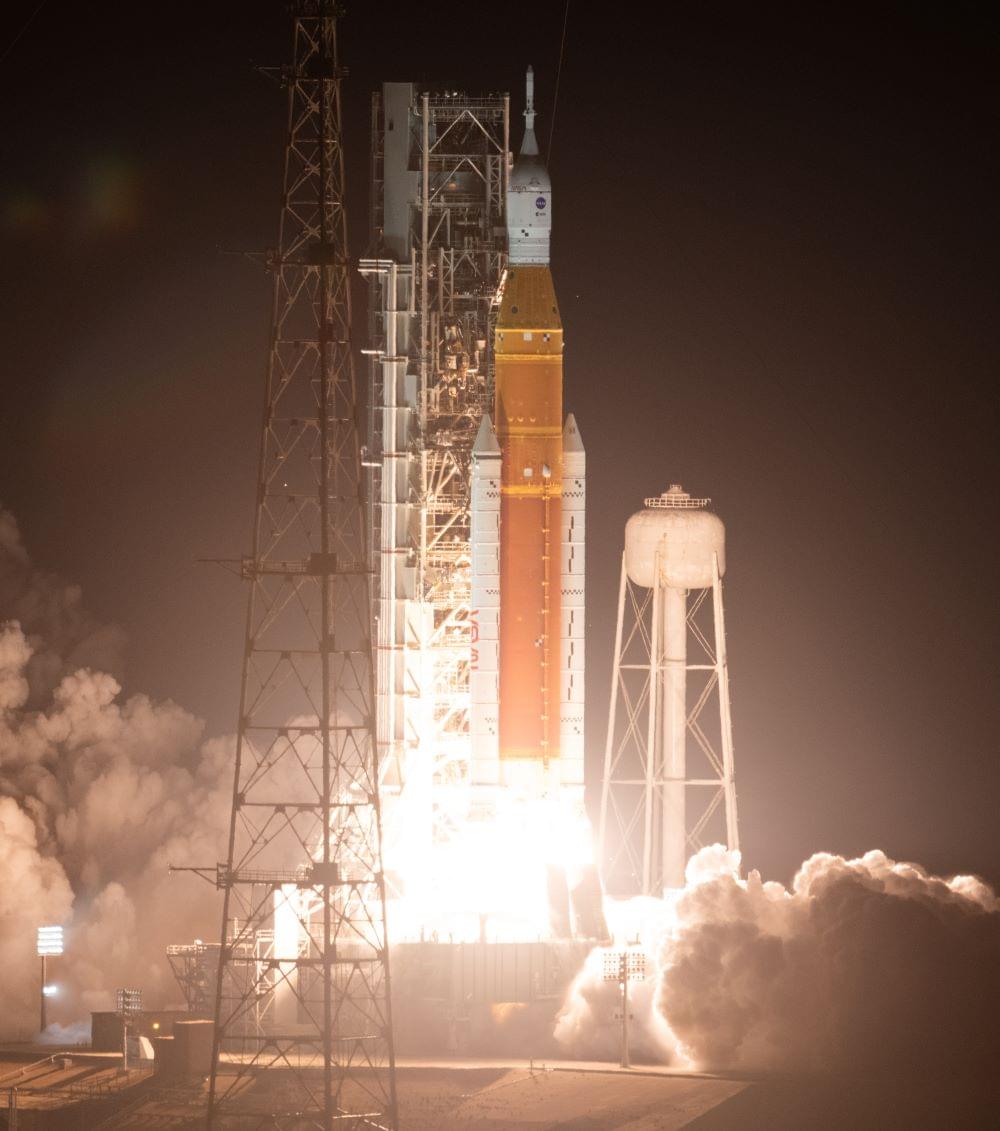



One year ago today, NASA’s Artemis I mission with its Orion spacecraft lifted off into the heavens and towards the Moon on its maiden flight aboard the mighty Space Launch System (SLS) at 1:47 am EST from historic Launch Complex 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The goal of the uncrewed mission was to conduct a shakedown of all systems and subsystems prior to crewed missions to the Moon and kicked off a new era in human spaceflight as no humans have ventured beyond low-Earth orbit since Apollo 17 in 1972.
Image of NASA’s Artemis I aboard the Space Launch System lifting off from historic Launch Complex 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center on November 16, 2023 at 1:47 a.m. EST. (Credit: NASA/Joel Kowsky)
Traveling a total of 1.3 million miles (2.1 million kilometers) during its achieved mission time of 25 days, 10 hours, and 53 minutes, Orion conducted two flybys of our nearest celestial neighbor, with its closest approach to the lunar surface occurring on December 5 at 79.5 miles (128 kilometers). Additionally, Orion broke the record for the farthest distance from Earth by an Earth-returning human-rated spacecraft by traveling almost 270,000 miles (435,000 kilometers), which surpassed the previous record of 248,655 miles (400,171 kilometers) conducted by Apollo 13 in 1970.

A recent study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences examines how marine phytoplankton throughout the North Atlantic Ocean has maintained its stability and numbers based on ice cores dating as far back as 800 years, which contradicts a 2019 study that concluded marine phytoplankton was on the decline by approximately 10 percent. The reason ice cores were examined was due to the methanesulfonic acid (MSA) deposits that fall from the sky and are the airborne products of phytoplankton, with the MSA initially starting off as dimethyl sulfide that is a byproduct of phytoplankton. This study was also presented at the AGU Fall Meeting in December 2022.
“Greenland ice cores show a decline in MSA concentrations over the industrial era, which was concluded to be a sign of declining primary productivity in the North Atlantic,” said Ursula Jongebloed, who is a PhD student in atmospheric sciences at the University of Washington (UW) and lead author of the study. “But our study of sulfate in a Greenland ice core shows that MSA alone can’t tell us the whole story when it comes to primary productivity.”

‘Neural networks today are about as similar to a brain as an airplane is to a bird.’ — Kwabena Boahen, PhD, professor of bioengineering and of electrical engineering One problem, as Boahen sees it, is that AI relies on a “synaptocentric” mode of computing, in that half of the nodes — lines of binary…
Do nerve cells hold the key to an epic advance in computing?
By John Sanford
Photography by Misha Gravenor.
Kwabena Boahen, PhD, a professor of bioengineering and of electrical engineering, right, and H.-S. Philip Wong, PhD, professor of electrical engineering and the Willard R. and Inez Kerr Bell Professor in the School of Engineering.

face_with_colon_three Basically although some or all coding jobs could be absorbed I remain positive because now everyone be a god now when infinite computation comes out and also infinite agi.
Jay Hack, an AI researcher with a background in natural language processing and computer vision, came to the realization several years ago that large language models (LLMs) — think OpenAI’s GPT-4 or ChatGPT — have the potential to make developers more productive by translating natural language requests into code.
After working at Palantir as a machine learning engineer and building and selling Mira, an AI-powered shopping startup for cosmetics, Hack began experimenting with LLMs to execute pull requests — the process of merging new code changes with main project repositories. With the help of a small team, Hack slowly expanded these experiments into a platform, Codegen, that attempts to automate as many mundane, repetitive software engineering tasks as possible leveraging LLMs.
“Codegen automates the menial labor out of software engineering by empowering AI agents to ship code,” Hack told TechCrunch in an email interview. “The platform enables companies to move significantly quicker and eliminates costs from tech debt and maintenance, allowing companies to focus on product innovation.”
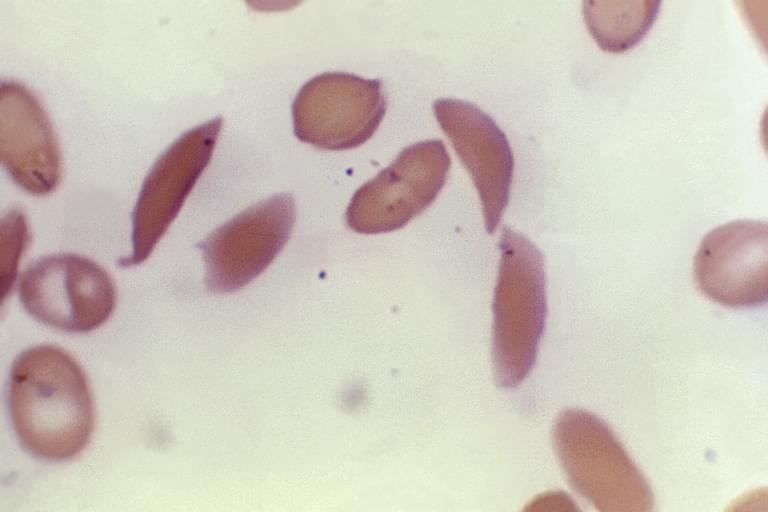
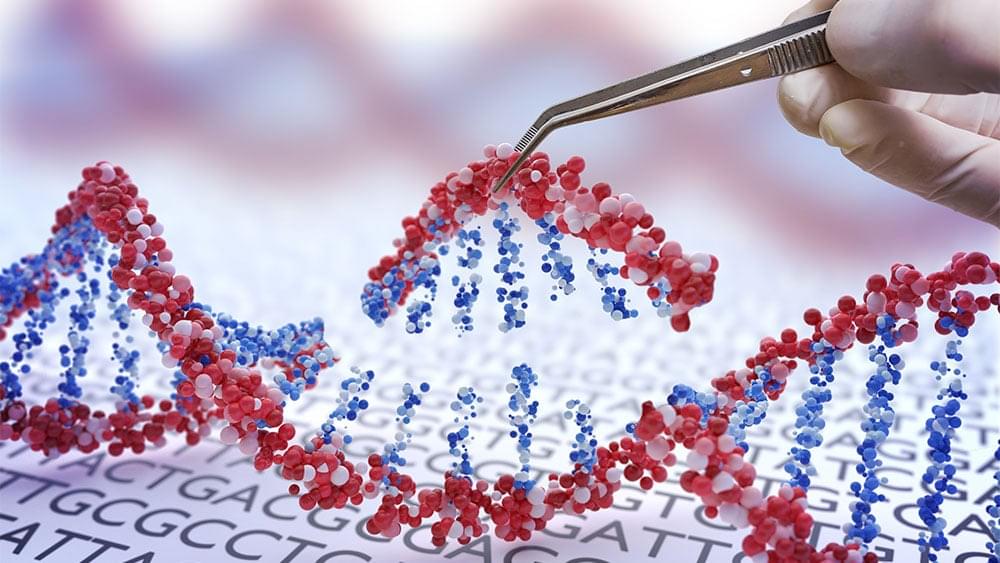
LONDON (AP) — Britain’s medicines regulator has authorized the world’s first gene therapy treatment for sickle cell disease, in a move that could offer relief to thousands of people with the crippling disease in the U.K. In a statement Thursday, the Medicines and Healthcare Regulatory Agency said it approved Casgevy, the first medicine licensed using the gene editing tool CRISPR, which won its makers a Nobel prize in 2020. The agency approved…
