Scientists have seen what happens during the violent events that forge the gold on your finger in detail for the first time.

According to a widely distributed study covered by all the majors, Tesla drivers are way at the top of the list of the worst drivers on earth. Brian White has gone super deep to uncover whether there is any truth in this story and why it might have been written at all.
Scientists introduce Zman-seq, a method revolutionizing our understanding of dynamic cellular changes in the human body over time. Read more about this groundbreaking study.
In a recent study published in Cell, scientists led by Prof. Ido Amit at the Weizmann Institute of Science have introduced Zman-seq. This revolutionary method breaks through the temporal barriers of cellular analysis.
This innovative approach allows tracking and measuring changes in individual cells within the body over time.
“Knowing what preceded what is not enough to deduce causality, but without this knowledge, we don’t have a chance of understanding what the cause and effect are,” said Prof. Amit in a press release.
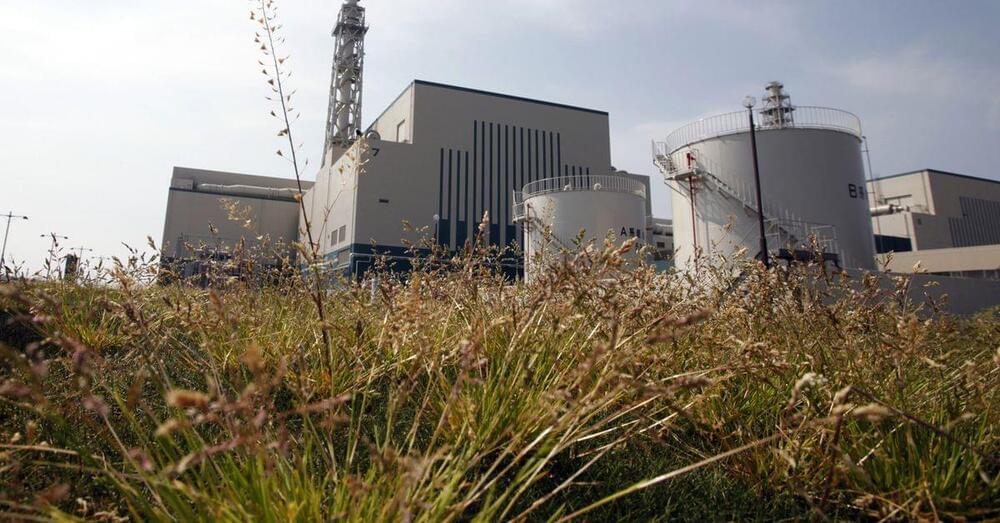

TOKYO, Dec 27 (Reuters) — Japan’s nuclear power regulator on Wednesday lifted an operational ban imposed on Tokyo Electric Power’s (9501.T) Kashiwazaki-Kariwa nuclear power plant two years ago, allowing it to work towards gaining local permission to restart.
Tepco has been eager to bring the world’s largest atomic power plant back online to slash operating costs, but a resumption still needs consent from the local governments of Niigata prefecture, Kashiwazaki city and Kariwa village, where it is located.
When that might happen is unknown.
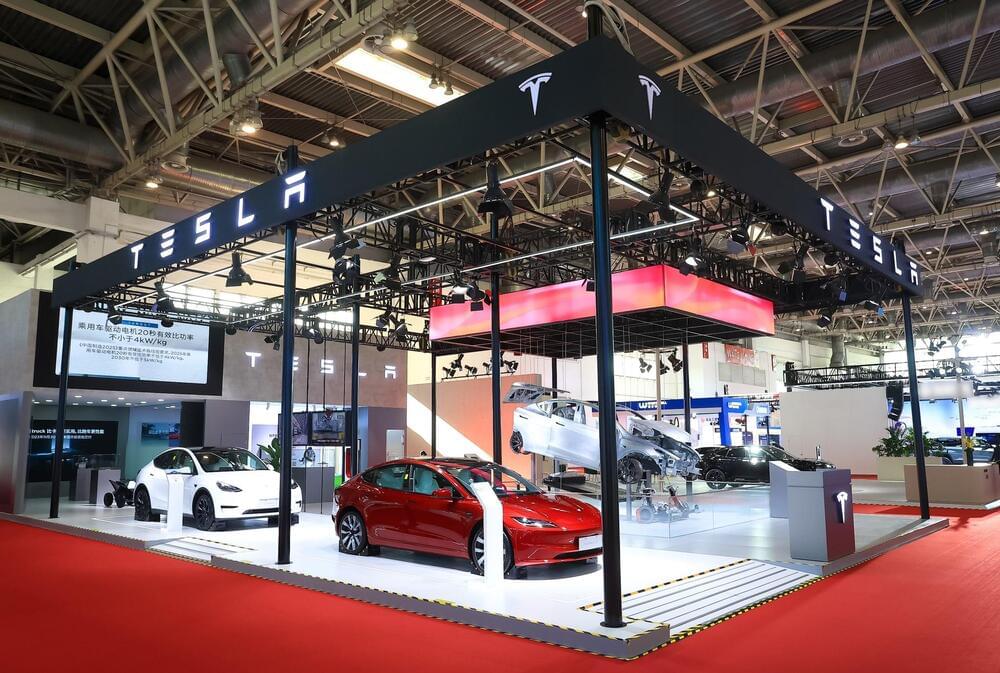

Tesla Giga Shanghai plans to release 2024 Model Y refresh as competition heats up in China.
People familiar with the matter told Bloomberg that Gigafactory Shanghai is already preparing to produce the 2024 refresh Model Y. Mass production on the new Model Y is expected to start by mid-2024.
The new Model Y units will be produced in the new phase of Gigafactory Shanghai. Production in the second phase of Tesla China’s factory will be suspended during New Year’s for upgrades. More updates to the Model Y assembly line will be made after the holidays.

NASA has recently invested in a class of small, low-cost planetary missions called SIMPLEx, which stands for Small, Innovative Missions for PLanetary Exploration. These missions save costs by tagging along on other launches as what is called a rideshare, or secondary payload.
One example is the Lunar Trailblazer. Like VIPER, Lunar Trailblazer will look for water on the moon.
But while VIPER will land on the Moon’s surface, studying a specific area near the south pole in detail, Lunar Trailblazer will orbit the moon, measuring the temperature of the surface and mapping out the locations of water molecules across the globe.

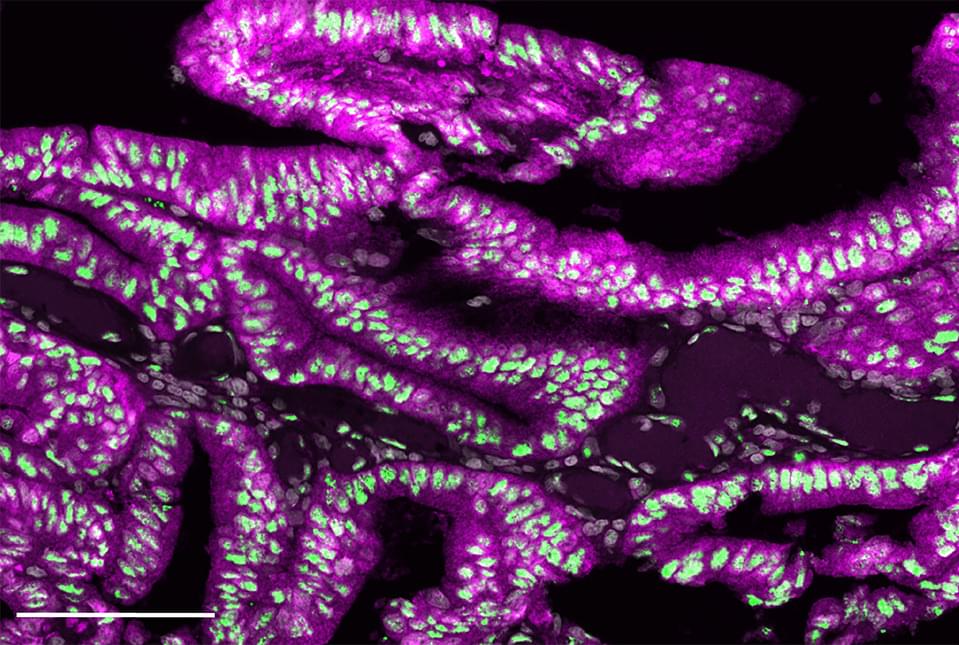
Hard-to-detect colorectal pre-cancerous lesions known as serrated polyps, and the aggressive tumors that develop from them, depend heavily on the ramped-up production of cholesterol, according to a preclinical study from researchers at Weill Cornell Medicine. The finding points to the possibility of using cholesterol-lowering drugs to prevent or treat such tumors.
In the study, published Oct. 13 in Nature Communications, the researchers analyzed mice that develop serrated polyps and tumors, detailing the chain of molecular events in these tissues that leads to increased cholesterol production.
They confirmed their findings in analyses of human serrated polyps and tumors, and showed in mouse models that replicate the human cancer that blocking cholesterol production prevented the progression of these types of intestinal tumors.
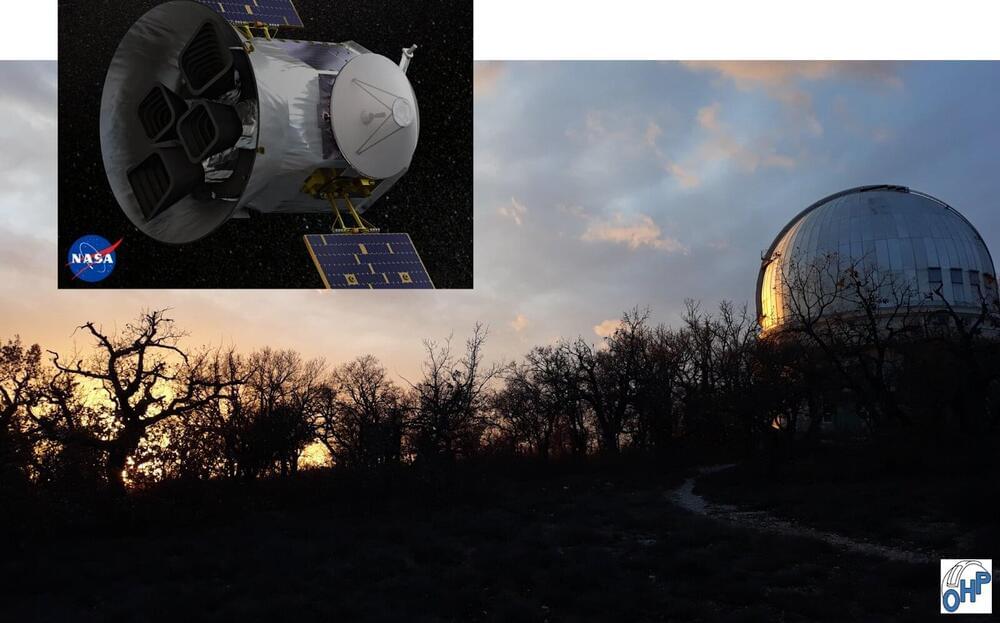

A study published today (Dec. 15) in the journal Astronomy & Astrophysics reveals the discovery of two new planetary systems orbiting stars similar to our sun, also known as solar analogs.
The study was led by Dr. Eder Martioli, a full researcher at the Laboratório Nacional de Astrofísica (LNA/MCTI) and an associate researcher at the Institut d’astrophysique de Paris (IAP), and by Dr. Guillaume Hébrard, a researcher at the Institut d’astrophysique de Paris (IAP).
Observations responsible for detecting these two systems, named TOI-1736 and TOI-2141, were conducted using NASA’s TESS space telescope and the SOPHIE spectrograph installed on the 1.93 m telescope at the Observatoire de Haute-Provence (OHP) in southern France, both illustrated in Figure 1.
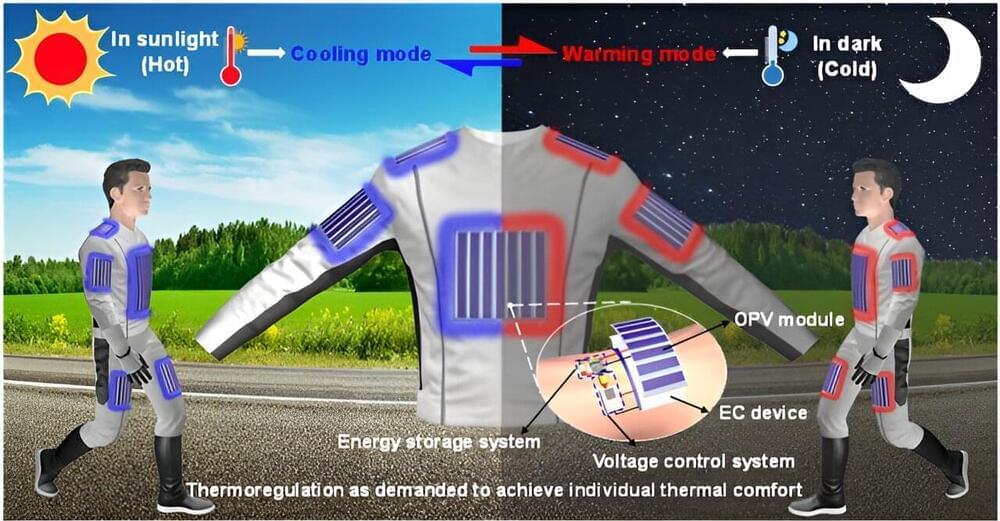
A team of engineers, materials scientists and chemists at Nankai University, in China, has developed a microfiber-based meta-fabric that provides full-day thermoregulation of body temperature during periods of changing external temperatures.
In their paper published in the journal Science, the group describes how they developed their fabrics, how they work and how well they performed when tested. Xingyi Huang and Pengli, both with Shanghai Jiao Tong University, in China, have published a Perspective piece in the same journal issue outlining the work done by the team.
As the researchers note, clothing keeps people warm when it is cold, and in some cases, can help people stay cool in hot temperatures. Prior research efforts have attempted to extend the capabilities of clothing by adding heating or cooling elements, but thus far, most such products have proven to be too bulky for general use.