Ok… here we go again! (Yes, this is real. Already being tested in full wafers.)
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.

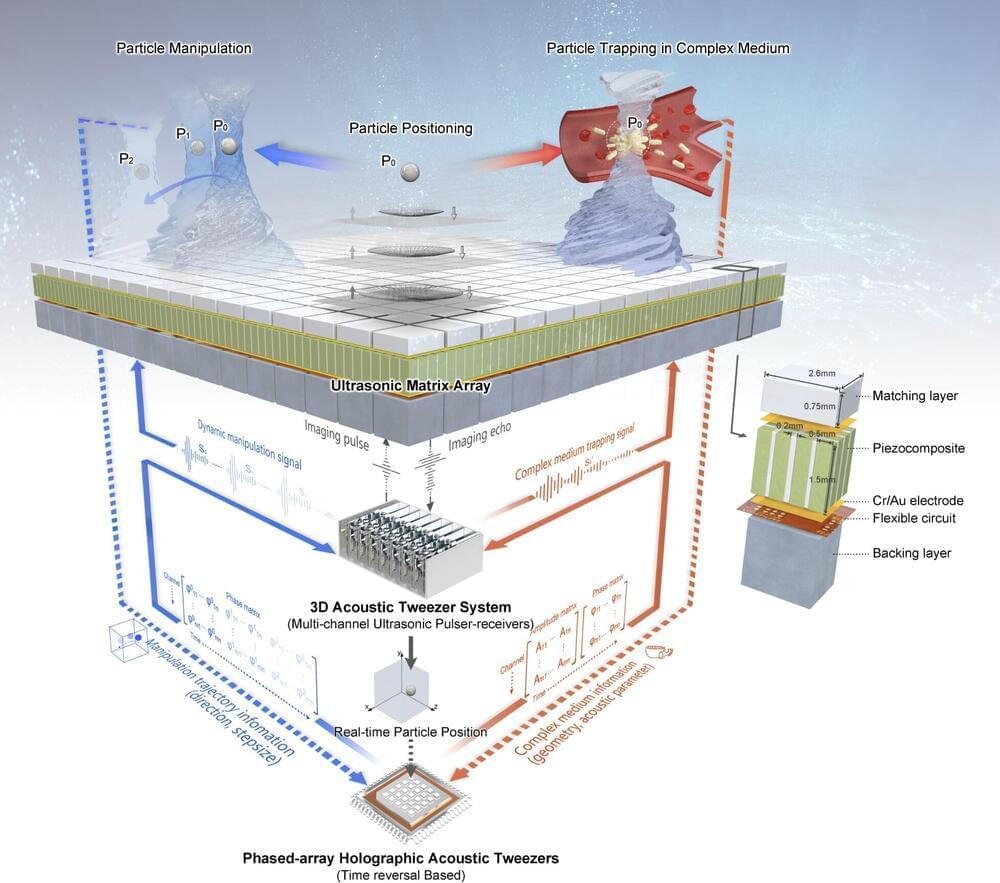
Scientists develop new technology for targeted cancer therapy
Acoustic tweezers can control target movement through the interaction of momentum between an acoustic wave and an object. Due to their high tissue penetrability and strong acoustic radiation force, such tweezers overcome the limitations of optical and magnetic tweezers, thus making them suitable for in vivo cell manipulation.
A research team led by Prof. Zheng Hairong from the Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology (SIAT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) has recently developed a new type of acoustic tweezers —the phased-array holographic acoustic tweezers (PAHAT) system—which is based on a high-density planar array transducer capable of generating tunable three-dimensional bulk acoustic waves. The researchers hope this system can realize a pharmacological version of “telekinesis.” The study was published in Nature Communications on June 6.
The in vivo environment is extremely complex, due to the different characteristics of various tissues, organs, bones, blood vessels, and blood flow. Such a complex environment creates a huge challenge: How can acoustic methods be used to “trap” bacteria so they can produce therapeutic effects on tumors?

Large language models improve annotation of prokaryotic viral proteins
The latest in the intersection of large language models and life science: virus sequences, virus proteins, and their function.
Large language models improve annotation of prokaryotic viral proteins.
Ocean viral proteome annotations are expanded by a machine learning approach that is not reliant on sequence homology and can annotate sequences not homologous to those seen in training.
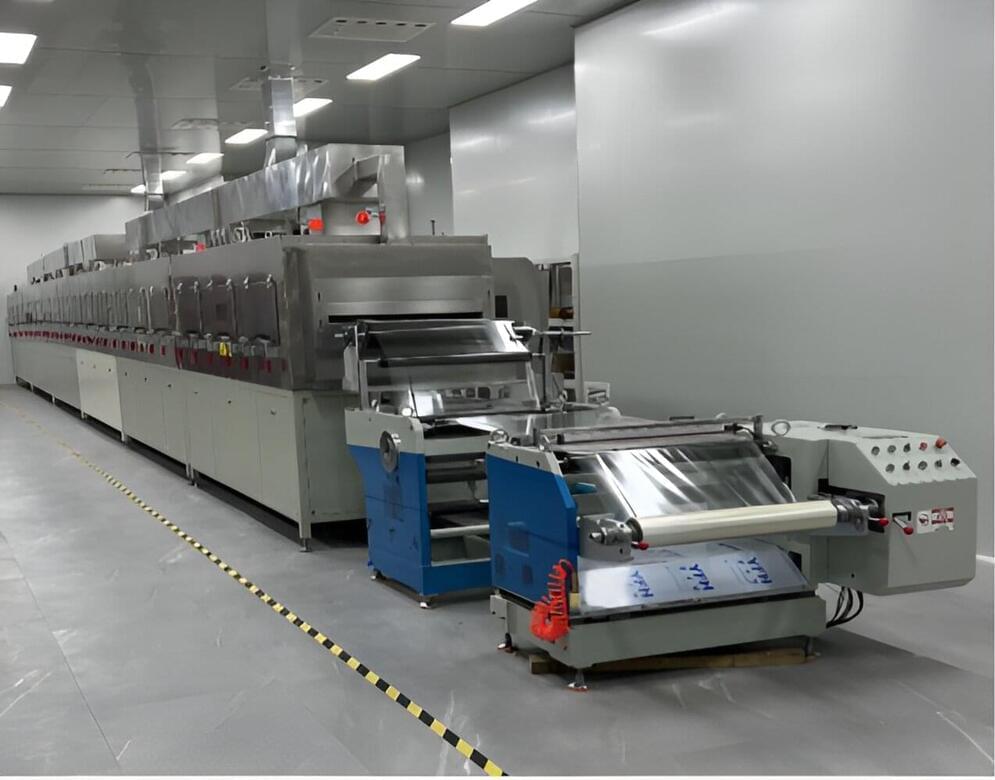

A method to fabricate long rolls of subnanocomposite dielectric polymers
Engineers and material scientists have been trying to develop increasingly advanced devices, to meet the growing needs of the electronics industry. These devices include electrostatic capacitors, devices that can store electrical energy in a dielectric between a pair of electrodes through the accumulation of electric charge on the dielectric surfaces.
These capacitors are crucial components of various technologies, including electric vehicles and photovoltaics (PVs). They are often fabricated using polymers as dielectric materials, synthetic substances made up of large organic molecules with good intrinsic flexibility and insulating properties.
Researchers at Tsinghua University and other institutes in China recently introduced a new strategy to fabricate polymer composites filled with subnanosheets exhibiting highly advantageous properties. Their proposed method, outlined in a Nature Energy paper, allowed them to fabricate a 100-meter-long roll of a polymer-based subnanocomposite film.

Elon Musk’s Neuralink implants first brain chip in human
The ambition is to supercharge human capabilities, treat neurological disorders like ALS or Parkinson’s, and may be one day achieve a symbiotic relationship between humans and artificial intelligence.
“The first human received an implant from Neuralink yesterday and is recovering well,” Musk said in a post on X, formerly Twitter.
“Initial results show promising neuron spike detection,” he added.

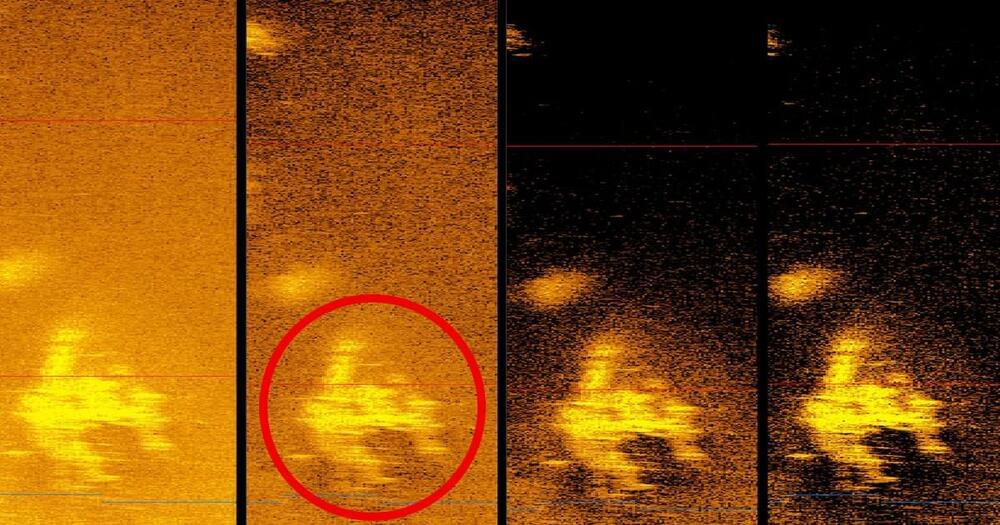
Scientists Say They’ve Finally Found the Wreckage of Amelia Earhart’s Plane
South Carolina-based ocean exploration company Deep Sea Vision claims to have found the aircraft of American aviation pioneer Amelia Earhart, who famously disappeared back in 1937 while trying to become the first female pilot to circumnavigate the globe.
If confirmed, the discovery could be a huge development in one of aviation’s greatest mysteries.
With the help of an underwater drone equipped with a high-tech radar and a 16-member crew, Deep Sea Vision claims to have come across an object that closely resembles Earhart’s Lockheed Electra aircraft roughly 16,000 feet below the surface and 100 miles off Howland Island, a location where the two were supposed to land to refuel.
New Vaccine design uses Immunity against Influenza to offer Faster Protection against Emerging Pathogens
After COVID vaccination, it usually takes weeks for our bodies to develop protective antibody responses. Imagine, however, a vaccine that speeds up the production of antibodies against SARS-CoV-2, the virus that spreads COVID-19.
A research team led by Rong Hai, an associate professor of microbiology and plant pathology at the University of California, Riverside, has developed such a vaccine by using preexisting immunity to a separate virus (the influenza virus) to help kickstart the process of making antibodies against SARS-CoV-2.
“Any delay in the immune response to SARS-CoV-2 means there is some time when people are left poorly protected against the virus,” Hai said. “Our vaccine is designed to get people those protective antibody responses faster, so they are not vulnerable to the coronavirus. This is better protection for everyone. It could be especially valuable for people who still lack immunity to SARS-CoV-2, such as children.”
Engineered Bacteria Eat Waste Plastic and Make Spider Silk — “Nature’s Kevlar”
For the first time, researchers have used bacteria to “upcycle” waste polyethylene.
Move over Spider-Man: Researchers at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute have developed a strain of bacteria that can turn plastic waste into a biodegradable spider silk with multiple uses.
Transforming Plastic Into Protein