A magnitude 5.0 earthquake hit near the Mexican resort town of Acapulco on the Pacific coast on Saturday afternoon, according to the country’s national seismological service.



Spilling your hopes, secrets, and fantasies to your AI girlfriend? You might want to reconsider.
In a new report, experts at the Mozilla Foundation warn that AI companion bots — including the popular app Replika — are plagued by deeply concerning privacy pitfalls and murky data use policies.
“So-called ‘AI soulmates’ are giving Mozilla the ick when it comes to how much personal information they collect,” reads the Mozilla report, “especially given the lack of transparency and user control over how this data is protected from abuse.”


ChatGPT maker OpenAI stepped up the race in generative artificial intelligence Thursday when it unveiled its text-to-video generation tool, Sora, viewed as an impressive but potentially dangerous step in the booming AI economy amid concerns about disinformation spread.
“Game on,” said the CEO and cofounder of rival video generator Runway after OpenAI teased content from its latest AI tool.

Biopharmaceutical impurities such as host cell proteins can delay biologics development and production. These elements can have immunogenic effects in patients, forcing scientists to restart process development. Thus, detecting and removing biopharmaceutical impurities is necessary for maintaining drug efficacy and ensuring patient safety.
In this webinar brought to you by Cytiva, Andrew Hamilton and Joe Hirano will discuss how to identify, detect, and measure impurities in biologics manufacturing.
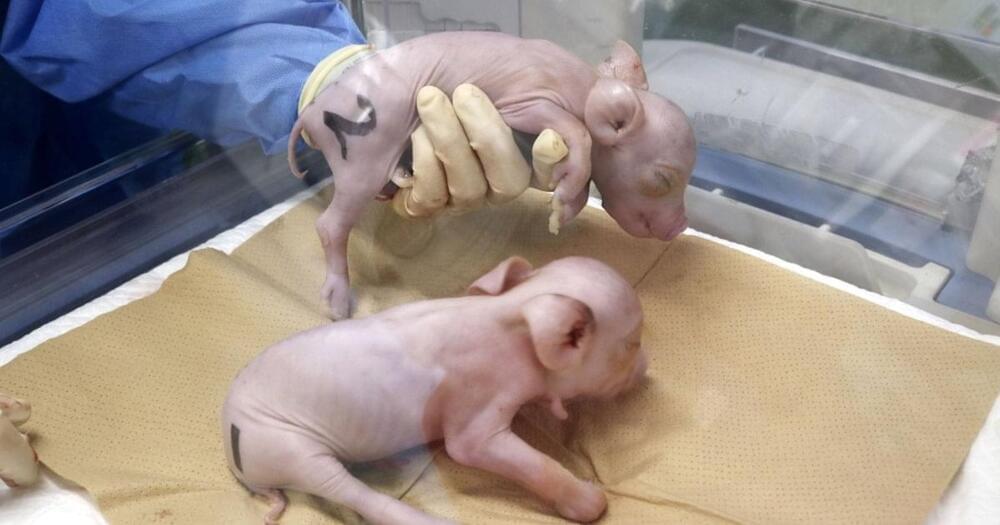
Japanese startup PorMedTec says it’s have cloned three piglets with the express purpose of having their organs be viable for transplantation to humans, without being rejected by the immune system.
The company imported gene-edited cells from a US biotech startup called eGenesis and used them to create genetically modified embryos, the Japan Times reports, which were then implanted into the uterus of a pig.
“The realization of xenotransplantation has been long awaited in Japan for several years, but it remained in the basic research stage because pigs that could withstand clinical application were still under development,” the company said in a statement.


Sounds like the video game/movie “The Last of Us” though there was a somewhat similar X Files episode as well before that. Though I doubt it’ll be a zombie plague, it could be like another pandemic someday or an issue such as a deadly fungal outbreak they had in Portland, Oregon before if I recall.
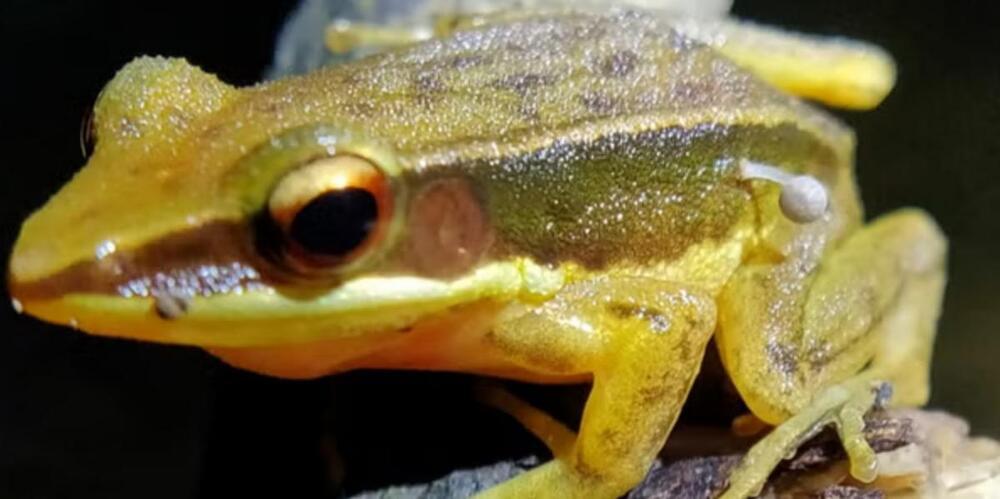
Scientists have been left concerned after making the surprise discovery of a frog with a small mushroom sprouting from its leg.
The amphibian was discovered in the foothills of India’s Western Ghats and researchers stated that it’s the first time a mushroom has been found growing on live animal tissue.
Researchers affiliated with the World Wildlife Fund released findings on the species, known as Rao’s intermediate golden-backed frog (Hylarana intermedia), in a new study published in the journal Reptiles and Amphibians.