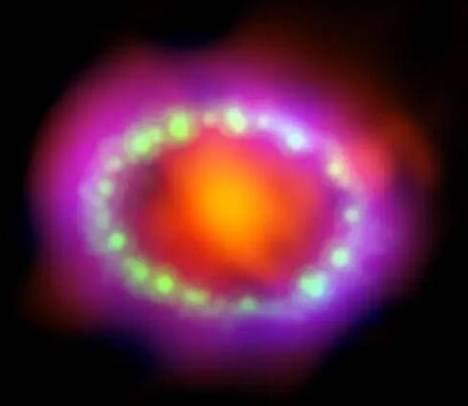
The youngest neutron star detected so far turned 37 years old last week. To celebrate, James Webb Space Telescope has finally found the most direct evidence of it, hiding among the remains of the supernova cloud it was born in.
Usually when we’re talking about the age of astronomical objects, it’s in the millions or billions of years – so finding something that’s younger than Lady Gaga feels weird. Even weirder is being able to trace its birth to a specific date – February 23, 1987, meaning it just clocked over to its 37th birthday last Friday.
The reason we can so confidently pinpoint the date is because its birth was the result of an event that only happens once every few centuries: a supernova that’s close enough to be observed from Earth with the naked eye. SN 1987A lit up the night sky for a few months in early 1987, and was quickly traced to the Large Magellanic Cloud, a dwarf galaxy orbiting the Milky Way, about 168,000 light-years away. There, a blue supergiant star appeared to have collapsed and exploded, which should have left either a black hole or a neutron star.