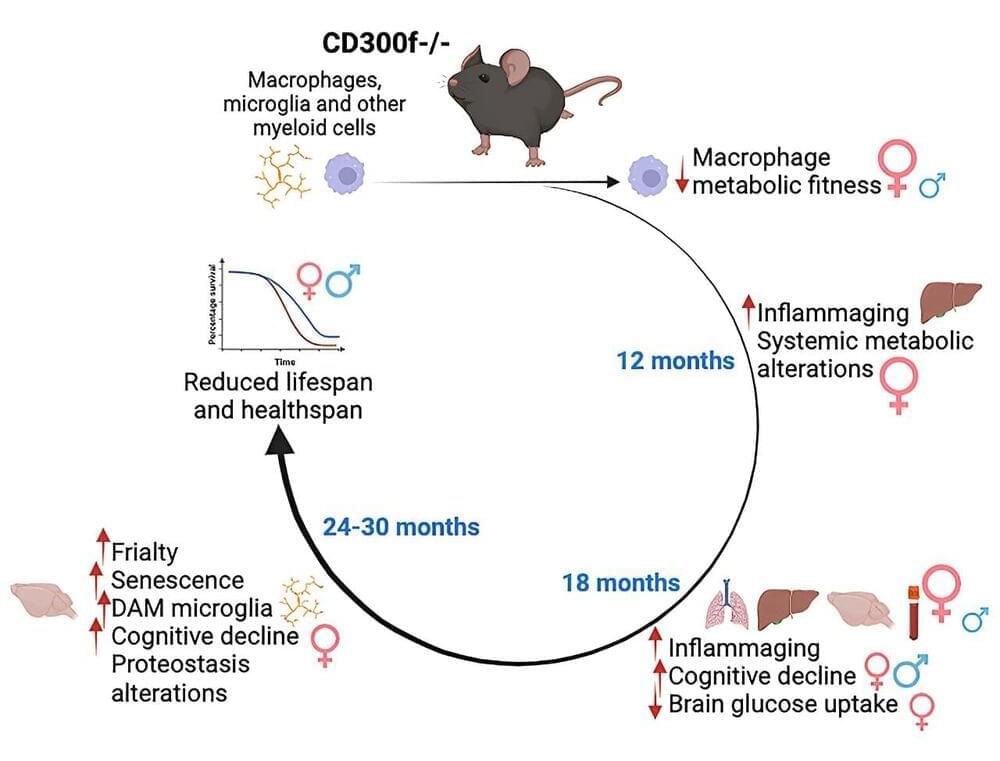
Life expectancy and healthy aging in mice can be determined by a protein present in some cells of the immune system, according to a study published in the journal Cell Reports. When this protein—known as the CD300f immune receptor—is absent, animal models have a shorter life expectancy and suffer from pathologies associated with cognitive decline and premature aging, especially in females.
“Our study indicates that alterations in immune system cells, for instance, in macrophages and microglia, can determine the healthy aging degree in mice,” notes Hugo Peluffo, leader of this study and member of the Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences and the Institute of Neurosciences (UBneuro) of the University of Barcelona.
Understanding how the CD300f immune receptor —and the myeloid cells of the immune system—can determine by themselves the onset rate of aging-associated pathologies, “will help to better understand this process, and it will contribute to the design of strategies to regulate its action. For instance, using the immune receptor CD300f as a target in biomedicine,” notes the expert. “Also, our team has previously shown that some variants of the CD300f immune receptor could be useful as biomarkers in patients.”