Differentiating consciousness from the concept of Mind2.


Search The Best Results For Pipeline Management Software. Click Here.

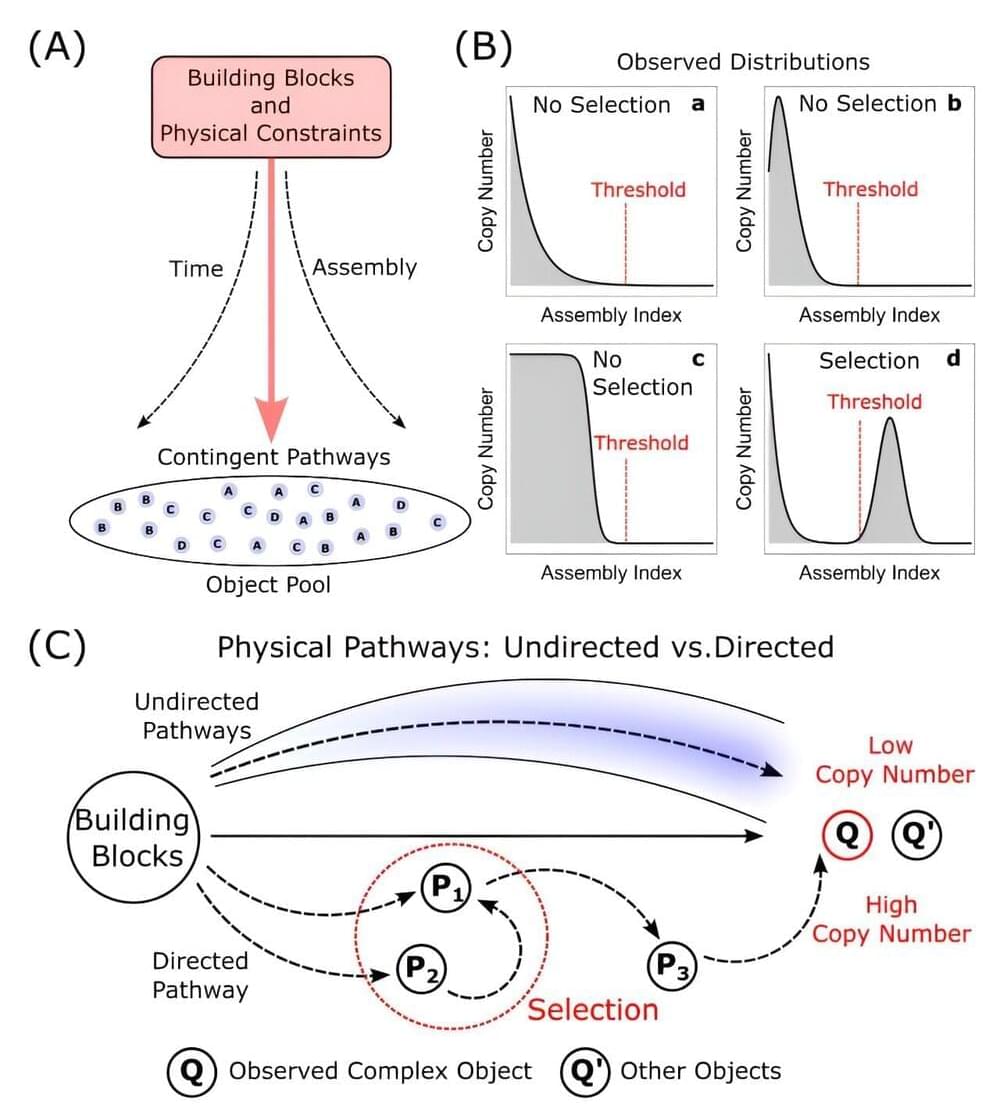
An international team of researchers has developed a new theoretical framework that bridges physics and biology to provide a unified approach for understanding how complexity and evolution emerge in nature.
This new work on “assembly theory,” published today in Nature, represents a major advance in our fundamental comprehension of biological evolution and how it is governed by the physical laws of the universe. The paper is titled “Assembly Theory Explains and Quantifies Selection and Evolution.”
This research builds on the team’s previous work developing assembly theory as an empirically validated approach to life detection, with implications for the search for alien life and efforts to evolve new life forms in the laboratory.
Artificial intelligence is changing health care. It promises better diagnoses and fewer mistakes and all in less time. While some associate AI with a frightening dystopian future, many doctors see it as a source of support.
To help them care for patients, doctors are programming apps and supplying AI with data. At Berlin’s Charité hospital, Professor Surjo Soekadar is researching how neurotechnology might support paralysis patients in their everyday lives — for example, via assistance systems that are controlled via their thoughts.
This could offer hope to people like Guido Schule and Anne Nitzer had a stroke shortly after the birth of her second child and has been unable to move or speak since then — even though she is fully conscious.
At Vienna General Hospital (AKH) Professor Ursula Schmidt-Erfurth has already developed an AI-based diagnostic tool that has been licensed for use. Nowadays, she is researching how AI could improve both the diagnosis and the treatment of age-related macular degeneration (AMD). This chronic eye disease can lead to loss of vision — even with treatment. This is a fate that Oskar Zlamala could face. But since the retiree began treatment at the AKH Vienna, he is hoping that it might be possible to halt the progression of his illness.
Computer science experts and medics are also working together to help the Essen University Hospital go digital. Dr. Felix Nensa and Professor Arzu Oezcelik are improving care for transplant patients with the help of artificial intelligence. AI can calculate the size of organs, like the liver, for example, much more precisely and more quickly than people — and thereby improve outcomes and the safety of the procedure.
#documentary #dwdocumentary #health #artificialintelligence.
This is a sci-fi documentary, looking at the 100 years it will take a nuclear fusion spacecraft to travel to Proxima Centauri b. The closest habitable planet to Earth, with a distance of 4.24 light years.
A journey venturing far beyond Earth’s solar system, showing the future science of space travel, exploration, and future space technology.
Personal inspiration in creating this video comes from: the movie Interstellar, The Expanse TV show, and Carl Sagan’s Cosmos TV show.
Other topics in the video include: the population growth over the 100 year timelapse journey to Proxima Centauri b, how bacteria evolves in a closed loop system, the design of the spaceship habitat ring, the rotations per minute needed to generate 1-g of artificial gravity, the conservation of angular momentum in space, the living conditions on Proxima Centauri b (the higher gravity, and the red light), and time dilation is explained (how many extra days will pass on Earth when the spaceship arrives at the destination planet – just like the movie Interstellar).
Created by: Jacob B
Narration by: Alexander Masters.
Proxima Centauri B concept art: ESO/M. Kornmesser.
In September 2020 we sat down with Robert Sapolsky, Stanford professor and the author of Human Behavioral Biology lectures (https://youtu.be/NNnIGh9g6fA) to discuss if it’s possible for our society to reconcile our understanding of justice with scientific understanding of human behaviour.
Why do humans, most likely, have no free will? How does that link to depression and other psychiatric disorders? Can people accept the idea that there is no free will and start using, what science tells us about the reasons behind our behaviour, as a basis for making sense of justice and morality? If yes, can we even imagine what such society would look like?
This is a third interview with Robert. The first (https://youtu.be/VrQkl7PaA1s) and the second (https://youtu.be/yp9HE5xfojY) talks are available on our channel.

According to Fioretto et al. [9], whole organ pancreas transplantation is a viable therapeutic option, since it improves the patient’s quality of life and promotes regression of some late complications associated with T1D. However, this procedure constitutes a major surgical intervention, which requires a strict immunosuppressive regimen and heavily depends on properly functioning of the donor pancreas for a successful treatment, being recommended only for patients with brittle/labile T1D who also need a kidney transplant [10]. Pancreatic islets transplantation, introduced in Brazil by our research group [11, 12], has been shown to be a promising alternative to whole organ pancreas transplantation, since it is a simpler and less invasive procedure. According to Hering et al. [13], transplantation of pancreatic islets is a safe and efficient treatment option for T1D patients with hypoglycemia. Nevertheless, there are still some factors that limit this procedure, such as the low availability of pancreas donors and the requirement for constant patient immunosuppression [10, 14].
Chronic usage of immunosuppressant medication becomes necessary for immunological acceptance of the islet allograft; however, this regimen is associated with various side effects, such as oral sores, gastrointestinal diseases, hypertension, dyslipidemia, anemia, increased infection susceptibility, cancer and systemic toxicity [15]. Therefore, encapsulation of pancreatic islets has emerged as a promising strategy to avoid the need for these immunosuppressive drugs. Production of semipermeable microcapsules for biological application, containing cells or proteins, was initially suggested in the 90’s [16], but considerable progress has been achieved in the field since then, with a major increase in application possibilities, including as an alternative for T1D treatment.
To avoid using steroid-based agents that damage β-cells and are known to be diabetogenic or induce peripheral insulin resistance, a glucocorticoid-free immunosuppressive protocol was developed by the Shapiro’s Group [17], for usage in islet transplantation trials. This protocol includes sirolimus, low dosage of tacrolimus and a monoclonal antibody against the interleukin-2 receptor (daclizumab). Their findings, in a study with T1D patients, indicate that islet transplantation alone is associated with minimal risks for the patient and results in good metabolic control, with normalization of glycated hemoglobin values and restricted requirement for exogenous insulin [17]. This protocol, known as the Edmonton Protocol, was considered as a breakthrough, becoming the standard procedure for islet transplantation, constituting a promising step toward the development of a cure for T1D [18]. However, the standard procedure for pancreatic islets transplantation is based on isolation and purification of islet cells from deceased donors, a process that requires two to four donors per patient, since the efficiency of islet isolation is well below 100% and, additionally, only about 50% of the implanted islets survive after transplantation [19]. In addition, several factors interfere with the viability of the graft after transplantation, such as quality of the donated organ, viability and functionality of the purified islets and the patient’s own immune response [20]. Although many advances have been reached in the field, the need for a large number of viable islets, along with the low availability of donors, is still an important factor that compromise the viability of this methodology.
At Google, we care deeply about the power of technology to change people’s lives for the better. We’re particularly passionate about the ways in which it can impact users with a range of disabilities. In this video, Danny’s daily experiences and challenges living with cerebral palsy help us understand how the innovation happening both inside and outside of Google could close the gaps and make a fundamental difference in people’s lives. Learn more about accessibility at Google (https://www.google.com/accessibility/) and the Google Impact Challenge: Disabilities (https://www.google.org/impactchallenge/disabilities/).

Today’s milestone comes less than two months after Virgin Galactic launched the first former Olympian and the first mother-daughter duo to the final frontier on its Galactic 2 flight. The daughter in that duo, 18-year-old Anastatia Mayers, also became the youngest-ever spaceflyer during that mission.
Related: Meet the crew of Virgin Galactic’s ‘Galactic 04’ mission
Galactic 4 began at 11:28 a.m. EDT (1528 GMT) this morning, when Virgin Galactic’s VSS Unity space plane lifted off beneath the wings of its carrier craft, known as VMS Eve.