Think big. Despite its research topic, this could well be the motto of the Graphene Flagship, which was launched in 2013: With an overall budget of one billion Euros, it was Europe’s largest research initiative to date, alongside the Human Brain Flagship, which was launched at the same time.
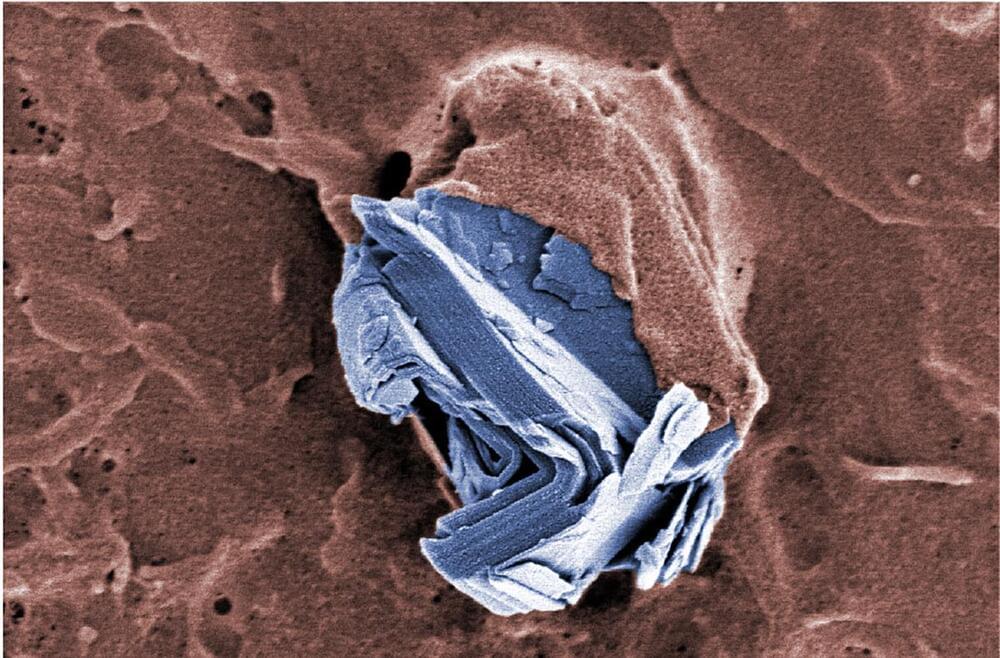
The same applies to the review article on the effects of graphene and related materials on health and the environment, which Empa researchers Peter Wick and Tina Bürki just published together with 30 international colleagues in the journal ACS Nano; they summarize the findings on the health and ecological risks of graphene materials, the reference list includes almost 500 original publications.
A wealth of knowledge—which also gives the all-clear. “We have investigated the potential acute effects of various graphene and graphene-like materials on the lungs, in the gastrointestinal tract and in the placenta—and no serious acute cell-damaging effects were observed in any of the studies,” says Wick, summarizing the results.