To monitor and navigate real-world environments, machines and robots should be able to gather images and measurements under different background lighting conditions. In recent years, engineers worldwide have thus been trying to develop increasingly advanced sensors, which could be integrated within robots, surveillance systems, or other technologies that can benefit from sensing their surroundings.
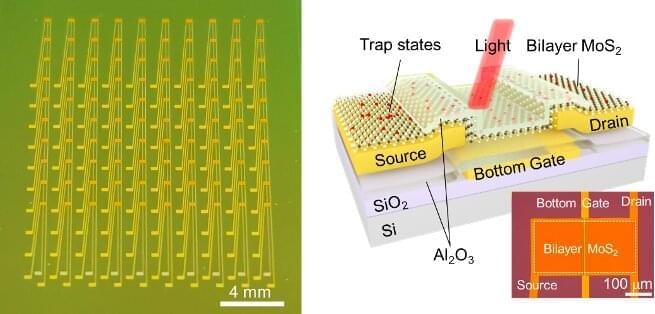
Researchers at Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Peking University, Yonsei University and Fudan University have recently created a new sensor that can collect data in various illumination conditions, employing a mechanism that artificially replicates the functioning of the retina in the human eye. This bio-inspired sensor, presented in a paper published in Nature Electronics, was fabricated using phototransistors made of molybdenum disulfide.
“Our research team started the research on optoelectronic memory five years ago,” Yang Chai, one of the researchers who developed the sensor, told TechXplore. “This emerging device can output light-dependent and history-dependent signals, which enables image integration, weak signal accumulation, spectrum analysis and other complicated image processing functions, integrating the multifunction of sensing, data storage and data processing in a single device.”