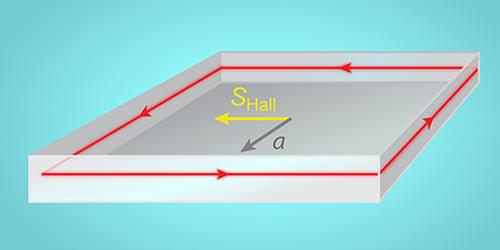
Light confined to an accelerating optical cavity could display a photonic counterpart of the electronic quantum Hall effect.
Place a conductor in a magnetic field and the electrical current driven by an applied voltage will not flow in a straight line but in a direction perpendicular to the electric field—a behavior known as the Hall effect [1]. Reduce the temperature to the point where the electrons manifest quantum-mechanical behavior, and the plot thickens. The conductivity (defined as the ratio between the sideways current and the voltage) exhibits discrete jumps as the magnetic field is varied—the quantum Hall effect [2]. Since electrons at low temperature and photons obey a similar wave equation [3], should we also expect a quantum Hall effect for light? This question has been bubbling under the surface for the past decade, leading to the observation of some aspects of an optical quantum Hall effect [4, 5]. But the analogy between photons and electrons remains incomplete.