If you create something that mimics you be aware that it will try to self-preserve when it sees you as a treath.
Enjoy the videos and music that you love, upload original content and share it all with friends, family and the world on YouTube.
If you create something that mimics you be aware that it will try to self-preserve when it sees you as a treath.
Enjoy the videos and music that you love, upload original content and share it all with friends, family and the world on YouTube.



Scientists at UCSF have uncovered how certain immune cells in the brain, called microglia, can effectively digest toxic amyloid beta plaques that cause Alzheimer’s. They identified a key receptor, ADGRG1, that enables this protective action. When microglia lack this receptor, plaque builds up quickly, causing memory loss and brain damage. But when the receptor is present, it seems to help keep Alzheimer's symptoms mild. Since ADGRG1 belongs to a drug-friendly family of receptors, this opens the door to future therapies that could enhance brain immunity and protect against Alzheimer’s in more people.
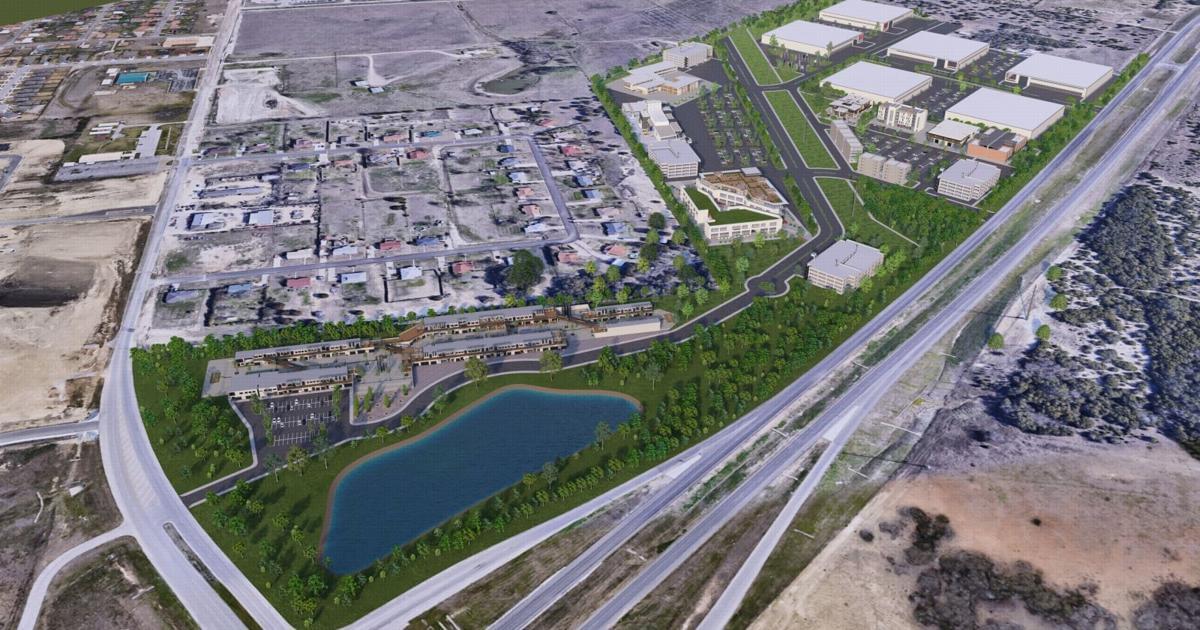

The establishment of a new business park in Killeen is underway.
Wolf Technology Park is set to inhabit 94-acres of real estate located on Texas Highway 195 in south Killeen.
“Wolf Technology Park is a cornerstone of our strategy to attract next-generation employers to Killeen,” Tyler Robert, vice president of the Killeen Economic Development Corporation, said. “With infrastructure investments already in place and sites ready for development, the park is well-positioned to support advanced manufacturing, federal services, health and life sciences, research and development, cybersecurity and semiconductor-related industries.”

IN A NUTSHELL 🚀 Brown University students developed a novel imaging technique using quantum entanglement to capture 3D images. 🔬 The method employs infrared light for illumination and visible light for imaging, enhancing depth resolution without costly infrared cameras. 🧪 The team solved the issue of phase wrapping by using two sets of entangled photons.
Quantum mechanics is generally regarded as the physical theory that is our best candidate for a fundamental and universal description of the physical world. The conceptual framework employed by this theory differs drastically from that of classical physics. Indeed, the transition from classical to quantum physics marks a genuine revolution in our understanding of the physical world.
One striking aspect of the difference between classical and quantum physics is that whereas classical mechanics presupposes that exact simultaneous values can be assigned to all physical quantities, quantum mechanics denies this possibility, the prime example being the position and momentum of a particle. According to quantum mechanics, the more precisely the position (momentum) of a particle is given, the less precisely can one say what its momentum (position) is. This is (a simplistic and preliminary formulation of) the quantum mechanical uncertainty principle for position and momentum. The uncertainty principle played an important role in many discussions on the philosophical implications of quantum mechanics, in particular in discussions on the consistency of the so-called Copenhagen interpretation, the interpretation endorsed by the founding fathers Heisenberg and Bohr.
This should not suggest that the uncertainty principle is the only aspect of the conceptual difference between classical and quantum physics: the implications of quantum mechanics for notions as (non)-locality, entanglement and identity play no less havoc with classical intuitions.
Black holes played a critical role in the formation of the early universe. However, astronomers have been debating for a long time just how critical, as the information we had about early black holes, which exist at high red-shifts, was relatively limited.
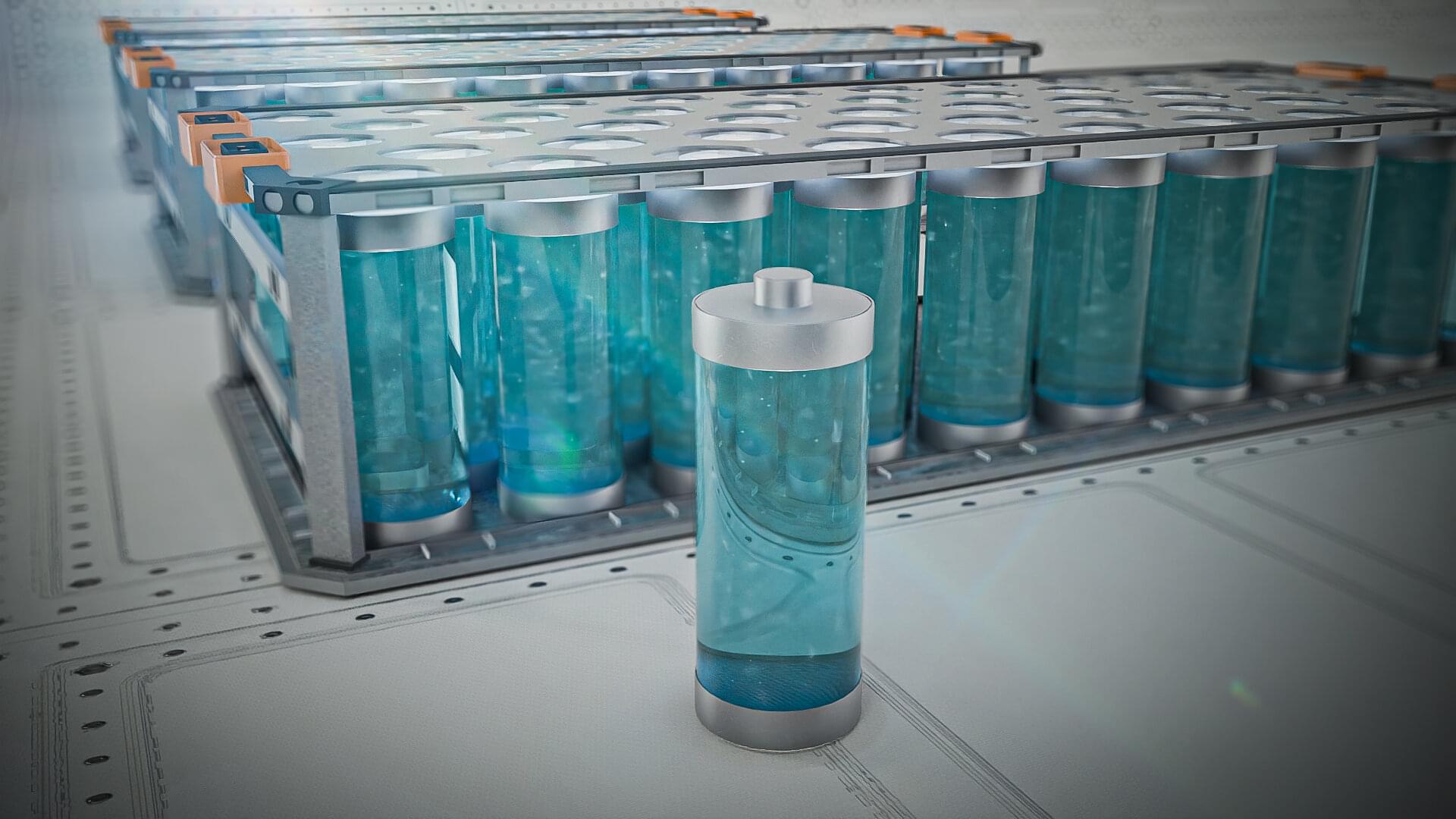

Scientists at King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST) have uncovered a critical molecular cause keeping aqueous rechargeable batteries from becoming a safer, economical option for sustainable energy storage.
Their findings, published in Science Advances, reveal how water compromises battery life and performance and how the addition of affordable salts—such as zinc sulfate—mitigates this issue, even increasing the battery lifespan by more than ten times.
One of the key determinants of the lifespan of a battery—aqueous or otherwise—is the anode. Chemical reactions at the anode generate and store the battery’s energy. However, parasitic chemical reactions degrade the anode, compromising the battery lifespan.
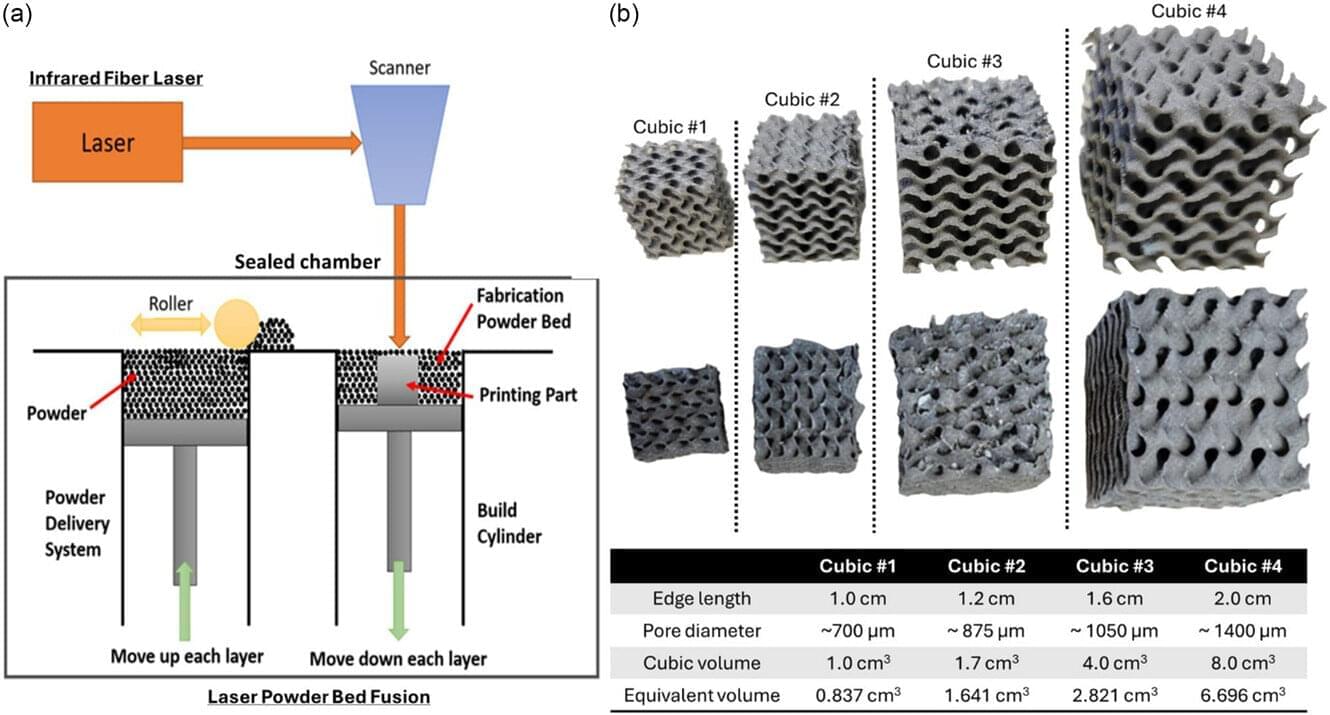
Engineering innovations generally require long hours in the lab, with a lot of trial and error through experimentation before zeroing in on the best solution.
But sometimes, if you’re lucky, the answer can be right under your nose—or in this case, beneath your feet.
Binghamton University Professor Seokheun “Sean” Choi has developed a series of bacteria-fueled biobatteries over the past decade, building on what he has learned to improve the next iteration. The biggest limitation isn’t his imagination—he’s always juggling several projects at once—but the materials he has to work with.