Oct 3, 2022
Deep stimulation improves cognitive control
Posted by Dan Breeden in categories: biotech/medical, neuroscience
In a new study that could improve the therapeutic efficacy of deep-brain stimulation (DBS) for psychiatric disorders such as depression, a team of scientists shows that, when DBS is applied to a specific brain region, it improves patients’ cognitive control over their behavior by increasing the power of a specific low-frequency brain rhythm in their prefrontal cortex.
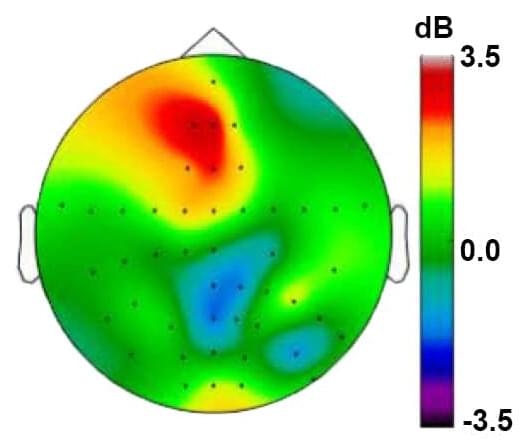
The findings, published April 4 in Nature Communications, suggest that the increase in “theta” rhythms, readily detectable in EEG recordings, could provide neurosurgeons and psychiatrists with the reliable, objective and rapid feedback they’ve needed to properly fine-tune the placement and “dosage” of DBS electrical stimulation. In Parkinson’s disease, where DBS has been most successful, that kind of feedback is available through a reduction in a patient’s tremors. But for depression or obsessive-compulsive disorder, symptoms can be more subtle, subjective and slowly emergent.
“This is a major step forward for psychiatric brain stimulation,” said Alik Widge, the lead and corresponding author on the paper. Widge began the work while a clinical fellow at the Picower Institute for Learning and Memory at MIT and a research fellow at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH). He is now an Assistant Professor of Psychiatry at the University of Minnesota Medical School. “This study shows us a specific mechanism of how DBS improves patients’ brain function, which should let us better identify who can benefit and how to optimize their individual treatment.”