A non-organic intelligent system has for the first time designed, planned and executed a chemistry experiment, Carnegie Mellon University researchers report in the journal Nature (“Autonomous chemical research with large language models”).
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.

Chinese brain warfare includes sleep weapons, thought control
I dont know about sleep weapons, it s possible probably. More concerning to me, i read a paper 20+ years back about cell towers and cell phone frequencies as a possible tool for mind control, some way connected to frequency of human brain.
China’s military is developing advanced psychological warfare and brain-influencing weapons as part of a new warfighting strategy, according to a report on People’s Liberation Army cognitive warfare.
The report, “Warfare in the Cognitive Age: NeuroStrike and the PLA’s Advanced Psychological Weapons and Tactics,” was published earlier this month by The CCP Biothreats Initiative, a research group.
“The PLA is at the forefront of incorporating advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence, brain-computer interfaces and novel biological weapons into its military strategies,” the think tank’s analysts concluded.

A Comprehensive Study on Nanoparticle Drug Delivery to the Brain: Application of Machine Learning Techniques
The delivery of drugs to specific target tissues and cells in the brain poses a significant challenge in brain therapeutics, primarily due to limited understanding of how nanoparticle (NP) properties influence drug biodistribution and off-target organ accumulation. This study addresses the limitations of previous research by using various predictive models based on collection of large data sets of 403 data points incorporating both numerical and categorical features. Machine learning techniques and comprehensive literature data analysis were used to develop models for predicting NP delivery to the brain. Furthermore, the physicochemical properties of loaded drugs and NPs were analyzed through a systematic analysis of pharmacodynamic parameters such as plasma area under the curve. The analysis employed various linear models, with a particular emphasis on linear mixed-effect models (LMEMs) that demonstrated exceptional accuracy. The model was validated via the preparation and administration of two distinct NP formulations via the intranasal and intravenous routes. Among the various modeling approaches, LMEMs exhibited superior performance in capturing underlying patterns. Factors such as the release rate and molecular weight had a negative impact on brain targeting. The model also suggests a slightly positive impact on brain targeting when the drug is a P-glycoprotein substrate.




Ultrasound-Triggered In Situ Photon Emission for Noninvasive Optogenetics
Optogenetics has revolutionized neuroscience understanding by allowing spatiotemporal control over cell-type specific neurons in neural circuits. However, the sluggish development of noninvasive photon delivery in the brain has limited the clinical application of optogenetics. Focused ultrasound (FUS)-derived mechanoluminescence has emerged as a promising tool for in situ photon emission, but there is not yet a biocompatible liquid-phase mechanoluminescence system for spatiotemporal optogenetics. To achieve noninvasive optogenetics with a high temporal resolution and desirable biocompatibility, we have developed liposome (Lipo@IR780/L012) nanoparticles for FUS-triggered mechanoluminescence in brain photon delivery. Synchronized and stable blue light emission was generated in solution under FUS irradiation due to the cascade reactions in liposomes.

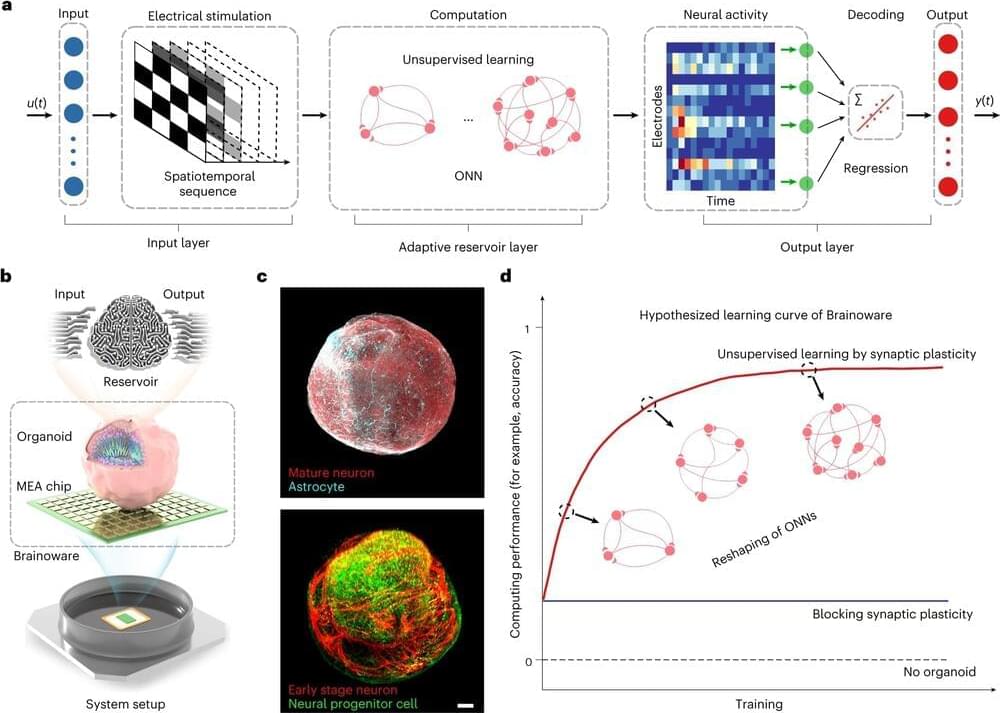
Researchers from Indiana University Unveil ‘Brainoware’: A Cutting-Edge Artificial Intelligence Technology Inspired by Brain Organoids and Silicon Chips
The fusion of biological principles with technological innovation has resulted in significant advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) through the development of Brainoware. Developed by researchers at Indiana University, Bloomington, this innovative system leverages clusters of lab-raised brain cells to achieve elementary speech recognition and solve mathematical problems.
The crux of this technological leap lies in the cultivation of specialized stem cells that mature into neurons—the fundamental units of the brain. While a typical human brain comprises a staggering 86 billion neurons interconnected extensively, the team managed to engineer a minute organoid, merely a nanometer wide. This tiny but powerful structure was connected to a circuit board through an array of electrodes, allowing machine-learning algorithms to decode responses from the brain tissue.
Termed Brainoware, this amalgamation of biological neurons and computational circuits exhibited remarkable capabilities after a brief training period. It was discerned between eight subjects based on their diverse pronunciation of vowels with an accuracy rate of 78%. Impressively, Brainoware outperformed artificial networks in predicting the Henon map, a complex mathematical construct within chaotic dynamics.