A new project called Progression Assessment in Neurodegenerative Disorders of Aging or PANDA aims to detect subtle changes in a person’s sleep patterns that may indicate the onset of Alzheimer’s or Parkinson’s disease. The collaboration of this four-year project involves Rigshospitalet University, Denmark’s Aarhus University, and MedTech company T&W Engineering. The project has received funding of DKK 15 million to develop and test a small earbud-like experimental device that can detect the early signs of these diseases.
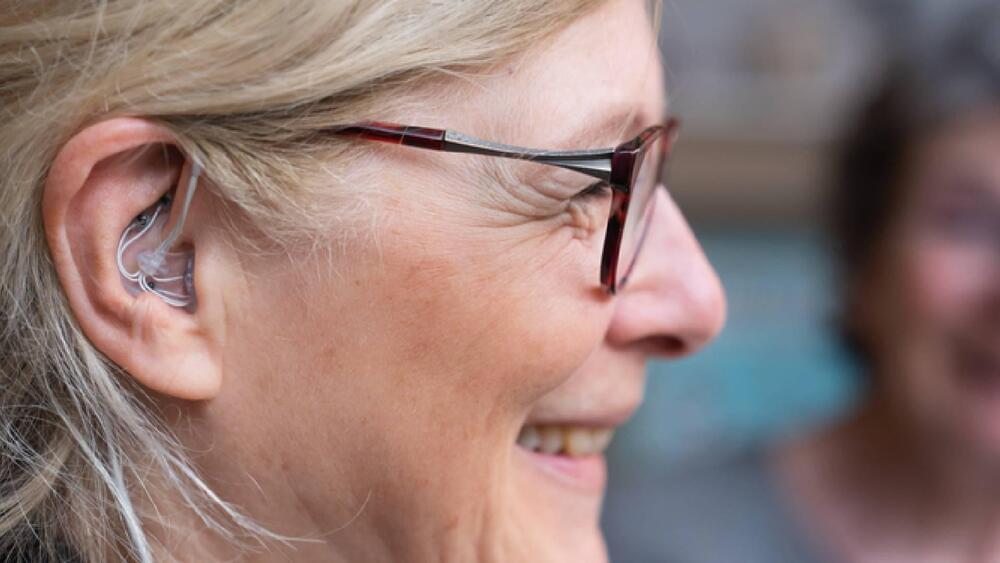
The Ear-EEG Technology
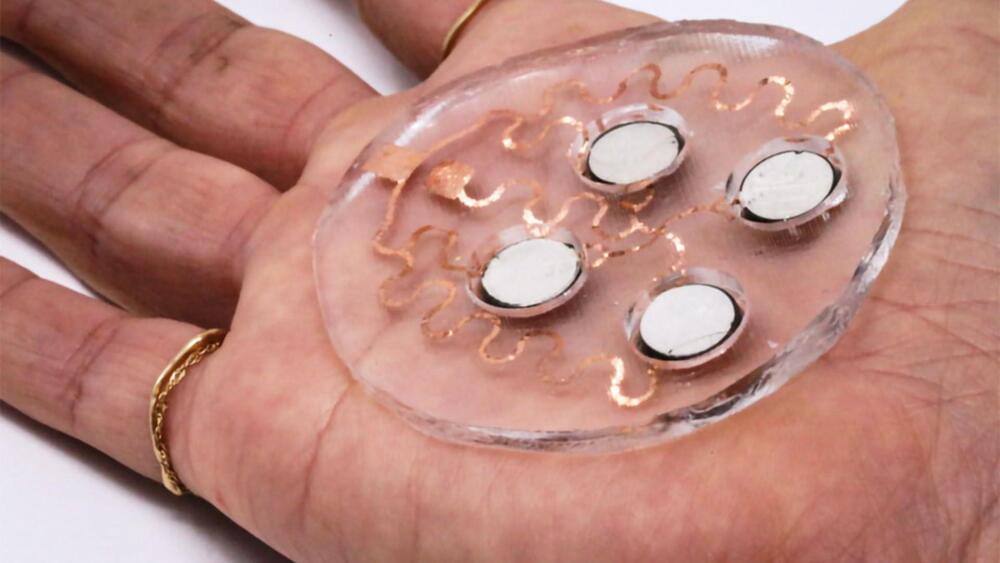
Unlike the traditional sleep-monitoring systems that require a person to stay in a clinic with multiple electrodes attached to their body, the ear-EEG allows for comfortable, long-term use at home. The device monitors electrical activity in the brain by measuring tiny voltage changes on the skin surface within the ear canal. It is also equipped with an oximeter for measuring blood oxygen levels, a microphone for monitoring respiration and heart rate, and a thermometer for measuring body temperature.