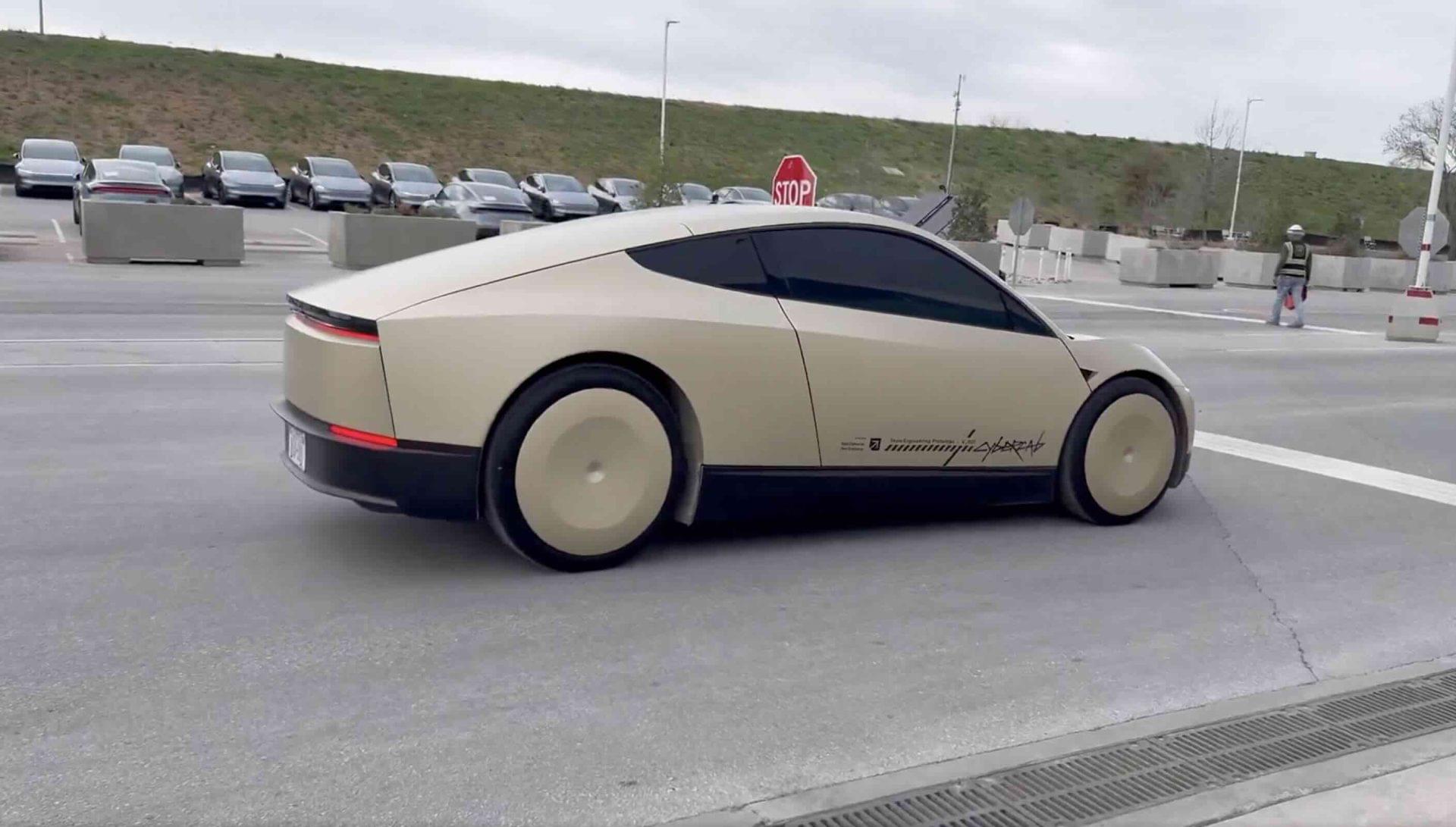
Tesla is preparing to launch its robo taxi in June, leveraging its unique autonomy and data advantages to navigate challenges such as new tariffs and production shifts, while positioning itself for significant growth amid declining competitor viability ## Questions to inspire discussion ## Tesla’s Robo Taxi Service.
🚕 Q: When and where is Tesla launching its robo taxi service? A: Tesla’s robo taxi service is set to launch in Austin, Texas in June 2025, with plans for a nationwide rollout in the US later that year.
🏎️ Q: What vehicles will be eligible for Tesla’s robo taxi service? A: The service will be available on all vehicles equipped with Full Self-Driving (FSD) capability, including existing Model 3 and Model Y, not just the upcoming Cybertruck.
💰 Q: How will Tesla’s robo taxi network economics work? A: The economics will be based on cost per mile, factoring in low capital costs of Tesla EVs and low power consumption of their onboard autonomy systems.
📊 Q: What competitive advantage does Tesla have in the robo taxi market? A: Tesla’s existing fleet of billions of miles of deployed vehicles and hundreds of thousands of users provide a massive data advantage for improving and assessing the service. ## Tariffs and Supply Chain.
🏭 Q: What is Tesla’s supply chain strategy? A: Tesla aims to build cars where sold for environmental reasons, which is considered best practice in network design but extremely difficult to implement.