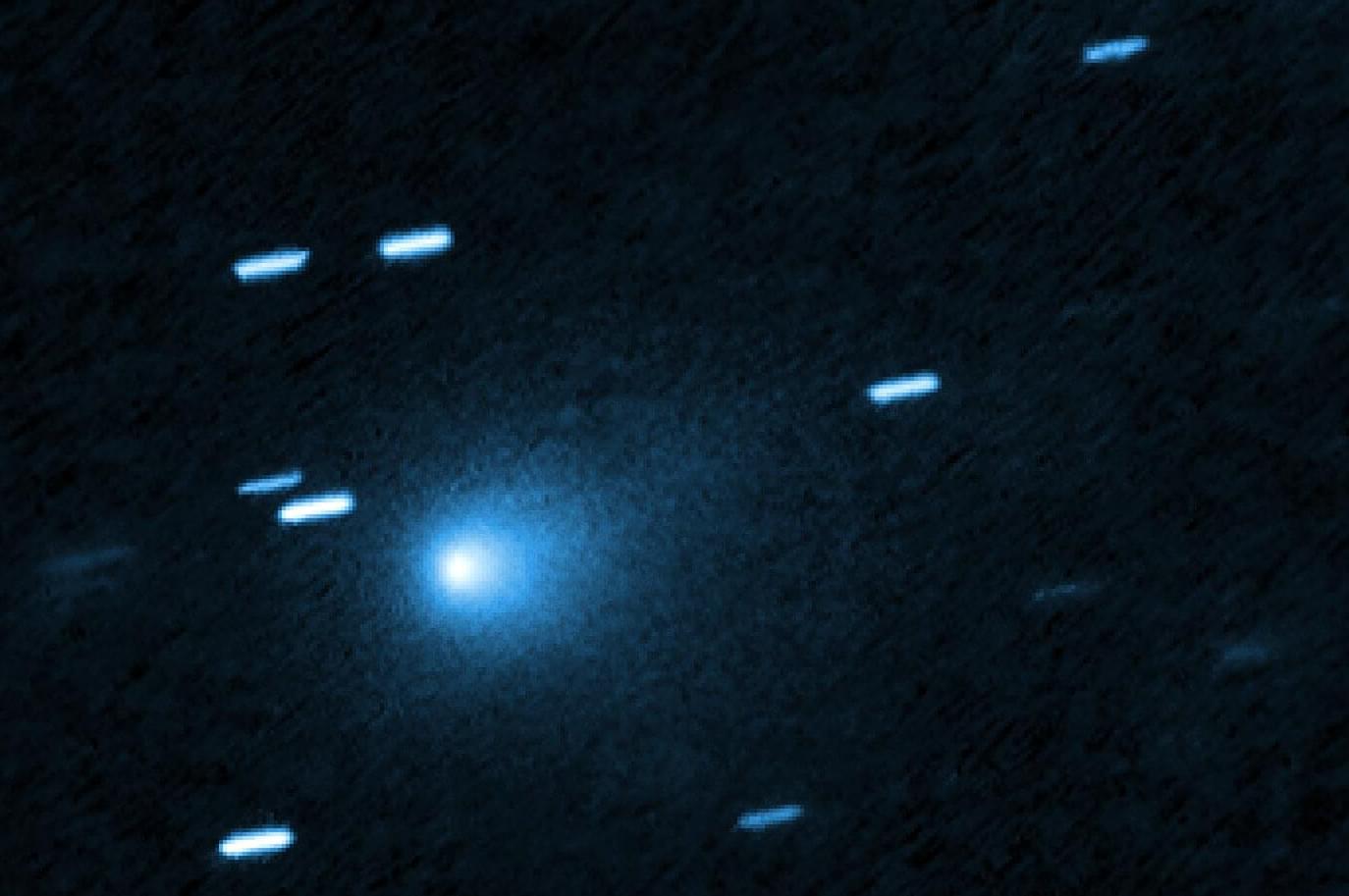
Researchers have identified a distinctive ultraviolet signature of water in the interstellar comet known as 3I/ATLAS.



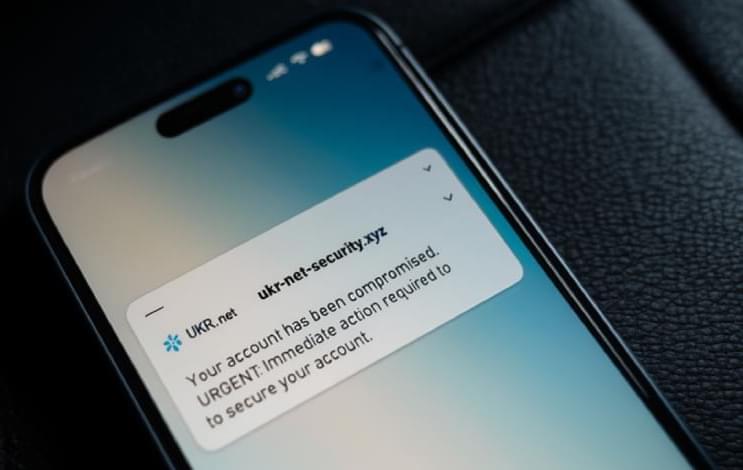
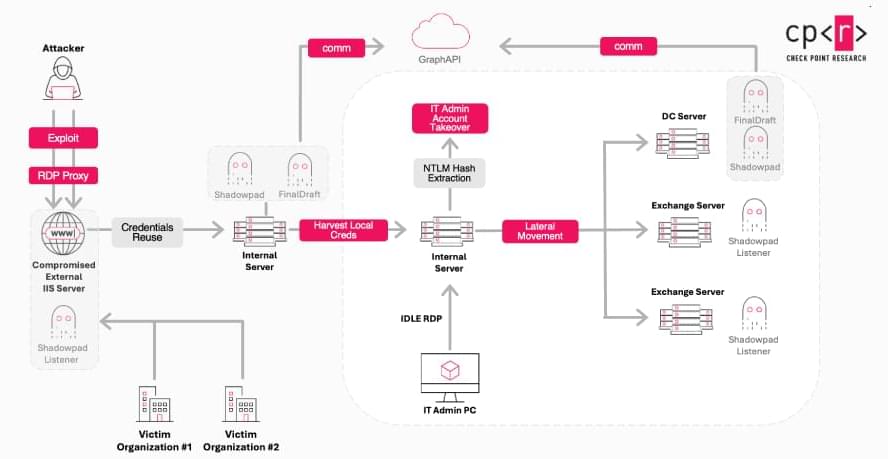
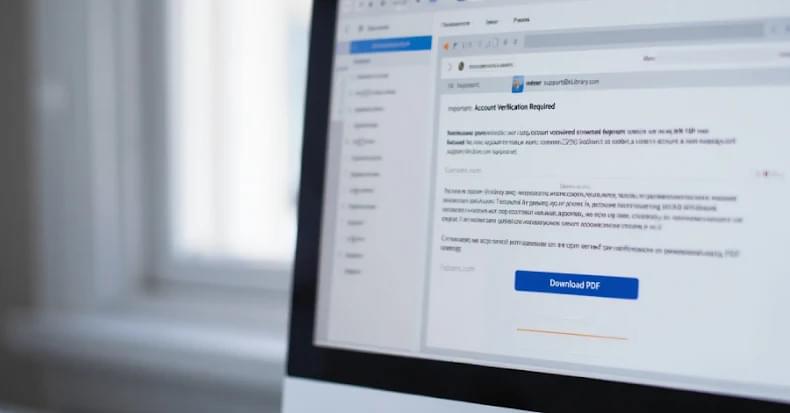
Cisco has alerted users to a maximum-severity zero-day flaw in Cisco AsyncOS software that has been actively exploited by a China-nexus advanced persistent threat (APT) actor codenamed UAT-9686 in attacks targeting Cisco Secure Email Gateway and Cisco Secure Email and Web Manager.
The networking equipment major said it became aware of the intrusion campaign on December 10, 2025, and that it has singled out a “limited subset of appliances” with certain ports open to the internet. It’s currently not known how many customers are affected.
“This attack allows the threat actors to execute arbitrary commands with root privileges on the underlying operating system of an affected appliance,” Cisco said in an advisory. “The ongoing investigation has revealed evidence of a persistence mechanism planted by the threat actors to maintain a degree of control over compromised appliances.”


A new distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) botnet known as Kimwolf has enlisted a massive army of no less than 1.8 million infected devices comprising Android-based TVs, set-top boxes, and tablets, and may be associated with another botnet known as AISURU, according to findings from QiAnXin XLab.
“Kimwolf is a botnet compiled using the NDK [Native Development Kit],” the company said in a report published today. “In addition to typical DDoS attack capabilities, it integrates proxy forwarding, reverse shell, and file management functions.”
The hyper-scale botnet is estimated to have issued 1.7 billion DDoS attack commands within a three-day period between November 19 and 22, 2025, around the same time one of its command-and-control (C2) domains – 14emeliaterracewestroxburyma02132[.]su – came first in Cloudflare’s list of top 100 domains, briefly even surpassing Google.



French authorities arrested a 22-year-old suspect on Tuesday for a cyberattack that targeted France’s Ministry of the Interior earlier this month.
In a statement issued by Public Prosecutor Laure Beccuau, officials said the suspected hacker was arrested on December 17, 2025, as part of an investigation into the attack.
“A person was arrested on December 17, 2025, as part of the investigation opened by the cybercrime unit of the Paris public prosecutor’s office, on charges including unauthorized access to an automated personal data processing system implemented by the State, committed by an organized group, following the cyberattack against the Ministry of the Interior,” reads the statement translated into English.